Abstract
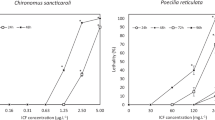
Cemeteries are among the most polluting sources of groundwater and surface water in the world. Necro-leachate, a liquid released during the putrefaction of corpses, is the main culprit of such pollution. Among the compounds in this liquid are the potentially toxic amines cadaverine and putrescine, which are still poorly understood in terms of the environmental health risks they pose. This study evaluated the acute toxicity of cadaverine and putrescine, using efficient contamination bioindicators of aquatic environments. Danio rerio and Daphnia magna were exposed to both amines individually or in a mixture. Acute toxicity (LC50) was then observed in both organisms after exposure to the amines individually. Cadaverine showed higher lethality for D. magna (LC50 – 9.5 mg. L−1) and D. rerio (LC50—335.5 mg. L−1) than did putrescine (LC50—36.7 mg. L−1 and LC50- 452.6 mg. L−1, respectively). In embryotoxicity tests with D. rerio (hatching rate and malformations), delayed hatching, vertebral column malformations, and pericardial edema were observed after exposure to an amine mixture. However, co-exposure to cadaverine and putrescine was not toxic to D. magna. The results of this study confirmed the efficiency of the bioindicators used to assess contaminants in cemeteries and raised awareness of the toxic potential of cadaveric decomposition by-products.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abuhlega, T. A., & Ali, M. R. (2022). Biogenic amines in fish: Prevention and reduction. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.16883
Afangideh, C. B., & Udokpoh, U. U (2022). Environmental impact assessment of groundwater pollution within cemetery surroundings. International Journal of Engineering, 19(51), 100–115.
Anifowoshe, A. T., Roy, D., Dutta, S., & Nongthomba, U. (2022). Evaluation of cytogenotoxic potential and embryotoxicity of KRS-Cauvery River water in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 233, 113320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113320
Batista, F. S., Cruz, M. J. M., dos Anjos, J. Â. S. A., Gonçalves, M. V. P., da Porciúncula, D. C. L., & de Souza Andrade, J. J. (2022). Geo-environmental assessment and quality of groundwater in the complex of cemiteries: Quinta Dos Lázaros Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. International Journal of Human Sciences Research, 2, 2–25. https://doi.org/10.22533/at.ed.558282201042
Belaid, C., Sbartai, I (2021) Assessing the effects of Thiram to oxidative stress responses in a freshwater bioindicator cladoceran (Daphnia magna), Chemosphere. Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128808
Cooman, T., Bergeron, S. A., Coltogirone, R., Horstick, E., & Arroyo, L. (2022). Evaluation of fentanyl toxicity and metabolism using a zebrafish model. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 42, 706–714. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.4253
Crisanto-Perrazo, T., Guayasamín-Vergara, J., Mayorga-Llerena, E., Sinde-Gonzalez, I., Vizuete-Freire, D., Toulkeridis, T., Gomez, G. F., Fierro-Naranjo, G (2022). Determination of empirical environmental indices for the location of cemeteries—An innovative proposal for worldwide use. Sustain, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106284
da Silva, R. B. P., Campos, M. C. C., Silva, L. S., de Brito Filho, E. G., de Lima, A. F. L., Pinheiro, E. N., & Cunha, J. M. (2020). Concentration of heavy metals in soils under cemetery occupation in Amazonas, Brazil. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 29, 192–208. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2019.1696280
Dasa, F., Bejo, W., & Abdo, T. (2022). Importance and toxicity of biogenic amines in fresh and processed foods. Journal of Food Technology & Nutrition Sciences, 4, 1–8.
del Rio, B., Redruello, B., Linares, D. M., Ladero, V., Ruas-Madiedo, P., Fernandez, M., Martin, M. C., & Alvarez, M. A. (2019). The biogenic amines putrescine and cadaverine show in vitro cytotoxicity at concentrations that can be found in foods. Science and Reports, 9, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-36239-w
Donato, F., Greco, R., Carpentieri, C., Pittore, B., D’Orlando, C., Donato, A., Malara, N., & Donato, G. (2022). All ptomaines fault! The strange story of the cadaveric alkaloids, from forensic medicine to molecular biology passing through the asylum. Medical History, 6(1), 2022009.
