Abstract
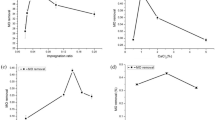
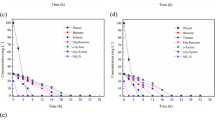
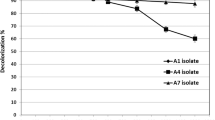
Bioremediation of azo dye wastewater has been recognized as the most promising approach. However, azo dye biodecolorization is usually performed using free bacterial cells under anaerobic conditions, which has issues in practical application like solid–liquid separation, sensitivity to toxic dyes, and reusability. In this work, we adopt cell immobilization strategy to solve these problems and investigate the biodecolorization of cationic red X-GRL (X-GRL), a typical azo dye, by immobilized cells of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 (MR-1). Results indicated that under aerobic conditions, immobilized cells of MR-1 could effectively decolorize 100 mg/L X-GRL, while its free cells could hardly do it under the same conditions. X-GRL biodecolorization by immobilized MR-1 was affected by initial dye concentration, number and size of immobilized beads, static or shaking culture, medium pH, and incubation temperature, but above 83% of X-GRL could be decolorized within 48 h in a pH range of 6.0–7.5 and a temperature range of 20–35 °C. The optimal conditions for X-GRL biodecolorization by immobilized MR-1 were as follows: 15 beads of 4.5 mm in diameter, pH 7.0, 30 °C, shaking, and aerobic culture, under which immobilized MR-1 could almost decolorize all of X-GRL (100 mg/L) in 48 h, but an economical decolorization time period was 12 h due to 87.3% X-GRL decolorization efficiency achieved. Additionally, the results of repeated-batch biodecolorization experiments revealed that the immobilized beads were of excellent reusability and long-term X-GRL degradation activity as nearly 80% of initial activity was retained after 5 cycles (240 h). The phytotoxicity assay results indicated that the phytotoxicity of X-GRL was significantly reduced after biodecolorization by immobilized MR-1. This study demonstrates that the biological process using immobilized MR-1 has great potential in the treatment of azo dye wastewater containing X-GRL.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abarian, M., Hassanshahian, M., & Esbah, A. (2019). Degradation of phenol at high concentrations using immobilization of Pseudomonas putida P53 into sawdust entrapped in sodium-alginate beads. Water Science and Technology, 79(7), 1387–1396. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2019.134
Alam, R., Ardiati, F. C., Solihat, N. N., Alam, M. B., Lee, S. H., Yanto, D. H. Y., Watanabe, T., & Kim, S. (2021). Biodegradation and metabolic pathway of anthraquinone dyes by Trametes hirsuta D7 immobilized in light expanded clay aggregate and cytotoxicity assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 405, 124176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124176
Aoyagi, R., Terada, A., & Tokuyama, H. (2020). Oxygen diffusivity and reaction rate in spherical gel entrapping ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 164, 107788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2020.107788
Asses, N., Ayed, L., Hkiri, N., & Hamdi, M. (2018). Congo red decolorization and detoxification by Aspergillus niger: Removal mechanisms and dye degradation pathway. BioMed Research International, 2018, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3049686
Bhatia, D., Sharma, N. R., Singh, J., & Kanwar, R. S. (2017). Biological methods for textile dye removal from wastewater: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 47(19), 1836–1876. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2017.1393263
Booth, I. R. (1985). Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in bacteria. Microbiological Reviews, 49(4), 359–378. https://doi.org/10.1128/mr.49.4.359-378.1985
Bouabidi, Z. B., El-Naas, M. H., & Zhang, Z. (2018). Immobilization of microbial cells for the biotreatment of wastewater: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 17(1), 241–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0795-7
Buntić, A. V., Pavlović, M. D., Antonović, D. G., Šiler-Marinković, S. S., & Dimitrijević-Branković, S. I. (2017). A treatment of wastewater containing basic dyes by the use of new strain Streptomyces microflavus CKS6. Journal of Cleaner Production, 148, 347–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.164
Cai, F., Lei, L., Li, Y., & Chen, Y. (2021). A review of aerobic granular sludge (AGS) treating recalcitrant wastewater: Refractory organics removal mechanism, application and prospect. Science of the Total Environment, 782, 146852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146852
Cao, G. M., Zhao, Q. X., Sun, X. B., & Zhang, T. (2002). Characterization of nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria coimmobilized in PVA and kinetics model of biological nitrogen removal by coimmobilized cells. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 30(1), 49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0141-0229(01)00458-6
Cao, D. M., Xiao, X., Wu, Y. M., Ma, X. B., Wang, M. N., Wu, Y. Y., & Du, D. L. (2013). Role of electricity production in the anaerobic decolorization of dye mixture by exoelectrogenic bacterium Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Bioresource Technology, 136, 176–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.02.083
