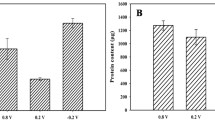
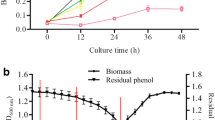
Abstract
Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 degrades various azo dyes under microaerophilic and anaerobic conditions, but this process is inhibited under aerobic conditions. The mechanisms underlying azo dye biodegradation and inhibition remain unknown. Therefore, we investigated metabolic and transcriptional changes in strain MR-1, which was cultured under different conditions, to elucidate these mechanisms. At the transcriptional level, genes involved in certain metabolic processes, particularly the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, amino acid biodegradation, and the electron transfer system, were significantly altered (M ≧ 2, p > 0.8 ) in the presence of methyl orange (MO). Moreover, a high concentration of dissolved oxygen heavily impacted the expression levels of genes involved in fatty acid biodegradation. Metabolome analysis revealed significant alteration (p < 0.05) in the concentrations of nine metabolites when strain MR-1 was cultured under aerobic conditions; the majority of these metabolites were closely associated with amino acid metabolism and DNA replication. Accordingly, we propose a possible pathway for MO biodegradation and discuss the most likely causes of biodegradation inhibition due to dissolved oxygen.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen AE, Dupont CL, Obornik M, Horak A, Nunes-Nesi A, McCrow JP, Zheng H, Johnson DA, Hu HH, Fernie AR, Bowler C (2011) Evolution and metabolic significance of the urea cycle in photosynthetic diatoms. Nature 473(7346):203–207
Ando T, Endo Y, Abe M, Kumagai K (1994) Stimulation of the synthesis of histamine and putrescine in mice by a peptidoglycan of gram-positive bacteria. Microbiol Immunol 38(3):209–215
Brige A, Motte B, Borloo J, Buysschaert G, Devreese B, Van Beeumen JJ (2008) Bacterial decolorization of textile dyes is an extracellular process requiring a multicomponent electron transfer pathway. Microb Biotechnol 1(1):40–52
Bylesjo M, Rantalainen M, Cloarec O, Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Trygg J (2006) OPLS discriminant analysis: combining the strengths of PLS-DA and SIMCA classification. J Chemom 20(8–10):341–351
Cao DM, Xiao X, Wu YM, Ma XB, Wang MN, Wu YY, Du DL (2013) Role of electricity production in the anaerobic decolorization of dye mixture by exoelectrogenic bacterium Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Bioresour Technol 136:176–181
Carbo R, Ginovart M, Carta A, Portell X, del Valle LJ (2015) Effect of aerobic and microaerophilic culture in the growth dynamics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and in training of quiescent and non-quiescent subpopulations. Arch Microbiol 197(8):991–999
Cloarec O, Dumas ME, Trygg J, Craig A, Barton RH, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK, Holmes E (2005) Evaluation of the orthogonal projection on latent structure model limitations caused by chemical shift variability and improved visualization of biomarker changes in H-1 NMR spectroscopic metabonomic studies. Anal Chem 77(2):517–526
Ellis RP, Spicer JI, Byrne JJ, Sommer U, Vian MR, White DA, Widdicombe S (2014) H-1 NMR metabolomics reveals contrasting response by male and female mussels exposed to reduced seawater pH, increased temperature, and a pathogen. Environ Sci Technol 48(12):7044–7052
Eriksson L, Trygg J, Wold S (2008) CV-ANOVA for significance testing of PLS and OPLS (R) models. J Chemom 22(11–12):594–600
Fan WMT (1996) Metabolite profiling by one- and two-dimensional NMR analysis of complex mixtures. Prog Nucl Mag Res Sp 28:161–219
Fan WMT, Lane AN (2008) Structure-based profiling of metabolites and isotopomers by NMR. Prog Nucl Mag Res Sp 52(2–3):69–117
Forgacs E, Cserhati T, Oros G (2004) Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environ Int 30(7):953–971
Fouquerel E, Sobol RW (2014) ARTD1 (PARP1) activation and NAD(+) in DNA repair and cell death. DNA Repair 23:27–32
Hafshejani MK, Ogugbue CJ, Morad N (2014) Application of response surface methodology for optimization of decolorization and mineralization of triazo dye Direct Blue 71 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 3. Biotech 4(6):605–619
He ZX, Yao YL, Lu ZM, Ye YF (2014) Dynamic metabolic and transcriptional profiling of Rhodococcus sp strain YYL during the degradation of tetrahydrofuran. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(9):2656–2664