Franco, D. S., Georgin, J., Villarreal Campo, L. A., Mayoral, M. A., Goenaga, J. O., Fruto, C. M., Neckel, A., Oliveira, M. L., & Ramos, C. G. (2022). The environmental pollution caused by cemeteries and cremations: A review. Chemosphere, 307, 136025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136025
Gómez, F.G., Crisanto-Perrazo, T., Toulkeridis, T., Fierro-Naranjo, G., Guevara-García, P., Mayorga-Llerena, E., Vizuete-Freire, D., Salazar, E., Sinde-Gonzalez, I. (2022). Proposal of an initial environmental management and land use for critical cemeteries in central ecuador. Sustain, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031577
Gonçalves, L. R., Roberto, M. M., Braga, A. P. A., Barozzi, G. B., Canizela, G. S., de Souza Gigeck, L., de Souza, L. R., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2022). Another casualty of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic—the environmental impact. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 1696–1711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17098-x
Howe, K., Clark, M. D., Torroja, C. F., et al. (2013). The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature, 496, 498–503. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12111
Idehen, O. (2020). A comparative investigation of groundwater contamination in typical dumpsites and cemetery using ert and physicochemical analysis of water in Benin Metropolis, Nigeria. Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 08, 72–85. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2020.81005
Idehen, O., & Ezenwa, I. (2019). Influence of third cemetery location on the quality of domestic and groundwater resources in Benin City, Nigeria. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 23, 5. https://doi.org/10.4314/jasem.v23i1.1
Iqubal, A., Ahmed, M., Ahmad, S., Sahoo, C. R., Iqubal, M. K., & Haque, S. E. (2020). Environmental neurotoxic pollutants: Review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 41175–41198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10539-z
Kumar, S., Arockiaraj, M., Esokkiya, A., Sudalaimani, S., Hansda, S., Sivakumar, C., Sulaiman, Y., Khan, M. M., & Giribabu, K. (2021). Ion-pair facilitated non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of cadaverine and putrescine. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 168, 047505. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/abf263
Lee, Y. L., Shih, Y. S., Chen, Z. Y., Cheng, F. Y., Lu, J. Y., Wu, Y. H., & Wang, Y. J. (2022). Toxic effects and mechanisms of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles on zebrafish embryos in aquatic ecosystems. Nanomaterials, 12, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040717
Lovern, S. B., & Hart, R. V. (2022). Impact of oxytetracycline exposure on the digestive system microbiota of Daphnia magna. PLoS One, 17, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0265944
Massei, R., Hollert, H., Krauss, M., von Tümpling, W., Weidauer, C., Haglund, P., Küster, E., Gallampois, C., Tysklind, M., Brack, W. (2019). Toxicity and neurotoxicity profiling of contaminated sediments from Gulf of Bothnia (Sweden): a multi-endpoint assay with Zebrafish embryos. Environmental Sciences Europe, 31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-019-0188-y
Neckel, A., Costa, C., Mario, D. N., Sabadin, C. E. S., Bodah, E. T. (2017) Environmental damage and public health threat caused by cemeteries: a proposal of ideal cemeteries for the growing urban sprawl. urbe. Revista Brasileira de Gestão Urbana. https://doi.org/10.1590/2175-3369.009.002.ao05
Neckel, A., Korcelski, C., Kujawa, H. A., Schaefer da Silva, I., Prezoto, F., Walker Amorin, A. L., Maculan, L. S., Gonçalves, A. C., Bodah, E. T., Bodah, B. W., Dotto, G. L., Silva, L. F. O. (2021). Hazardous elements in the soil of urban cemeteries; constructive solutions aimed at sustainability. Chemosphere, 262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128248
Netto, L. G., Filho, W. M., Moreira, C. A., di Donato, F. T., & Helene, L. P. I. (2021). Delineation of necroleachate pathways using electrical resistivity tomography (ERT): Case study on a cemetery in Brazil. Environmental Challenges, 5, 100344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100344
OECD. Organisation for economic co-operation and development. (2013). Test No.236: Fish embryo acute toxicity (FET) Test. OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Paris, France.