Cao, X., Qi, Y., Xu, C., Yang, Y., & Wang, J. (2017). Transcriptome and metabolome responses of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 to methyl orange under microaerophilic and aerobic conditions. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 101, 3463–3472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8087-2
Chen, G., hong Huang, M., Chen, L., & hui Chen, D. (2011). A batch decolorization and kinetic study of Reactive Black 5 by a bacterial strain Enterobacter sp. GY-1. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 65(6), 790–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.05.003
Chittal, V., Gracias, M., Anu, A., Saha, P., & Bhaskara Rao, K. V. (2019). Biodecolorization and biodegradation of azo dye Reactive Orange-16 by marine Nocardiopsis sp. Iranian Journal of Biotechnology, 17(3), e1551. https://doi.org/10.29252/ijb.1551
Cui, D., Shen, D., Wu, C., Li, C., Leng, D., & Zhao, M. (2017). Biodegradation of aniline by a novel bacterial mixed culture AC. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 125, 86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.08.010
Daigle, D. J., & Cotty, P. J. (1997). The effect of sterilization, pH, filler and spore inoculum concentration on the preparation of alginate pellets. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 7(1), 3–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/09583159730992
Dong, X. (2005). Decolorization of anthraquinone dye with immobilized Penicillium jensenii. Journal of Environmental Biology, 26(3), 475–478.
Dzionek, A., Wojcieszyńska, D., & Guzik, U. (2022). Use of xanthan gum for whole cell immobilization and its impact in bioremediation-a review. Bioresource Technology, 351, 126918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.126918
Fu, X., Wang, H., Bai, Y., Xue, J., Gao, Y., Hu, S., Wu, T., & Sun, J. (2020). Systematic degradation mechanism and pathways analysis of the immobilized bacteria: Permeability and biodegradation, kinetic and molecular simulation. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, 2, 100028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2020.100028
Hameed, B. B., & Ismail, Z. Z. (2018). Decolorization, biodegradation and detoxification of reactive red azo dye using non-adapted immobilized mixed cells. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 137, 71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2018.05.018
Joshi, S. J., & Abed, R. M. M. (2017). Biodegradation of polyacrylamide and its derivatives. Environmental Processes, 4(2), 463–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-017-0224-0
Kardi, S. N., Rashid, N. A. A., Ibrahim, N., & Ahmad, A. (2016). Biodegradation of Remazol Black B in sequential microaerophilic–aerobic operations by NAR-2 bacterial consortium. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5984-8
Kasai, T., Suzuki, Y., Kouzuma, A., & Watanabe, K. (2019). Roles of d-lactate dehydrogenases in the anaerobic growth of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 on sugars. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 85(3), e02668-e2718. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02668-18
Knapp, J. S., & Newby, P. S. (1995). The microbiological decolorization of an industrial effluent containing a diazo-linked chromophore. Water Research, 29(7), 1807–1809. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)00341-4
Lei, L., Dai, Q., Zhou, M., & Zhang, X. (2007). Decolorization of cationic red X-GRL by wet air oxidation: Performance optimization and degradation mechanism. Chemosphere, 68(6), 1135–1142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.01.075
Li, Q., Feng, X., Lu, X., Li, T., Han, X., Xiao, X., Wu, X., Liu, Z., Yang, M., & Feng, Y. (2018a). Combined intra- and extracellular reduction involved in the anaerobic biodecolorization of cationic azo dye by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Chemosphere, 211, 701–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.08.006
Li, Q., Feng, X. L., Li, T. T., Lu, X. R., Liu, Q. Y., Han, X., Feng, Y. J., Liu, Z. Y., Zhang, X. J., & Xiao, X. (2018b). Anaerobic decolorization and detoxification of cationic red X-GRL by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Environmental Technology, 39(18), 2382–2389. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1355933
Liu, W., Liu, L., Liu, C., Hao, Y., Yang, H., Yuan, B., & Jiang, J. (2016). Methylene blue enhances the anaerobic decolorization and detoxication of azo dye by Shewanella onediensis MR-1. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 110, 115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2016.02.012
Liu, C., You, Y., Zhao, R., Sun, D., Zhang, P., Jiang, J., Zhu, A., & Liu, W. (2017). Biosurfactant production from Pseudomonas taiwanensis L1011 and its application in accelerating the chemical and biological decolorization of azo dyes. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 145, 8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.07.012
