Abstract
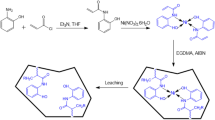
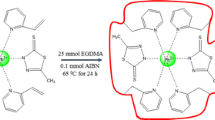
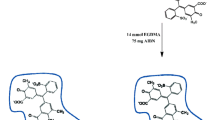
A selective porous ion imprinted polymer (IIP) coated on Fe3O4@SiO2 nanocomposite as the adsorbent combined with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry (ETAAS) was applied for preconcentration and determination of lead ion in real samples including water samples, and cosmetics. The IIP was synthesized using styrene as a functional monomer in the presence of Pb (II) ions as the main template and ZnO nanoparticles as the sacrificial template, which were co-imprinted. The synthesized nanocomposites were characterized by FTIR, VSM, XRD, and scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis. The Plackett Burman design (PBD) of experiments was used to screen the relative importance of the variables such as the amount of sorbent, pH, monomer to template ratio, polymerization time, extraction time, and some other factors. In the following, the optimization process was carried out using the central compound design (CCD). A calibration curve was constructed and a regression equation was intended. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) were 0.0002 and 0.0007μg L−1 respectively. A dynamic linear range (DLR) of 0.0007–100 μg L−1 was found with the correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.9978. Reproducibility was obtained with a relative standard deviation (RSD) value of 6.8%. The method was applied for the determination of trace Pb (II) in the real samples, like the drinking water, wastewater, as well as nail polish and lipstick from the category of cosmetics with relative recoveries of 90.069–109.014%.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information files. Should any raw data files be needed in another format they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Source data are provided with this paper. I do not want the data from this research to be shared openly before final publication in the journal. This decision was made to protect the privacy of the study participants.
References
Adil, H. I., Thalji, M. R., Yasin, S. A., Saeed, I. A., Assiri, M. A., Chong, K. F., & Ali, G. A. M. (2022). Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) based Nano fiber architectures for the removal of heavy metal ions. RSC Advances, 12(3), 1433–1450. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra07034g
Al-Saleh, I., Al-Enazi, S., & Shinwari, N. (2009). Assessment of lead in cosmetic products. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 54(2), 105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2009.02.005
Biela, R., Kučera, T. (2015). Arsenic removal from water by using sorption materials. Al Ali, M., Platko, P. (ed.) Advances and Trends in Engineering Sciences and Technologies, Taylor and Francis Group, Leiden
Biela, R., Sopikova, L. (2017). Efficiency of sorption materials on the removal of lead from water. Ecology and Environmental Research, 15(3), 1527–1536. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1503_15271536
Bruynooghe, S., Bertin, F., Chabli, A., Gay, J. C., Blanchard, B., & Couchaud, M. (1998). Infrared spectroscopic ellipsometry for residual water detection in annealed sol-gel thin layers. Thin Solid Films, 313–314, 722–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(97)00985-1
Chauhan, B. S., & Johnson, D. E. (2010). Implications of narrow crop row spacing and delayed Echinochloa colona and Echinochloa crus-galli emergence for weed growth and crop yield loss in aerobic rice. Field Crops Research, 117(22–3), 177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2010.02.014
Chen, L., Dai, J., Hu, B., Wang, J., Wu, Y., Dai, J., Meng, M., Li, C., & Yan, Y. (2019). Recent progresses on the adsorption and separation of ions by imprinting routes. Separation & Purification Reviews, 49(4), 265–293. https://doi.org/10.1080/15422119.2019.1596134
Dehghani, M. H., Sardari, S. A., Afsharnia, M., Qasemi, M., & Shams, M. (2023). Removal of toxic lead from aqueous solution using a low-cost adsorbent. Scientific Reports., 13, 3278. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-29674-x
Gatabi, J., Sarrafi, Y., Lakouraj, M. M., & Taghavi, M. (2020). Facile and efficient removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution by chitosan-lead ion imprinted polymer network. Chemosphere, 240, 124772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124772
Guo, Y., & Kannan, K. (2013). A survey of phthalates and parabens in personal care products from the United States and its implications for human exposure. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(24), 14442–14449. https://doi.org/10.1021/es4042034
