Abstract
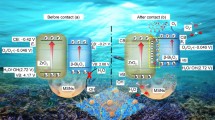
The degradation of the antibiotics discharged into water, and wastewater has become a challenge in environmental engineering. A new Z-scheme nanocomposite was designed, synthesized, and characterized for photooxidative degradation of the binary antibiotics (doxycycline and tetracycline) in an aqueous solution simultaneously. Firstly, the proposed nanocomposite was created from dendric fibrous nano-silica (KCC-1), as support, improved with Ti(VI)-salen, as an organometallic complex, and its structural and morphological properties were investigated. The band-gap energy achieved from the Tauc equation was in good accordance with the calculated one by the Gaussian software. Analysis of the band structure was used to deduce the probable Z-scheme heterojunction mechanism for the proposed photocatalyst. The photodegradation procedure was studied in terms of pH (2.0–6.0), catalyst amount (1.5–7.5 mg mL−1), the concentration of H2O2 (0–0.08% w/v), and irradiation time (5–25 min) under UV light. In optimal conditions, employing the simplex non-linear optimization algorithm, the photodegradation of doxycycline and tetracycline showed efficiencies higher than 95%. Optimal circumstances leading to the maximum simultaneous removal of doxycycline and tetracycline were discovered as pH of 3.6, catalyst dose of 6 mg mL−1, H2O2 amount of 0.06%w/v, and irradiation time of 16 min. Under the optimal circumstances, the kinetics data for investigated antibiotics were fitted employing a pseudo-first-order model. The nanocomposite could successfully remove doxycycline and tetracycline contaminations. Regarding the high degradation efficiency as well as fast kinetics, the observations suggest that the proposed photocatalyst has a significant capability of reducing antibiotic pollutants.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abolhasani, S., Ahmadpour, A., Rohani Bastami, T., & Yaqubzadeh, A. (2019). Facile synthesis of mesoporous carbon aerogel for the removal of ibuprofen from aqueous solution by central composite experimental design (CCD). Journal of Molecular Liquids, 281, 261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2019.02.084
Alamgholiloo, H., Nazari, S., Asgari, E., Sheikhmohammadi, A., Hashemzadeh, B., Ghasemian, N., et al. (2022). Facile fabrication of Z-scheme TiO2/ZnO@MCM-41 heterojunctions nanostructures for photodegradation and bioactivity performance. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 364, 119990. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2022.119990
Ali, A., Pervaiz, M., Saeed, Z., Younas, U., Bashir, R., Ullah, S., et al. (2022). Synthesis and biological evaluation of 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde derivatives of Schiff bases metal complexes: A review. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 145, 109903. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INOCHE.2022.109903
Ayodhya, D., Venkatesham, M., Kumari, A. S., Reddy, G. B., Ramakrishna, D., & Veerabhadram, G. (2015). Synthesis, characterization, fluorescence, photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of CdS nanoparticles using Schiff base. Journal of Fluorescence, 25(5), 1481–1492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-015-1639-5
Ayodhya, D., Venkatesham, M., Santoshi kumari, A., Bhagavanth Reddy, G., & Veerabhadram, G. (2015). One-pot sonochemical synthesis of CdS nanoparticles: photocatalytic and electrical properties. International Journal of Industrial Chemistry, 6(4), 261–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40090-015-0047-7
Bayal, N., Singh, B., Singh, R., & Polshettiwar, V. (2016). Size and fiber density controlled synthesis of fibrous nanosilica spheres (KCC-1). Scientific Reports, 6(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24888
Bouhrara, M., Ranga, C., Fihri, A., Shaikh, R. R., Sarawade, P., Emwas, A. H., et al. (2013). Nitridated fibrous silica (KCC-1) as a sustainable solid base nanocatalyst. ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 1(9), 1192–1199. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc400126h
Cao, Z., Zhang, T., Ren, P., Cao, D., Lin, Y., Wang, L., et al. (2020). Doping of chlorine from a neoprene adhesive enhances degradation efficiency of dyes by structured TiO2-coated photocatalytic fabrics. Catalysts, 10(1), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010069
Chen, P., Zhang, P., Cui, Y., Fu, X., & Wang, Y. (2023). Recent progress in copper-based inorganic nanostructure photocatalysts: properties, synthesis and photocatalysis applications. Materials Today Sustainability, 21, 100276. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MTSUST.2022.100276