Liu, J., Pan, D., Wu, X., Chen, H., Cao, H., Li, Q. X., & Hua, R. (2018). Enhanced degradation of prometryn and other s-triazine herbicides in pure cultures and wastewater by polyvinyl alcohol-sodium alginate immobilized Leucobacter sp JW-1. Science of the Total Environment, 615, 78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.208
Lu, M., Chan, S., Babanova, S., & Bretschger, O. (2017). Effect of oxygen on the per-cell extracellular electron transfer rate of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 explored in bioelectrochemical systems. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 114(1), 96–105. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26046
Mehrotra, T., Zaman, M. N., Prasad, B. B., Shukla, A., Aggarwal, S., & Singh, R. (2020). Rapid immobilization of viable Bacillus pseudomycoides in polyvinyl alcohol/glutaraldehyde hydrogel for biological treatment of municipal wastewater. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(9), 9167–9180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07296-z
Nie, H., Nie, M., Diwu, Z., Wang, L., Yan, H., Lin, Y., Zhang, B., & Wang, Y. (2020). Biological treatment of high salinity and low pH produced water in oilfield with immobilized cells of P. aeruginosa NY3 in a pilot-scale. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 381, 121232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121232
Nie, Z., Yan, B., Xu, Y., Awasthi, M. K., & Yang, H. (2021). Characterization of pyridine biodegradation by two Enterobacter sp. strains immobilized on Solidago canadensis L. stem derived biochar. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 414, 125577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125577
Ren, G. Q., Li, Q., Li, Y., Li, J., Adomako, M. O., Dai, Z. C., Li, G. L., Wan, L. Y., Zhang, B., Zou, C. B., Ran, Q., & Du, D. L. (2019). The enhancement of root biomass increases the competitiveness of an invasive plant against a co-occurring native plant under elevated nitrogen deposition. Flora, 261, 151486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flora.2019.151486
Roy, U., Sengupta, S., Banerjee, P., Das, P., Bhowal, A., & Datta, S. (2018). Assessment on the decolourization of textile dye (Reactive Yellow) using Pseudomonas sp. immobilized on fly ash: Response surface methodology chock for optimization and toxicity evaluation. Journal of Environmental Management, 223, 185–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.06.026
Sam, S. P., Adnan, R., & Ng, S. L. (2021). Statistical optimization of immobilization of activated sludge in PVA/alginate cryogel beads using response surface methodology for p-nitrophenol biodegradation. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 39, 101725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101725
San, N. O., Celebioglu, A., Tümtaş, Y., Uyar, T., & Tekinay, T. (2014). Reusable bacteria immobilized electrospun nanofibrous webs for decolorization of methylene blue dye in wastewater treatment. RSC Advances, 4(61), 32249–32255. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA04250F
Saratale, R. G., Saratale, G. D., Chang, J. S., & Govindwar, S. P. (2011). Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: A review. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 42(1), 138–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2010.06.006
Saratale, R. G., Gandhi, S. S., Purankar, M. V., Kurade, M. B., Govindwar, S. R., Oh, S. E., & Saratale, G. D. (2013). Decolorization and detoxification of sulfonated azo dye CI Remazol Red and textile effluent by isolated Lysinibacillus sp. RGS. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 115(6), 658–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.12.009
Saroj, S., Kumar, K., Pareek, N., Prasad, R., & Singh, R. P. (2014). Biodegradation of azo dyes Acid Red 183, Direct Blue 15 and Direct Red 75 by the isolate Penicillium oxalicum SAR-3. Chemosphere, 107, 240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.12.049
Shabbir, S., Faheem, M., Ali, N., Kerr, P. G., & Wu, Y. (2017a). Evaluating role of immobilized periphyton in bioremediation of azo dye amaranth. Bioresource Technology, 225, 395–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.11.115
Shabbir, S., Faheem, M., Ali, N., Kerr, P. G., & Wu, Y. (2017b). Periphyton biofilms: A novel and natural biological system for the effective removal of sulphonated azo dye methyl orange by synergistic mechanism. Chemosphere, 167, 236–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.002
Sharma, S. C. D., Sun, Q., Li, J., Wang, Y., Suanon, F., Yang, J., & Yu, C. P. (2016). Decolorization of azo dye methyl red by suspended and co-immobilized bacterial cells with mediators anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 112, 88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.04.035
Sudha, M., Bakiyaraj, G., Saranya, A., Sivakumar, N., & Selvakumar, G. (2018). Prospective assessment of the Enterobacter aerogenes PP002 in decolorization and degradation of azo dyes DB 71 and DG 28. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6(1), 95–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.11.050
