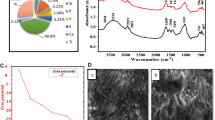
Abstract
Synthetic dyes are highly endangering the environment and widely contributing to the water pollution. Congo red is also a synthetic dye with which many research works have been done to remove Congo red (CR) using adsorption technology. However, the adsorption capacity is still unsatisfactory. This work deeply investigated the CR removal utilizing engineered nanosilica, derived from paddy husk. The engineered nanosilica was produced from paddy husk at 700 °C for 6 h following the activation process using CaCl2 at 500 °C for 30 min. Adsorptive experiments were done under a set of experimental conditions (dosage, 0.5 g/L; pH 6; rpm 150; holding time 24 h) to identify the best adsorption capacity. The engineered nanosilica with the highest adsorptive capacity (Qe), among other adsorbents considered, (Qe of raw paddy husk -18.48 mg/g; Qe of biochar -25.42 mg/g; nanosilica - 48.53mg/g; and engineered nanosilica - 57.2 mg/g) was chosen for further studies: kinetics, thermodynamics, isotherm, and rate-limiting analysis, so as to understand the mechanism of adsorption of engineered nanosilica for CR removal. Additionally, to understand the functional properties of engineered nanosilica, the point of zero charge (pzc) and FTIR analysis were performed. Results revealed that the addition of the catalyst (CaCl2) improved surface functional groups (oxygen containing functional groups) remarkably. Moreover, the removal of CR declined with raising temperature, representing endothermic adsorption process. Pseudo-second order kinetic model and Freundlich isotherm model were highly suitable for explaining the adsorptive mechanism of engineered nanosilica for CR removal. The first-time use of Boyd’s external diffusion model clearly explained the strong involvement of chemisorption process in the removal of CR by the novel engineered nanosilica. All in all, the engineered nanosilica is an effective, environmentally benign, and affordable biomaterial to remove CR from polluted water.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used in this study will be made available up on the request.
References
Achour, Y., Bahsis, L., Ablouh, E. H., Yazid, H., Laamari, M. R., & Haddad, M. . El. (2021). Insight into adsorption mechanism of Congo red dye onto Bombax Buonopozense bark Activated-carbon using Central composite design and DFT studies. Surfaces and Interfaces, 23(April), 100977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.100977
Adeyemo, A. A., Adeoye, I. O., & Bello, O. S. (2017). Adsorption of dyes using different types of clay: A review. Applied Water Science, 7(2), 543–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0322-y
Ajien, A., Idris, J., Sofwan, N., Husen, R., & Seli, H. (2023). Coconut shell and husk biochar : A review of production and activation technology, economic, financial aspect and application. Waste Management & Research, 41(1), 37–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X221127167
Akhayere, E., Kavaz, D., & Vaseashta, A. (2022). Efficacy studies of silica nanoparticles synthesized using agricultural waste for mitigating waterborne contaminants. Applied Sciences (switzerland), 12(18), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189279
Al-ghouti, M. A., & Da, D. A. (2020). Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 122383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122383
Al-tohamy, R., Ali, S. S., Li, F., Okasha, K. M., Mahmoud, Y. A., Elsamahy, T., Jiao, H., Fu, Y., & Sun, J. (2022). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater : Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 231, 113160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113160
Ali, I. H. (2021). Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution using eco-friendly adsorbent of nanosilica. Baghdad Science Journal, 366–373. https://doi.org/10.21123/bsj.2021.18.2.0366
Aljeboree, A. M., Alshirifi, A. N., & Alkaim, A. F. (2014). Kinetics and equilibrium study for the adsorption of textile dyes on coconut shell activated carbon. Arabian Journal Of Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.01.020
Aoopngan, C., Nonkumwong, J., Phumying, S., Promjantuek, W., Maensiri, S., Noisa, P., Pinitsoontorn, S., Ananta, S., & Srisombat, L. (2019). Amine-functionalized and hydroxyl-functionalized magnesium ferrite nanoparticles for Congo red adsorption. Applied Nano Materials. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b01305
Bashir, S., Zhu, J., Fu, Q., & Hu, H. (2018). Comparing the adsorption mechanism of Cd by rice straw pristine and KOH-modified biochar. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1292-z
Beatriz, G., Hall, K., & Spokas, K. A. (2019). Understanding activation effects on low-temperature biochar for optimization of herbicide sorption. Agronomy. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9100588
Bhattacharya, S. S. A. (2017). Drinking water contamination and treatment techniques. Applied Water Science, 7(3), 1043–1067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0455-7
Chen, J., Nie, X. A., Jiang, J. C., & Zhou, Y. H. (2018). Thermal degradation and plasticizing mechanism of poly(vinyl chloride) plasticized with a novel cardanol derived plasticizer. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 292(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/292/1/012008
