Abstract
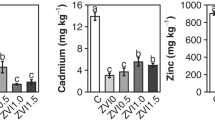
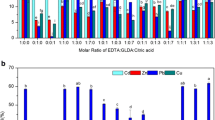
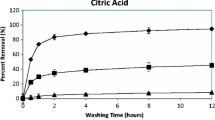
The influence of different pH conditions and simulated inter-root environmental solutions on the release behavior of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, and Zn) from contaminated soils was investigated. The results indicate that heavy metal leaching from the soil is more likely to occur under acidic conditions and there is a risk of sustained presence of heavy metals in the inter-root solution. To address this issue, soil washing experiments were conducted, showing that the overall heavy metals removal efficiency by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt (EDTA) is higher than other agents such as citric acid, malic acid, HCl, and HNO3. Under the optimal conditions, the removal rates of Cu, Zn, and Pb from the soil are 43.9%,73.1%, and 41.5%, respectively. Single-factor experimental studies show a strong positive correlation between leaching concentration and temperature. Thermodynamic calculations suggest the feasibility of EDTA as a soil washing agent for remediation, as the process is found to be spontaneous, endothermic, and entropically favorable. The combined results of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis and density functional theory (DFT) calculations suggest that EDTA is particularly effective in removing steady-state Pb, while citric acid has an insignificant effect on Pb removal. EDTA has a stronger ability to remove lead than citric acid attributed to the higher complexing strength of EDTA with Pb and the better water solubility of EDTA metal complexes. In addition, the removal efficiency of Zn and Cu with EDTA is significantly (p < 0.05) greater compared to that with citric acid.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Alghanmi, S. I., Al Sulami, A. F., El-Zayat, T. A., Alhogbi, B. G., & Abdel Salam, M. (2015). Acid leaching of heavy metals from contaminated soil collected from Jeddah, Saudi Arabia: Kinetic and Thermodynamics Studies. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 3, 196–208.
Arwidsson, Z., Johansson, E., von Kronhelm, T., Allard, B., & van Hees, P. (2010). Remediation of metal contaminated soil by organic metabolites from fungi I-Production of organic acids. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 205, 215–226.
Ash, C., Tejnecky, V., Boruvka, L., & Drabek, O. (2016). Different low-molecular-mass organic acids specifically control leaching of arsenic and lead from contaminated soil. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 187, 18–30.
Bhatnagar, A., Minocha, A. K., Jeon, B.-H., & Park, J.-M. (2007). Adsorptive removal of cobalt from aqueous solutions by utilizing industrial waste and its cement fixation. Separation Science and Technology, 42, 1255–1266.
Borggaard, O. K., Holm, P. E., & Strobel, B. W. (2019). Potential of dissolved organic matter (DOM) to extract As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn from polluted soils: A review. Geoderma, 343, 235–246.
Chen, S., Fei, X., Zhang, C., Chen, Y., & Ge, Q. (2021). Release behavior of heavy metals from soil in ultrasound-assisted EDTA washing. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 21, 3825–3833.
Cheng, S., Lin, Q., Wang, Y., Luo, H., Huang, Z., Fu, H., Chen, H., & Xiao, R. (2020). The removal of Cu, Ni, and Zn in industrial soil by washing with EDTA-organic acids. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 13, 5160–5170.
Cho, K., Myung, E., Kim, H., Park, C., Choi, N., & Park, C. (2020). Effect of soil washing solutions on simultaneous removal of heavy metals and arsenic from contaminated soil. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17, 3133.
Chu, C., Darling, K., Netusil, R., Doyle, R. P., & Zubieta, J. (2011). Synthesis and structure of a lead(II)-citrate: Na(H2O)(3) Pb-5(C6H5O7)(3)(C6H6O7)(H2O)(3) center dot 9.5H(2)O. Inorganica Chimica Acta, 378, 186–193.
do Nascimento, C. W. A., Amarasiriwardena, D., & Xing, B. S. (2006). Comparison of natural organic acids and synthetic chelates at enhancing phytoextraction of metals from a multi-metal contaminated soil. Environmental Pollution, 140, 114–123.
Geng, H., Wang, F., Yan, C., Tian, Z., Chen, H., Zhou, B., Yuan, R., & Yao, J. (2020). Leaching behavior of metals from iron tailings under varying pH and low-molecular-weight organic acids. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 383, 121136.
Guo, X., Zhao, G., Zhang, G., He, Q., Wei, Z., Zheng, W., Qian, T., & Wu, Q. (2018). Effect of mixed chelators of EDTA, GLDA, and citric acid on bioavailability of residual heavy metals in soils and soil properties. Chemosphere, 209, 776–782.
Gusiatin, Z. M., Kulikowska, D., & Klik, B. (2020). New-generation washing agents in remediation of metal-polluted soils and methods for washing effluent treatment: A review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17, 6220.