Chen, Z., Ou, D., Gu, G., Gao, S., Li, X., Hu, C., et al. (2023). Removal of tetracycline from water by catalytic photodegradation combined with the microalga Scenedesmus obliquus and the responses of algal photosynthesis and transcription. Journal of Environmental Management, 326, 116693. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2022.116693
Cheng, J., Wei, K., Ma, X., Zhou, X., & Xiang, H. (2013). Synthesis and photophysical properties of colorful salen-type schiff bases. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117(32), 16552–16563. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp403750q
Da Silva, C. M., Da Silva, D. L., Modolo, L. V., Alves, R. B., De Resende, M. A., Martins, C. V. B., & De Fátima, Â. (2011). Schiff bases: A short review of their antimicrobial activities. Journal of Advanced Research, 2(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2010.05.004
Das, S., Das, S., Nair, R. G., & Chowdhury, A. (2023). Magnetically separable ZnFe2O4 grafted g-C3N4/rGO ternary nanocomposites for enhanced photo-Fenton catalytic activity under visible light. Materials Today Sustainability, 21, 100263. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MTSUST.2022.100263
Doan, V. D., Huynh, B. A., Le Pham, H. A., Vasseghian, Y., & Le, V. T. (2021). Cu2O/Fe3O4/MIL-101(Fe) nanocomposite as a highly efficient and recyclable visible-light-driven catalyst for degradation of ciprofloxacin. Environmental Research, 201, 111593. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2021.111593
Dong, F., Wang, Z., Li, Y., Ho, W. K., & Lee, S. C. (2014). Immobilization of polymeric g-C3N4 on structured ceramic foam for efficient visible light photocatalytic air purification with real indoor illumination. Environmental Science and Technology, 48(17), 10345–10353. https://doi.org/10.1021/es502290f
Fauzi, A. A., Jalil, A. A., Mohamed, M., Triwahyono, S., Jusoh, N. W. C., Rahman, A. F. A., et al. (2018). Altering fiber density of cockscomb-like fibrous silica–titania catalysts for enhanced photodegradation of ibuprofen. Journal of Environmental Management, 227, 34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.08.073
Fauzi, A. A., Jalil, A. A., Hassan, N. S., Aziz, F. F. A., Azami, M. S., Abdullah, T. A. T., et al. (2022). An intriguing Z-scheme titania loaded on fibrous silica ceria for accelerated visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin. Environmental Research, 211, 113069. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2022.113069
Fu, F., Shen, H., Xue, W., Zhen, Y., Soomro, R. A., Yang, X., et al. (2019). Alkali-assisted synthesis of direct Z-scheme based Bi2O3/Bi2MoO6 photocatalyst for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of phenol and hydrogen evolution reaction. Journal of Catalysis, 375, 399–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCAT.2019.06.033
Han, W., Shou, J., Yang, Y., Chen, L., Zhang, L., Chen, Y., et al. (2022). High-efficient removal of tetracycline in water via porous magnetic Ce/Fe photocomposite under visible light. Journal of Rare Earths. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JRE.2022.07.015
Hemmat, K., Khodabakhshi, M. R., & Zeraatkar Moghaddam, A. (2021). Synthesis of nanoscale zero-valent iron modified graphene oxide nanosheets and its application for removing tetracycline antibiotic: Response surface methodology. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 35(1), e6059. https://doi.org/10.1002/AOC.6059
Irfan, R. M., Jiang, D., Sun, Z., Zhang, L., Cui, S., & Du, P. (2017). Incorporating a molecular co-catalyst with a heterogeneous semiconductor heterojunction photocatalyst: Novel mechanism with two electron-transfer pathways for enhanced solar hydrogen production. Journal of Catalysis, 353, 274–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2017.06.010
Kim, K. S., Yang, C. S., & Mok, Y. S. (2013). Degradation of veterinary antibiotics by dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Chemical Engineering Journal, 219, 19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.12.079
Lan, L., Kong, X., Sun, H., Li, C., & Liu, D. (2019). High removal efficiency of antibiotic resistance genes in swine wastewater via nanofiltration and reverse osmosis processes. Journal of Environmental Management, 231, 439–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.073
Le, X., Dong, Z., Li, X., Zhang, W., Le, M., & Ma, J. (2015). Fibrous nano-silica supported palladium nanoparticles: An efficient catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol under mild conditions. Catalysis Communications, 59, 21–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2014.09.029
Liu, Y., Ji, G., Dastageer, M. A., Zhu, L., Wang, J., Zhang, B., et al. (2014). Highly-active direct Z-scheme Si/TiO2 photocatalyst for boosted CO2 reduction into value-added methanol. RSC Advances, 4(100), 56961–56969. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA10670A