Cheng, N., Wang, B., Wu, P., Lee, X., Xing, Y., Chen, M., & Gao, B. (2021). Adsorption of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater by modified biochar: A review. Environmental Pollution, 273, 116448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116448
Da, E. (2022). Nano-silica modified with diamine for capturing azo dye. Molecules, 27, 3366. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113366
Danish, M., & Ahmad, T. (2018). A review on utilization of wood biomass as a sustainable precursor for activated carbon production and application. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 87(April), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.02.003
Dechabun, S., Udomsap, P., Chollacoop, N., & Eiad-Ua, A. (2020). Influence of physical mixing ratio on pore development in highly porous carbon prepared from nipa palm husk using hydrothermal carbonization with chemical activation. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 893(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/893/1/012002
Dissanayake, M., Liyanage, N., Herath, C., Rathnayake, S., & Fernando, E. Y. (2021). Mineralization of persistent azo dye pollutants by a microaerophilic tropical lake sediment mixed bacterial consortium. Environmental Advances, 3(October), 100038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2021.100038
Eduardo, C., Silva, D. F., Maria, B., Heloiza, A., Almeida, J., Karla, A., & Abud, D. S. (2019). Journal of King Saud University – Engineering Sciences Basic-dye adsorption in albedo residue : Effect of pH, contact time, temperature, dye concentration, biomass dosage, rotation and ionic strength. Journal of King Saud University - Engineering Sciences, Xxxx. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2019.04.006
El-didamony, H., El-fadaly, E., & Amer, A. A. (2019). Synthesis and characterization of low cost nanosilica from sodium silicate solution and their applications in ceramic engobes. Ceramica y Vidrio, 59, 31–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bsecv.2019.06.004
Farias, R. S. D., Buarque, H. L. D. B., Cruz, M. R. D., Cardoso, L. M. F., Gondim, T. D. A., & Paulo, V. R. D. (2018). Adsorption of congo red dye from aqueous solution onto amino-functionalized silica gel. Engenharia sanitária e ambiental, 23, 1053–1060.
Foroutan, R., Mohammadi, R., Peighambardoust, S. J., Jalali, S., & Ramavandi, B. (2020). Application of nano-silica particles generated from offshore white sandstone for cadmium ions elimination from aqueous media. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 101031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101031
Guo, G., Tian, F., Zhang, C., Liu, T., Yang, F., & Hu, Z. (2019). Performance of a newly enriched bacterial consortium for degrading and detoxifying azo dyes. Water Science & Technology, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2019.210
Gwenzi, W., Chaukura, N., Noubactep, C., & Mukome, F. (2017). Biochar-based water treatment as a potential low-cost and sustainable technology for clean water provision in developing countries. Journal of Environmental Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.03.087
Han, M., Shena, X., Shaob, H., Wanga, X., Liua, Y., & Zhaia, Y. (2022). Adsorption of Congo red by fibrous xonotlite prepared from waste silicon residue. Water Science & Technology, 85(11), 3159–3168. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2022.169
Iqbal, J., Shah, N. S., Sayed, M., Khan, N., Imran, M., Ali, J., Ul, Z., Khan, H., Gamal, A., & Hussien, S. (2021). Nano-zerovalent manganese / biochar composite for the adsorptive and oxidative removal of Congo-red dye from aqueous solutions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 403(May), 123854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123854
Isinkaralar, K., & Turkyilmaz, A. (2022). Simultaneous adsorption of selected VOCs in the gas environment by low-cost adsorbent from Ricinus communis. Carbon Letters, 32(7), 1781–1789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-022-00399-7
Isinkaralar, K., Turkyilmaz, A., & Lakestani, S. (2023). Equilibrium study of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene (BTEX) from gas streams by black pine cones-derived activated carbon. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 31, 103209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2023.103209
Jabraili, A., Pirsa, S., Khalil, M., & Saber, P. (2021). Biodegradable nanocomposite film based on gluten / silica / calcium chloride : Physicochemical properties and bioactive compounds extraction capacity. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 0123456789,. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02050-4
Janu, R., Mrlik, V., Ribitsch, D., Hofman, J., & D, P. S., Bielsk´, L., & Soja, G. (2021). Biochar surface functional groups as affected by biomass feedstock, biochar composition and pyrolysis temperature. Carbon Resources Conversion, 4, 36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crcon.2021.01.003