Hong JH, Lee WC, Hsu YM, Liang HJ, Wan CH, Chien CL, Lin CY (2014) Characterization of the biochemical effects of naphthalene on the mouse respiratory system using NMR-based metabolomics. J Appl Toxicol 34(12):1379–1388
Hong Y, Xu M, Guo J, Xu Z, Chen X, Sun G (2007) Respiration and growth of Shewanella decolorationis S12 with an azo compound as the sole electron acceptor. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(1):64–72. doi:10.1128/AEM.01415-06
Hu TL (1994) Decolourization of reactive azo dyes by transformation with Pseudomonas luteola. Bioresour Technol 49(1):47–51
Işik M, Sponza DT (2003) Effect of oxygen on decolorization of azo dyes by Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas sp. and fate of aromatic amines. Process Biochem 38(8):1183–1192
Jhee KH, Niks D, McPhie P, Dunn MF, Miles EW (2002) Yeast cystathionine β-synthase reacts with L-allothreonine, a non-natural substrate, and L-homocysteine to form a new amino acid, 3-methyl-L-cystathionine. Biochemistry 41(6):1828–1835
Jin YJ, Li N, Liu HQ, Hua X, Zhang QY, Chen MD, Teng F (2014) Highly efficient degradation of dye pollutants by Ce-doped MoO3 catalyst at room temperature. Dalton T 43(34):12860–12870
Khan R, Khan Z, Nikhil B, Jyoti D, Datta M (2014a) Azo dye decolorization under microaerophilic conditions by a bacterial mixture isolated from anthropogenic dye-contaminated soil. Bioremediat J 18(2):147–157
Khan Z, Jain K, Soni A, Madamwar D (2014b) Microaerophilic degradation of sulphonated azo dye—Reactive Red 195 by bacterial consortium AR1 through co-metabolism. Int Biodeter Biodegr 94:167–175
Kim KH, Lopezcasillas F, Bai DH, Luo X, Pape ME (1989) Role of reversible phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in long-chain fatty-acid synthesis. FASEB J 3(11):2250–2256
Kudlich M, Keck A, Klein J, Stolz A (1997) Localization of the enzyme system involved in anaerobic reduction of azo dyes by Sphingomonas sp. strain BN6 and effect of artificial redox mediators on the rate of azo dye reduction. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(9):3691–3694
Kumari L, Tiwary D, Mishra PK (2016) Biodegradation of C.I. Acid Red 1 by indigenous bacteria Stenotrophomonas sp. BHUSSp X2 isolated from dye contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(5):4054–4062
Le Laz S, Kpebe A, Lorquin J, Brugna M, Rousset M (2014) H2-dependent azoreduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1: involvement of secreted flavins and both [Ni-Fe] and [Fe-Fe] hydrogenases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(6):2699–2707
Lechnera S, Praxa M, Lange B, Huber C, Eisenreich W, Herbig A, Nieselt K, Bertram R (2014) Metabolic and transcriptional activities of Staphylococcus aureus challenged with high-doses of daptomycin. Int J Med Microbiol 304(8):931–940
Li H, Zhu W, Zhang L, Lei H, Wu X, Guo L, Chen X, Wang Y, Tang H (2015) The metabolic responses to hepatitis B virus infection shed new light on pathogenesis and targets for treatment. Sci Rep 5:8421
Lindon JC, Holmes E, Nicholson JK (2001) Pattern recognition methods and applications in biomedical magnetic resonance. Prog Nucl Mag Res Sp 39(1):1–40
Liu XD, Luo YT, Mohamed OA, Liu DY, Wei GH (2014) Global transcriptome analysis of Mesorhizobium alhagi CCNWXJ12-2 under salt stress. BMC Microbiol 14:319
Mazin PV, Fisunov GY, Gorbachev AY, Kapitskaya KY, Altukhov IA, Semashko TA, Alexeev DG, Govorun VM (2014) Transcriptome analysis reveals novel regulatory mechanisms in a genome-reduced bacterium. Nucleic Acids Res 42(21):13254–13268
Payen VL, Porporato PE, Baselet B, Sonveaux P (2016) Metabolic changes associated with tumor metastasis, part 1: tumor pH, glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(7):1333–1348
Pradhan S, Bandhiwal N, Shah N, Kant C, Gaur R, Bhatia S (2014) Global transcriptome analysis of developing chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) seeds. Front. Plant Sci 5:698
Rochfort S (2005) Metabolomics reviewed: a new “omics” platform technology for systems biology and implications for natural products research. J Nat Prod 68(12):1813–1820
Romano S, Schulz-Vogt HN, Gonzalez JM, Bondarev V (2015) Phosphate limitation induces drastic physiological changes, virulence-related gene expression, and secondary metabolite production in Pseudovibrio sp strain FO-BEG1. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(10):3518–3528