Liu, J., Liu, D., Liu, S., Li, Z., Wei, X., Lin, S., & Guo, M. (2020). Preparation and characterization of sulfated cellulose nanocrystalline and its composite membrane for removal of tetracycline hydrochloride in water. Energy & Environmental Materials, 3(2), 209–215. https://doi.org/10.1002/EEM2.12055
Liu, X., Wang, J., Zhou, G., Tang, L., Xu, Y., Ma, C., et al. (2022). Construction of a direct Z-type heterojunction relying on Mos2 electronic transfer platform towards enhanced photodegradation activity of tetracycline. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 233(12), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11270-022-05995-X/METRICS
Lye, J. W. P., Saman, N., Noor, A. M. M., Mohtar, S. S., Othman, N. S., Sharuddin, S. S. N., et al. (2020). Application of nanoscale zero-valent iron-loaded natural zeolite for tetracycline removal process. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 43(7), 1285–1296. https://doi.org/10.1002/CEAT.201900479
Monteagudo, J. M., Carmona, M., & Durán, A. (2005). Photo-Fenton-assisted ozonation of p-Coumaric acid in aqueous solution. Chemosphere, 60(8), 1103–1110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.12.063
Najafi Chermahini, A., Shahangi, F., Dabbagh, H. A., & Saraji, M. (2016). Production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from fructose using a spherically fibrous KCC-1 silica catalyst. RSC Advances, 6(40), 33804–33810. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra03382b
Nasseri, M. A., Hemmat, K., Allahresani, A., & Hamidi-Hajiabadi, E. (2019). CoFe2O4@SiO2@Co(III) salen complex nanoparticle as a green and efficient magnetic nanocatalyst for the oxidation of benzyl alcohols by molecular O2. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 33(6), e4809–e4820. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4809
Nekouei, S., & Nekouei, F. (2018). Photocatalytic degradation of norfloxacin and its intermediate degradation products using nitrogen-doped activated carbon–CuS nanocomposite assisted by visible irradiation. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 32(9), e4418. https://doi.org/10.1002/AOC.4418
Nivetha, M. R. S., Kumar, J. V., Ajarem, J. S., Allam, A. A., Manikandan, V., Arulmozhi, R., & Abirami, N. (2022). Construction of SnO2/g-C3N4 an effective nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin and pharmaceutical effluent. Environmental Research, 209, 112809. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2022.112809
Omrani, E., Ahmadpour, A., Heravi, M., & Bastami, T. R. (2022). Novel ZnTi LDH/h-BN nanocomposites for removal of two different organic contaminants: Simultaneous visible light photodegradation of Amaranth and Diazepam. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 47, 102581. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JWPE.2022.102581
Pakzad, K., Alinezhad, H., & Nasrollahzadeh, M. (2020). Euphorbia polygonifolia extract assisted biosynthesis of Fe3O4@CuO nanoparticles: Applications in the removal of metronidazole, ciprofloxacin and cephalexin antibiotics from aqueous solutions under UV irradiation. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 34(11), e5910. https://doi.org/10.1002/AOC.5910
Panchal, D., Sharma, A., & Pal, S. (2023). Engineered MoS2 nanostructures for improved photocatalytic applications in water treatment. Materials Today Sustainability, 21, 100264. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MTSUST.2022.100264
Patel, M., Kumar, R., Kishor, K., Mlsna, T., Pittman, C. U., & Mohan, D. (2019). Pharmaceuticals of emerging concern in aquatic systems: Chemistry, occurrence, effects, and removal methods. Chemical Reviews, 119(6), 3510–3673. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.CHEMREV.8B00299/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/CR-2018-00299Y_0035.JPEG
Polshettiwar, V., Cha, D., Zhang, X., & Basset, J. M. (2010). High-surface-area silica nanospheres (KCC-1) with a fibrous morphology. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition, 49(50), 9652–9656. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201003451
Pulicharla, R., Brar, S. K., Drogui, P., Verma, M., & Surampalli, R. Y. (2015). Removal processes of antibiotics in waters and wastewaters: Crucial link to physical-chemical properties and degradation. Journal of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste, 19(4), 04015008–04015023. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)hz.2153-5515.0000285
Rahman, N., & Raheem, A. (2022). Graphene oxide/Mg-Zn-Al layered double hydroxide for efficient removal of doxycycline from water: Taguchi approach for optimization. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 354, 118899. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2022.118899
Ramirez, J. H., Costa, C. A., & Madeira, L. M. (2005). Experimental design to optimize the degradation of the synthetic dye Orange II using Fenton’s reagent. Catalysis Today, 107–108, 68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2005.07.060