Yu, K.L., Lee, X.J., Ong, H.C., Chen, W.H., Chang, J.S., Lin, C.S., Show, P.L. and Ling, T.C. (2020). Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue and anionic Congo red dyes using wet- torrefied microalgal biochar: Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism modeling. Environmental Pollution, 115986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115986
Kumar, N., & Sumana, M. (2018). Potentiality of banana peel for removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution : Isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Applied Water Science, 8(6), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0811-x
Lafi, R. (2019). Adsorption of Congo red dye from aqueous solutions by prepared activated carbon with oxygen-containing functional groups and its regeneration. Adsorption Science & Technology, 37, 160–181. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617418819227
Lal, P., Poudel, R., Poudel, S., & Bhattarai, A. (2022). Heliyon Adsorption and removal of crystal violet dye from aqueous solution by modified rice husk. Heliyon, 8(January), e09261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09261
Lima, E. C., Gomes, A. A., & Tran, H. N. (2020). Comparison of the nonlinear and linear forms of the van’t Hoff equation for calculation of adsorption thermodynamic parameters (∆S° and ∆H°). Journal of Molecular Liquids, 311, 113315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113315
Litefti, K., Freire, M. S., Stitou, M., & González-álvarez, J. (2019). Adsorption of an anionic dye ( Congo red ) from aqueous solutions by pine bark. Scientific Reports, 9, 16530. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53046-z
Liu, J., Wang, N., Zhang, H., & Baeyens, J. (2019). Adsorption of Congo red dye on FexCo3-x O4 nanoparticles. Journal of Environmental Management, 238, 473–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.03.009
Mahmoudi, E., Azizkhani, S., Mohammad, A. W., Ng, L. Y., Benamor, A., Ang, W. L., & Ba-abbad, M. (2020). Simultaneous removal of Congo red and cadmium ( II ) from aqueous solutions using graphene oxide – silica composite as a multifunctional adsorbent. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 98, 151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.05.013
Moon, S. A., Salunke, B. K., Saha, P., Deshmukh, A. R., & Kim, B. S. (2017). Comparison of dye degradation potential of biosynthesized copper oxide, manganese dioxide, and silver nanoparticles using Kalopanax pictus plant extract. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 34(7), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-017-0318-4
Muinde, V. M., Onyari, J. M., Wamalwa, B., Wabomba, J., & Nthumbi, R. M. (2017). Adsorption of malachite green from aqueous solutions onto rice husks : Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Journal of Environmental Protection, 8, 215–230. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2017.83017
Mujiyanti, D. R., Surianthy, M. D., & Junaidi, A. B. (2018). The initial characterization of nanosilica from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) with the addition polivynil alcohol by Fourier transform infra red. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 187(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/187/1/012056
Nai, P., Yek, Y., Peng, W., Chung, C., Keey, R., Ling, Y., Aghbashlo, M., Sonne, C., & Shiung, S. (2020). Engineered biochar via microwave CO 2 and steam pyrolysis to treat carcinogenic Congo red dye. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 395, 122636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122636
Nasron, A. N., Azman, N. S., Syaidatul, N., Mohd, S., Said, N. R., Branch, N. S., Campus, K. P., & Sembilan, N. (2018). Degradation of Congo red dye in aqueous solution by using advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Academia, 6(2), 1–11.
Nguyen, H. X., Dao, N. T. T., Nguyen, H. T. T., & Le, A. Q. T. (2019). Nanosilica synthesis from rice husk and application for soaking seeds Nanosilica synthesis from rice husk and application for soaking seeds. Earth and Environmental, 266, 012007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/266/1/012007
Oladoye, P. O. M. O., Bamigboye, O. D., Ogunbiyi, M. T., & Akano. (2022). Toxicity and decontamination strategies of Congo red dye. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 19, 100844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2022.100844
Pishnamazi, M., Khan, A., Kurniawan, T. A., Sanaeepur, H., Albadarin, A. B., & Soltani, R. (2021). Adsorption of dyes on multifunctionalized nano-silica KCC-1. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 116573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116573
Rafiee, E., Shahebrahimi, S., Feyzi, M., & Shaterzadeh, M. (2012). Optimization of synthesis and characterization of nanosilica produced from rice husk ( a common waste material). International Nano Letters, 2–29. https://doi.org/10.1186/2228-5326-2-29
Raghav, S., & Kumar, D. (2018). Adsorption equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies of fluoride adsorbed by tetrametallic oxide adsorbent. Journal of Chemical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.8b00024
Ranaraja, C. D. M. O., Arachchige, U. S. P. R., & Rasenthiran, K. (2019). Environmental pollution and its challenges in Sri Lanka. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 8(07), 417–419.