Rui B, Shen T, Zhou H, Liu JP, Chen JS, Pan XS, Liu HY, Wu JH, Zheng HR, Shi YY (2010) A systematic investigation of Escherichia coli central carbon metabolism in response to superoxide stress. BMC Syst Biol 4:122
Saroj S, Kumar K, Prasad M, Singh RP (2014) Differential expression of peroxidase and ABC transporter as the key regulatory components for degradation of azo dyes by Penicillium oxalicum SAR-3. Funct Integr Genomic 14(4):631–642
Seo JS, Keum YS, Li QX (2013) Metabolomic and proteomic insights into carbaryl catabolism by Burkholderia sp. C3 and degradation of ten N-methylcarbamates. Biodegradation 24(6):795–811
Silva SQ, Silva DC, Lanna MCS, Baeta BEL, Aquino SF (2014) Microbial dynamics during azo dye degradation in a UASB reactor supplied with yeast extract. Braz J Microbiol 45(4):1153–1160
Singh K, Arora S (2011) Removal of synthetic textile dyes from wastewaters: a critical review on present treatment technologies. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec 41(9):807–878
Snell EE, Guirard BM (1943) Some interrelationships of pyridoxine alanine and glycine in their effect on certain lactic acid bacteria. PNAS 29:66–73
Stolz A (2001) Basic and applied aspects in the microbial degradation of azo dyes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56(1–2):69–80
Tarazona S, Garcia-Alcalde F, Dopazo J, Ferrer A, Conesa A (2011) Differential expression in RNA-seq: a matter of depth. Genome Res 21(12):2213–2223
Tremaroli V, Workentine ML, Weljie AM, Vogel HJ, Ceri H, Viti C, Tatti E, Zhang P, Hynes AP, Turner RJ, Zannoni D (2009) Metabolomic investigation of the bacterial response to a metal challenge. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(3):719–728
Tyagi R, Rana P, Gupta M, Bhatnagar D, Srivastava S, Roy R, Khushu S (2014) H-1 NMR spectroscopic analysis detects metabolic disturbances in rat urine on acute exposure to heavy metal tungsten alloy based metals salt. Chem Biol Interact 211:20–28
Wang X, Jin MJ, Balan V, Jones AD, Li X, Li BZ, Dale BE, Yuan YJ (2014) Comparative metabolic profiling revealed limitations in xylose-fermenting yeast during co-fermentation of glucose and xylose in the presence of inhibitors. Biotechnol Bioeng 111(1):152–164
Willetts JRM, Ashbolt NJ (2000) Understanding anaerobic decolourisation of textile dye wastewater: mechanism and kinetics. Water Sci Technol 42(1–2):409–415
Wishart DS (2005) Metabolomics: the principles and potential applications to transplantation. Am J Transplant 5(12):2814–2820
Xiao Z, Lu JR (2014) Strategies for enhancing fermentative production of acetoin: a review. Biotechnol Adv 32(2):492–503
Yanagisawa Y, Piao R, Iguchi S, Nakagome H, Takao T, Kominato K, Hamada M, Matsumoto S, Suematsu H, Jin X, Takahashi M, Yamazaki T, Maeda H (2014) Operation of a 400 MHz NMR magnet using a (RE:rare earth)Ba2Cu3O7-x high-temperature superconducting coil: towards an ultra-compact super-high field NMR spectrometer operated beyond 1 GHz. J Magn Reson 249:38–48
Yang YY, Lu LL, Gao F, Zhao Y (2013) Characterization of an efficient catalytic and organic solvent-tolerant azoreductase toward methyl red from Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Environ Sci Pollut R 20(5):3232–3239
Ye YF, Zhang LM, Hao FH, Zhang JT, Wang YL, Tang HR (2012) Global metabolomic responses of Escherichia coli to heat stress. J Proteome Res 11(4):2559–2566
Zhang LM, Ye YF, An YP, Tian YA, Wang YL, Tang HR (2011) Systems responses of rats to aflatoxin B1 exposure revealed with metabonomic changes in multiple biological matrices. J Proteome Res 10(2):614–623
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 31400113), Funding Project of Sino-Africa Joint Research Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Y623321K01), and the Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Science (Y329671K01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain studies with human participants or animals by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 297 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X., Qi, Y., Xu, C. et al. Transcriptome and metabolome responses of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 to methyl orange under microaerophilic and aerobic conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 3463–3472 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8087-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8087-2