Roy, B., Ahrenkiel, S. P., & Fuierer, P. A. (2008). Controlling the size and morphology of TiO2 powder by molten and solid salt synthesis. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 91(8), 2455–2463. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02456.x
Shahbeig, H., Mehrnia, M. R., Mohammadi, A. R., Moghaddam, P. E., & Rouini, M. R. (2017). Pharmaceutical wastewater treatment using membrane bioreactor-ozonation system. Water and Environment Journal, 31(1), 57–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/WEJ.12222
Shao, B., Wang, J., Liu, Z., Zeng, G., Tang, L., Liang, Q., et al. (2020). Ti3C2T: X MXene decorated black phosphorus nanosheets with improved visible-light photocatalytic activity: Experimental and theoretical studies. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 8(10), 5171–5185. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta13610j
Singh, R., Bapat, R., Qin, L., Feng, H., & Polshettiwar, V. (2016). Atomic layer deposited (ALD) TiO2 on fibrous nano-silica (KCC-1) for photocatalysis: Nanoparticle formation and size quantization effect. ACS Catalysis, 6(5), 2770–2784. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.6b00418
Srivastava, A., Dave, H., Prasad, B., Maurya, D. M., Kumari, M., Sillanpää, M., & Prasad, K. S. (2022). Low cost iron modified syzygium cumini l. Wood biochar for adsorptive removal of ciprofloxacin and doxycycline antibiotics from aqueous solution. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 144, 109895. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INOCHE.2022.109895
Swedha, M., Balasurya, S., Syed, A., Das, A., & Sudheer Khan, S. (2022). Continuous photocatalysis via Z-scheme based nanocatalyst system for environmental remediation of pharmaceutically active compound: Modification, reaction site, defect engineering and challenges on the nanocatalyst. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 353, 118745. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2022.118745
Tan, T., Beydoun, D., & Amal, R. (2003). Effects of organic hole scavengers on the photocatalytic reduction of selenium anions. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology a: Chemistry, 159(3), 273–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(03)00171-0
Tan, S. S., Zou, L., & Hu, E. (2006). Photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide into gaseous hydrocarbon using TiO2 pellets. Catalysis Today, 115(1–4), 269–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CATTOD.2006.02.057
Tian, Y., Liu, F., Sun, B., Tong, Z., Fu, P., Zhang, J., et al. (2023). Efficient removal of doxycycline using Schwertmannite as a heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst over a wide pH range. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 11(2), 109441. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2023.109441
Wang, Q., Wilson, C., Blake, A. J., Collinson, S. R., Tasker, P. A., & Schröder, M. (2006). The one-pot halomethylation of 5-substituted salicylaldehydes as convenient precursors for the preparation of heteroditopic ligands for the binding of metal salts. Tetrahedron Letters, 47(50), 8983–8987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2006.09.149
Wang, T., Pan, X., Ben, W., Wang, J., Hou, P., & Qiang, Z. (2017). Adsorptive removal of antibiotics from water using magnetic ion exchange resin. Journal of Environmental Sciences (china), 52, 111–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.03.017
Zarei, F., Marjani, A., & Soltani, R. (2019). Novel and green nanocomposite-based adsorbents from functionalised mesoporous KCC-1 and chitosan-oleic acid for adsorption of Pb(II). European Polymer Journal, 119, 400–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.07.043
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Ferdowsi University of Mashhad and the University of Birjand, Iran, for access to their laboratory and analytical facility.
Funding
The authors appreciate the support of Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Iran (Grant No. 54010) for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FD: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, visualization. AA: conceptualization, review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition. AA: conceptualization, review and editing, advisor.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
The authors hereby consent to the publication of the work.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deymeh, F., Ahmadpour, A. & Allahresani, A. Binary Antibiotics Degradation Employing an Efficient Direct Z-Scheme Ti(VI)-Salen Complex Loaded on Dendritic Fibrous Nano-Silica. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 263 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06272-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06272-1