Pelka, K. E., Henn, K., Keck, A., Sapel, B., & Braunbeck, T. (2017). Size does matter – Determination of the critical molecular size for the uptake of chemicals across the chorion of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Aquatic Toxicology, 185, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.12.015
Rodrigues, L., & Pacheco, A. (2010). Groundwater contamination from cemeteries cases of study. Proceedings of the Environmental, 1–6.
Saad, M. A., Abd-Rabou, H. S., Elkhtab, E., Rayan, A. M., Abdeen, A., Abdelkader, A., Ibrahim, S. F., & Hussien, H. (2022). Occurrence of toxic biogenic amines in various types of soft and hard cheeses and their control by bacillus polymyxa D05–1. Fermentation, 8, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8070327
Saba, E. D., Saba, J. M., Mendes, T. A., & de Oliveira, A. E. (2023). Evaluating the impact of a cemetery on groundwater by multivariate analysis. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195, 270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10895-y
Spadotim, R. F. (2015). Avaliação Ecotoxicológica e identificação da toxicidade no Ribeirão Pires, Limeira - SP. Doctoral dissertation.
USEPA. (2002). Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms. Fifth edition, Washington.
Vallim, J. H., Clemente, Z., Castanha, R. F., do Espírito Santo Pereira, A., Campos, E. V. R., Assalin, M. R., Maurer-Morelli, C. V., Fraceto, L. F., de Castro, V. L. S. S. (2022). Chitosan nanoparticles containing the insecticide dimethoate: A new approach in the reduction of harmful ecotoxicological effects. NanoImpact, 27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2022.100408
Viegas, C., Cervantes, R., Dias, M., Gomes, B., Pena, P., Carolino, E., Twarużek, M., Kosicki, R., Soszczyńska, E., Viegas, S., Caetano, L. A. (2022). Six feet under microbiota: microbiologic contamination and toxicity profile in three urban cemeteries from Lisbon, Portugal. Toxins (Basel), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14050348
Wieczorek, K., Świątek, P., & Durak, R. (2021). Influence of selected biogenic amines on development and demographic parameters of a temperate population of Cinara (Cupressobium) cupressi (Hemiptera, Aphididae). Arthropod-Plant Interactions, 15, 583–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-021-09839-z
Wójcik, W., Łukasiewicz, M., & Puppel, K. (2020). Biogenic amines: Formation, action and toxicity – a review. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10928
Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., Chen, M., Yang, Q., Zhuang, S., Lv, L., Zuo, Z., & Wang, C. (2019). Exposure to low-level metalaxyl impacts the cardiac development and function of zebrafish embryos. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 85, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.03.019
Zhou, R., Yu, Q., Li, T., Long, M., Wang, Y., Feng, T., Su, W., Yang, J., & Li, H. (2021). Carcass decomposition influences the metabolic profiles and enriches noxious metabolites in different water types by widely targeted metabolomics. Chemosphere, 269, 129400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129400
Zychowski, J., & Bryndal, T. (2015). Impact of cemeteries on groundwater contamination by bacteria and viruses - A review. Journal of Water and Health, 13, 285–301. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2014.119
Funding
We would like to thank CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoa de Nível Superior) for supplying a scholarship to the first author and Embrapa Environment for providing support for the development of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Ana Paula Andrade Braga. José Henrique Vallim and Rodrigo Fernandes Castanha contributed to the performance of bioassays and data analysis. Vera Lucia Scherholz Salgado de Castro and Maria Aparecida Marin Morales acting in the supervision, conceptualization, and revision of the entire manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All experimental procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals registered nº 001/2022. Embrapa Environment, Brazil.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Braga, A.P.A., Vallim, J.H., Castanha, R.F. et al. Toxicity Assessment of the Biogenic Amines Cadaverine and Putrescine in Aquatic Organisms. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 197 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06983-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06983-z