Gusiatin, Z. M., & Klimiuk, E. (2012). Metal (Cu, Cd and Zn) removal and stabilization during multiple soil washing by saponin. Chemosphere, 86, 383–391.
He, D., Yang, C., Wu, Y., Liu, X., Xie, W., & Yang, J. (2017). PbSO4 leaching in citric acid/sodium citrate solution and subsequent yielding lead citrate via controlled crystallization. Minerals, 7, 93.
Hu, X. Y., Guo, X. J., He, M. C., & Li, S. S. (2016). pH-dependent release characteristics of antimony and arsenic from typical antimony-bearing ores. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 44, 171–179.
Hu, W., Niu, Y., Zhu, H., Dong, K., Wang, D., & Liu, F. (2021). Remediation of zinc-contaminated soils by using the two-step washing with citric acid and water-soluble chitosan. Chemosphere, 282, 131092.
Huang, Z., Jiang, L., Wu, P., Dang, Z., Zhu, N., Liu, Z., & Luo, H. (2020). Leaching characteristics of heavy metals in tailings and their simultaneous immobilization with triethylenetetramine functioned montmorillonite (TETA-Mt) against simulated acid rain. Environmental Pollution, 266, 115236.
Jeong, H., Choi, J. Y., & Ra, K. (2021). Heavy metal pollution assessment in stream sediments from urban and different types of industrial areas in South Korea. Soil & Sediment Contamination, 30, 804–818.
Kumpiene, J., Carabante, I., Kasiuliene, A., Austruy, A., & Mench, M. (2021). Long-term stability of arsenic in iron amended contaminated soil. Environmental Pollution, 269, 116017.
Lago-Vila, M., Arenas-Lago, D., Rodriguez-Seijo, A., Luisa Andrade, M., & Vega, F. A. (2019). Ability of Cytisus scoparius for phytoremediation of soils from a Pb/Zn mine: Assessment of metal bioavailability and bioaccumulation. Journal of Environmental Management, 235, 152–160.
Le, T. K., Flahaut, D., Martinez, H., Andreu, N., Gonbeau, D., Pachoud, E., Pelloquin, D., & Maignan, A. (2011). The electronic structure of the CuRh1-xMgxO2 thermoelectric materials: An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 184, 2387–2392.
Li, X., Wu, Y., Zhang, C., Liu, Y., Zeng, G., Tang, X., Dai, L., & Lan, S. (2016). Immobilizing of heavy metals in sediments contaminated by nonferrous metals smelting plant sewage with sulfate reducing bacteria and micro zero valent iron. Chemical Engineering Journal, 306, 393–400.
Li, K., Cheng, J., Ye, Q., He, Y., Zhou, J., & Cen, K. (2017). In vivo kinetics of lipids and astaxanthin evolution in Haematococcus pluvialis mutant under 15% CO2 using Raman microspectroscopy. Bioresource Technology, 244, 1439–1444.
Li, L., Zhang, C., Yuan, Z., Xu, X., & Song, Z. (2019). AFM and DFT study of depression of hematite in oleate-starch-hematite flotation system. Applied Surface Science, 480, 749–758.
Liang, F., Guo, Z. H., Men, S. H., Xiao, X. Y., Peng, C., Wu, L. H., & Christie, P. (2019). Extraction of Cd and Pb from contaminated-paddy soil with EDTA, DTPA, citric acid and FeCl3 and effects on soil fertility. Journal of Central South University, 26, 2987–2997.
Liang, R.-H., Li, Y., Huang, L., Wang, X.-D., Hu, X.-X., Liu, C.-M., Chen, M.-S., & Chen, J. (2020). Pb2+ adsorption by ethylenediamine-modified pectins and their adsorption mechanisms. Carbohydrate Polymers, 234, 115911.
Liu, C., & Zhang, H. X. (2022). Modified-biochar adsorbents (MBAs) for heavy-metal ions adsorption: A critical review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10, 107393.
Moon, D. H., & Dermatas, D. (2007). Arsenic and lead release from fly ash stabilized/solidified soils under modified semi-dynamic leaching conditions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 141, 388–394.
Moon, D. H., Lee, J.-R., Wazne, M., & Park, J.-H. (2012). Assessment of soil washing for Zn contaminated soils using various washing solutions. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 18, 822–825.
Peters, R. W. (1999). Chelant extraction of heavy metals from contaminated soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 66, 151–210.
Piatak, N. M., Parsons, M. B., & Seal, R. R. (2015). Characteristics and environmental aspects of slag: A review. Applied Geochemistry, 57, 236–266.
Qiao, D., Han, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2022). Organic acids in conjunction with various oilseed sunflower cultivars promote Cd phytoextraction through regulating micro-environment in root zone. Industrial Crops and Products, 183, 114932.