Sun, X., Luo, C., & Luo, F. (2020). Preparation and properties of self-healable and conductive PVA-agar hydrogel with ultra-high mechanical strength. European Polymer Journal, 124, 109465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.109465
Vairavel, P., & Ramachandra Murty, V. (2020). Decolorization of Congo Red dye in a continuously operated rotating biological contactor reactor. Desalination and Water Treatment, 196, 299–314. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25931
Van der Zee, F. P., & Villaverde, S. (2005). Combined anaerobic–aerobic treatment of azo dyes—A short review of bioreactor studies. Water Research, 39(8), 1425–1440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.03.007
Varjani, S., Rakholiya, P., Ng, H. Y., You, S., & Teixeira, J. A. (2020). Microbial degradation of dyes: An overview. Bioresource Technology, 314, 123728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123728
Vikrant, K., Giri, B. S., Raza, N., Roy, K., Kim, K. H., Rai, B. N., & Singh, R. S. (2018). Recent advancements in bioremediation of dye: Current status and challenges. Bioresource Technology, 253, 355–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.029
Wang, Z. W., Liang, J. S., & Liang, Y. (2013). Decolorization of Reactive Black 5 by a newly isolated bacterium Bacillus sp. YZU1. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 76, 41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.06.023
Wang, J., Fan, Y. C., & Chen, Y. P. (2021). Nitrogen removal performance and characteristics of gel beads immobilized anammox bacteria under different PVA: SA ratios. Water Environment Research, 93(9), 1627–1639. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1547
Xiao, X., Liu, Q. Y., Li, T. T., Zhang, F., Li, W. W., Zhou, X. T., Xu, M. Y., Li, Q., & Yu, H. Q. (2017). A high-throughput dye-reducing photometric assay for evaluating microbial exoelectrogenic ability. Bioresource Technology, 241, 743–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.013
Xiao, X., Li, T. T., Lu, X. R., Feng, X. L., Han, X., Li, W. W., Li, Q., & Yu, H. Q. (2018). A simple method for assaying anaerobic biodegradation of dyes. Bioresource Technology, 251, 204–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.12.052
Yang, Y. Y., Du, L. N., Wang, G., Jia, X. M., & Zhao, Y. H. (2011). The decolorisation capacity and mechanism of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 for Methyl Orange and Acid Yellow 199 under microaerophilic conditions. Water Science and Technology, 63(5), 956–963. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2011.275
Yang, D., Guo, J., Lu, C., Song, Y., Li, H., Chen, Z., & Xie, Z. (2018). A quasi-homogeneous catalysis and electron transfer chain for biodecolorization of azo dye by immobilized phenazine redox mediator. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 126, 69–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.09.018
Yu, C., Zhang, Y., Fang, Y., Tan, Y., Dai, K., Liu, S., & Huang, Q. (2020). Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 impregnated Ca-alginate capsule for efficient Cr(VI) reduction and Cr(III) adsorption. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(14), 16745–16753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06832-1
Zabłocka-Godlewska, E., Przystaś, W., & Grabińska-Sota, E. (2015). Dye decolourisation using two Klebsiella strains. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 226(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2249-6
Zhang, X., Song, H., Chen, Y., Zhuang, M., & Liu, W. (2021). Microbially mediated cleavage of Reactive Black 5 in attached growth bioreactors with immobilized Shewanella indica strain on different carriers. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 157, 105142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2020.105142
Zhou, M., & He, J. (2008). Degradation of cationic red X-GRL by electrochemical oxidation on modified PbO2 electrode. Journal of Hazard Mater, 153(1–2), 357–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.08.056
Zhu, Y., Song, K., Jiang, S., Chen, J., Tang, L., Li, S., Fan, J., Wang, Y., Zhao, J., & Liu, T. (2017). Numerical simulation of mass transfer and three-dimensional fabrication of tissue-engineered cartilages based on chitosan/gelatin hybrid hydrogel scaffold in a rotating bioreactor. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 181(1), 250–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2210-9
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51478208), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32271587), Postgraduate Research Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province General Universities (SJCX21_1709), Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality Technology Innovation Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20220030), and the Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD-2018–87).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Huang, Y., Du, Y. et al. Biodecolorization of Cationic Red X-GRL by Immobilized Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 279 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06295-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06295-8