Rathi, B. S., & Kumar, P. S. (2021). Application of adsorption process for effective removal of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater. Environmental Pollution, 280, 116995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116995
Revellame, E. D., Lord, D., Sharp, W., Hernandez, R., & Zappi, M. E. (2020). Adsorption kinetic modeling using pseudo- fi rst order and pseudo-second order rate laws : A review. Cleaner Engineering and Technology, 100032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2020.100032
Saha, D., & Grappe, H. A. (2017). Adsorption properties of activated carbon fibers. Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100660-3.00005-5
Sahoo, T. R., & Prelot, B. (2020). Chapter 7 - Adsorption processes for the removal of contaminants from wastewater: The perspective role of nanomaterials and nanotechnology. Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818489-9.00007-4
Siddiqui, S. I., Allehyani, E. S., Al-harbi, S. A., Hasan, Z., Abomuti, M. A., Rajor, H. K., & Oh, S. (2023). Investigation of Congo red toxicity towards different living organisms : A review. Processes, 11, 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030807
Sirajudheen, P., Raja, M., Karthikeyan, P., & Meenakshi, S. (2020). Perceptive removal of toxic azo dyes from water using magnetic Fe 3 O 4 reinforced graphene oxide – carboxymethyl cellulose recyclable composite : Adsorption investigation of parametric studies and their mechanisms. Surfaces and Interfaces, 21(July), 100648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100648
Sunthar, L., & Asharp, T. (2023). Insights into mechanisms of novel engineered biochar derived from neem chips via iron catalyst for the removal of methyl orange from aqueous phase. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06187-x
Swaminathen, A. N., Kumar, C. V., Ravi, S. R., & Debnath, S. (2021). Materials today : Proceedings evaluation of strength and durability assessment for the impact of rice husk ash and metakaolin at high performance concrete mixes. Materials Today: Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.05.449
Teng, Y., Liu, Z., Xu, G., & Zhang, K. (2017). Desorption kinetics and mechanisms of CO2 on amine-based mesoporous silica materials. Energies, 10(1), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10010115
To, P. K., Ma, H. T., Hoang, L. N., & Nguyen, T. T. (2020). Nitrate removal from waste-water using silica nanoparticles. Journal of Chemistry, 6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8861423
Tsamo, C., Dourandi, G., Dieudonne, K., & Dahaina, C. (2020). Removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution using silica extracted from rice husk. SN Applied Sciences, 2(2), 256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2057-0
Vasamsetti, S., Dumpala, L., & Subbarao, V. V. (2018). Synthesis, characterization and hardness studies of nano rice husk ash reinforced al6061 nanocomposites. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 13(9), 2916–2929.
Wang, B., Gao, B., Wang, B., Gao, B., & Fang, J. (2018). Recent advances in engineered biochar productions and applications. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 1–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2017.1418580
Wekoye, J. N., Wanyonyi, W. C., Wangila, P. T., & Tonui, M. K. (2020). Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology kinetic and equilibrium studies of Congo red dye adsorption on cabbage waste powder. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, 2, 24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enceco.2020.01.004
Wu, K., Nan, Q., & Wu, T. (2020a). Philosophical analysis of the meaning and nature of entropy and negative entropy theories. Complexity, 2020, 11.
Wu, Z., Ye, X., Liu, H., Zhang, H., Liu, Z., Guo, M., Li, Q., & Li, J. (2020b). Interactions between adsorbents and adsorbates in aqueous solutions. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 92(10), 1655–1662.
Zheng, Y., Cheng, B., Fan, J., Yu, J., & Ho, W. (2020). Review on nickle-based adsorption materials for Congo red. Journal of Hazardous Materials. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123559
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to appreciate the Department of Agricultural Engineering, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Jaffna, Sri Lanka, for providing resources and financial support. We would like to extend our gratitude to the Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Jaffna, for providing instrumental support. The contribution given by Professor.G.Sashikesh for FTIR analysis is highly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shankar, M., Sunthar, L., Asharp, T. et al. Engineered Nanosilica, Derived from Paddy Husk, for the Removal of Congo Red from Polluted Water: an Exploratory Study Using Mathematical Models and Adsorptive Experiments. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 166 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06931-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06931-x