Gupta, A. K., & Gupta, M. (2005). Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials, 26(18), 3995–4021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.10.012
Hall, C. A., Kelly, J. D., Whitlock, H. V., & Ritchie, L. (1981). Prolonged anthelmintic effect of closantel and disophenol against a thiabendazole selected resistant strain of Haemonchus contortus in sheep. Research in Veterinary Science, 31, 104–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-5288(18)32531-1
Hasnidawania, J. N., Azlina, H. N., Norita, H., Bonnia, N. N., Ratim, S., & Ali, E. S. (2016). Synthesis of ZnO Nanostructures Using Sol-Gel Method. Procedia Chemistry, 19, 211–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2016.03.095
He, C., Long, Y., Pan, J., Li, K., & Liu, F. (2008). Molecularly imprinted silica prepared with immiscible ionic liquid as solvent and porogen for selective recognition of testosterone. Talanta, 74, 1126–1131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2007.08.009
Jalilzadeh, M., & Ṣenel, S. (2016). Removal of Cu (II) ions from water by ion-imprinted magnetic and non-magnetic cryogels: A comparison of their selective Cu (II) removal performances. Water Process Engineering, 13, 143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.08.010
Javaheri, F., & Hassanajili, S. (2016). Synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2@MPS@P4VP nanoparticles for nitrate removal from aqueous solutions. Applied Polymer Science., 133(48), 44330. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44330
Jeyaseelan, A., & Viswanathan, N. (2020). Design of amino-functionalized benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylic acid-fabricated lanthanum-based metal–organic frameworks for defluoridation of water. Chemical & Engineering Data, 65(11), 5328–5340. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.0c00492
Jeyaseelan, A., & Viswanathan, N. (2021). Facile synthesis of tunable rare earth based metal organic frameworks for enhanced fluoride retention. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 326(15), 115163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.115163
Kamgar, A., Hassanajili, Sh., & Karimipourfard, G. (2018). Fe3O4@SiO2@MPS core/shell nanocomposites: The effect of the core weight on their magnetic properties and oil separation performance. Environmental Chemical Engineering., 6, 3034–3040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.04.057
Klein, J. U., Whitcombe, M. J., Mulholl, F., & Vulfson, E. N. (1999). Template-mediated synthesis of a polymeric receptor specific to amino acid sequences. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 38, 2057. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1521-3773(19990712)38:13/14%3c2057:aid-anie2057%3e3.0.co;2-g
Kwei, G. H., Canfield, P. C., Fisk, Z., Thompson, J. D., & Von Dreele, R. B. (1991). Structure of the new “120 1” lead cuprate superconductor. Physica C: Superconductivity, 176(1–3), 57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-4534(91)90695-U
Lee, C. S., Lee, H., & Westervelt, R. M. (2001). Micro electromagnets for the control of magnetic nanoparticles. Physics Letters, 79, 3308. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1419049
Lilley, S. G., Florence, T. M., & Stauber, J. L. (1988). The use of sweat to monitor lead absorption through the skin. Science of the Total Environment, 76(2–3), 267–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(88)90112-X
Lu, A. H., Salabas, E. L., & Schth, F. (2007). Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 46(8), 1222–1244. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200602866
Mehrandish, R., Rahimian, A., & Shahriary, A. (2019). Heavy metals detoxification: A review of herbal compounds for chelation therapy in heavy metals toxicity. Herbmed Pharmacology., 8(2), 69–77. https://doi.org/10.15171/jhp.2019.12
Mondal, J., Sen, T., & Bhaumik, A. (2012). Fe3O4@mesoporous SBA-15: a robust and magnetically recoverable catalyst for one-pot synthesis of 3, 4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones via the Biginelli reaction. Dalton Transactions, 41, 6173–6181. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2DT30106G
Nkansah, M. A., Owusu-Afriyie, E., & Opoku, F. (2018). Determination of lead and cadmium contents in lipstick and their potential health risks to consumers. Consumer Protection and Food Safety, 13, 367–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-018-1180-y