Ramamurthy, A. S., Vo, D., Li, X. J., & Qu, J. (2008). Surfactant-enhanced removal of Cu (II) and Zn (II) from a contaminated sandy soil. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 190, 197–207.
Rosa, M. A., Egido, J. A., & Marquez, M. C. (2017). Enhanced electrochemical removal of arsenic and heavy metals from mine tailings. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 78, 409–415.
Salam, M. A. (2013). Coating carbon nanotubes with crystalline manganese dioxide nanoparticles and their application for lead ions removal from model and real water. Colloids and Surfaces a-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 419, 69–79.
Su, S.-m, Zeng, X.-b, Bai, L.-y, & Li, L.-f. (2010). Action mechanisms of microorganisms on arsenic and the feasibility of utilizing fungi in remediation of arsenic-contaminated soil. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao, 21, 3266–3272.
Sun, X.-F., Wang, S.-G., Liu, X.-W., Gong, W.-X., Bao, N., & Gao, B.-Y. (2008). Competitive biosorption of zinc(II) and cobalt(II) in single- and binary-metal systems by aerobic granules. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 324, 1–8.
Sun, R., Gao, Y., & Yang, Y. (2022a). Leaching of heavy metals from lead-zinc mine tailings and the subsequent migration and transformation characteristics in paddy soil. Chemosphere, 291, 132792.
Sun, Y., Zhang, P., Li, Z., Chen, J., Ke, Y., Hu, J., Liu, B., Yang, J., Liang, S., Su, X., & Hou, H. (2022b). Iron-calcium reinforced solidification of arsenic alkali residue in geopolymer composite: Wide pH stabilization and its mechanism. Chemosphere, 312, 137063.
Wang, H., Pan, L.-x, Zhang, X.-y, Li, M., & Song, B.-h. (2013). Study on composite stabilization of arsenic (As) contaminated soil. Huanjing Kexue, 34, 3587–3594.
Wang, J. P., & Erdenebold, U. (2020). A study on reduction of copper smelting slag by carbon for recycling into metal values and cement raw material. Sustainability, 12, 1421.
Wang, Q., Wang, M., Wang, K., Sun, Y., Zhang, H., Lu, X., & Duan, K. (2020). Molecular mechanisms of interactions between BMP-2 and graphene: Effects of functional groups and microscopic morphology. Applied Surface Science, 525, 146636.
Wen, J., Stacey, S. P., McLaughlin, M. J., & Kirby, J. K. (2009). Biodegradation of rhamnolipid, EDTA and citric acid in cadmium and zinc contaminated soils. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 41, 2214–2221.
Wu, J., Ma, W., Wang, X., Jiao, F., & Qin, W. (2020). The effect of galvanic interaction between chalcopyrite and pyrite on the surface chemistry and collector adsorption: Flotation and DFT study. Colloids and Surfaces a-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 607, 125377.
Xu, D.-M., & Fu, R.-B. (2022). The mechanistic insights into the leaching behaviors of potentially toxic elements from the indigenous zinc smelting slags under the slag dumping site scenario. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 437, 129368.
Yang, D., Yang, S., Yuan, H., Wang, F., Wang, H., Xu, J., & Liu, X. (2021). Co-benefits of biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in simultaneously stabilizing soil heavy metals and reducing their bioaccessibility. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 418, 126292.
Zhang, C., Yu, Z., Zeng, G., Huang, B., Dong, H., Huang, J., Yang, Z., Wei, J., Hu, L., & Zhang, Q. (2016). Phase transformation of crystalline iron oxides and their adsorption abilities for Pb and Cd. Chemical Engineering Journal, 284, 247–259.
Zhang, H., Sun, W., Zhang, C., He, J., Chen, D., & Zhu, Y. (2022). Adsorption performance and mechanism of the commonly used collectors with oxygen-containing functional group on the ilmenite surface: A DFT study. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 346, 117829.
Zhao, L., Dai, S., Finkelman, R. B., French, D., Graham, I. T., Yang, Y., Li, J., & Yang, P. (2020). Leaching behavior of trace elements from fly ashes of five Chinese coal power plants. International Journal of Coal Geology, 219, 103381.
Zheng, X.-J., Li, Q., Peng, H., Zhang, J.-X., Chen, W.-J., Zhou, B.-C., & Chen, M. (2022). Remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils with soil washing: A review’. Sustainability, 14, 13058.
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out in part using hardware and/or software provided by the High-Performance Computing Centers of Central South University
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFC1803501), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52074357), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2022JJ30713).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Chen, P., Wang, H. et al. Remediation of Cu-, Zn-, and Pb-Contaminated Soil Using Different Soil Washing Agents: Removal Efficiencies and Mechanisms. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 476 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06463-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06463-w