Pakdel, P. M., & Peighambardoust, S. J. (2018). A review on acrylic based hydrogels and their applications in wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Management, 217(1), 123–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.076
Qi, P., Wang, J., Wang, L., Li, Y., Jin, J., Su, F., Tian, Y., & Chen, J. (2010). Molecularly imprinted polymers synthesized via semi-covalent imprinting with sacrificial spacer for imprinting phenols. Polymer, 51(23), 5417–5423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2010.09.037
Rajabi, M., Sarhadi, A., Bazregar, M., Asghari, A., & Mirparizi, E. (2017). Rapid derivatization and extraction of paraben preservatives by fast syringe-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction and their determination in cosmetic and aqueous sample solutions by gas chromatography. Analytical Methods, 9, 5963–5969. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7AY01375B
Ruchi, G., Anshu, G., & Khare, S. K. (2008). Lipase from solvent tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain: Production optimization by response surface methodology and application. Bioresource Technology, 99, 4796–4802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.09.053
Salihua, A., ZahangirAlam, Md., AbdulKarim, M. I., & Salleh, H. M. (2011). Optimization of lipase production by Candida cylindracea in palm oil mill effluent-based medium using statistical experimental design. Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 69, 66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2010.12.012
Saraji, M., & Mirmahdieh, Sh. (2009). Single-drop micro extraction followed by in-syringe derivatization and GC-MS detection for the determination of parabens in water and cosmetic products. Separation Science, 32, 988–995. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200800635
Stober, W., Fink, A., & Bohn, E. (1968). Controlled growth of mon disperse silica spheres in the micron size range. Colloid and Interface Science, 26, 62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(68)90272-5
Stolnik, S., Garnett, M. C., Davies, M. C., Illum, L., Bousta, M., Vert, M., & Davis, S. S. (1995). The colloidal properties of surfactant-free biodegradable nanospheres from poly (β-malic acid-co-benzyl malate) s and poly (lactic acid-co-glycolide). Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 97(3), 235–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-7757(95)03081-N
Tierui, Z., Jianping, G., Yongxing, H., Qiao, Z., Shaul, A., & Yadong, Y. (2008). Formation of hollow silica colloids through a spontaneous dissolution–regrowth process. Angewandte Chemie, 120, 5890–5895. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.200800927
Wanga, F., Yina, C., Weia, X., Wangab, Q., Cuia, L., Wangac, Y., Lia, T., & Li, J. (2014). Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles modified with oleic acid. Integrated Ferroelectrics, 153, 92–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/10584587.2014.903062
Woestenborghs, R., Hendrick, X., Michielsen, J. L., & Heykants, J. (1992). Quality assurance in the food control microbiological laboratory. FAO Food and Nutrition Paper, 41(5), 15–22.
Zakaria, A., & Bin Ho, Y. (2015). Heavy metals contamination in lipsticks and their associated health risks to lipstick consumers. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 73(1), 191–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2015.07.005
Zhao, B., He, M., Chen, B., & Hu, Bin. (2019). Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with double imprinted polymers for magnetic solid phase extraction of lead (II) from biological and environmental samples. Microchimica Acta, 775(12), 186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3819-5
Zhou, Y. L., Yang, H. H., & Wang, X. R. (2009). Grafting of molecularly imprinted polymers from the surface of silica gel particles via reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization: A selective sorbent for theophylline. Talanta, 79, 141–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2009.03.014
Zhou, X., Wang, B., & Wang, R. (2022). Insights into ion-imprinted materials for the recovery of metal ions: Preparation, evaluation and application. Separation and Purification Technology, 298, 121469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Omidvar-Motlagh, M., Es’haghi, Z. Magnetic Porous Ion Imprinted Polymer Based on Surface Polymerization and Nano-ZnO as Sacrificial Support for Selective Extraction and determination of Pb (II) in Water Samples and Cosmetics. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 211 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07013-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07013-8