Abstract
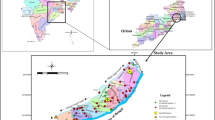
Seawater intrusion is a global phenomenon that affects the groundwater quality in coastal aquifers due to extensive urban developments associated with over-exploitation of groundwater resources for the activities such as drinking, industrial, and agricultural. Seawater intrusion poses a challenging environment for the freshwater management in coastal areas. Hence, present study is carried out in the coastal region of Mangaluru city, Karnataka, India, to investigate the possibility of the seawater intrusion. The study area is divided into six zones from the coast to inland and 35 groundwater samples were collected during each season of post-monsoon (Dec 2018–Jan 2019) and pre-monsoon (Mar 2020). Groundwater samples were analyzed for both in situ and laboratory water quality parameters. The seawater intrusion is assessed using the hydrochemical methods such as ionic ratio, index method, and graphical method. As per the results of Gibbs plot, hydrogeochemistry of the samples is influenced by rock-water interaction. The modified Piper identifies dominance of freshwater (Ca-HCO3 water type) in the inland areas (zones 3 to 6) and identifies slight intrusion (Na-Cl water type) in the near to the coastal line (zones 1 and 2). Further, the results of ionic ratio (Na/Cl; Ca/Mg; Ca/(HCO3 + SO4); and Cl/(HCO3 + CO3)), index method (BEX index), and graphical methods (EC v/s Cl plot, hydrochemical facies evaluation diagram) identify the influence of salinization due to seawater intrusion up to 2 km (zone 2) from coastal line. The findings of study help to establish a supportive base for the decision-makers for the improved coastal groundwater management.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to research was funded by Board of Research in Nuclear Science (BRNS), Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), Govt. of India, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alfarrah, N., & Walraevens, K. (2018). Groundwater overexploitation and seawater intrusion in coastal areas of arid and semi-arid regions. Water, 10(2), 143.
APHA, A. WEF (2012). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22. Washington, American Public Health Association, USA.
Asare, A., Appiah-Adjei, E. K., Ali, B., & Owusu-Nimo, F. (2021). Assessment of seawater intrusion using ionic ratios: The case of coastal communities along the Central Region of Ghana. Environmental Earth Sciences, 80(8), 1–14.
Antony, S., Dev, V. V., Kaliraj, S., Ambili, M. S., & Krishnan, K. A. (2020). Seasonal variability of groundwater quality in coastal aquifers of Kavaratti Island, Lakshadweep Archipelago, India. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 11, 100377.
Avvannavar, S. M., & Shrihari, S. J. E. M. (2008). Evaluation of water quality index for drinking purposes for river Netravathi, Mangalore, South India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 143, 279–290.
Balasubramanian, M., Sridhar, S. G. D., Ayyamperumal, R., Karuppannan, S., Gopalakrishnan, G., Chakraborty, M., & Huang, X. (2022). Isotopic signatures, hydrochemical and multivariate statistical analysis of seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifers of Chennai and Tiruvallur District, Tamil Nadu, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 174, 113232.
Bear, J., Cheng, A. H. D., Sorek, S., Ouazar, D., & Herrera, I. (Eds.). (1999). Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Concepts, methods and practices (Vol. 14). Springer Science & Business Media.
Bhagat, C., Puri, M., Mohapatra, P. K., & Kumar, M. (2021). Imprints of seawater intrusion on groundwater quality and evolution in the coastal districts of south Gujarat, India. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 3, 100101.
CGWB. (2012). Aquifer systems of Karnataka. New Delhi: Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India. http://cgwb.gov.in/aqm/Karnataka.pdf. Accessed 18 Jan 2022.
CGWB. (2014). Report on status of ground water quality in coastal aquifers of India. New Delhi: Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India. http://cgwb.gov.in/WQ/Costal%20Report.pdf. Accessed 28 July 2022.
CGWB. (2020). Block wise report of ground water resources assessment. New Delhi: Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India. http://cgwb.gov.in/GW-Assessment/2021-08-02-GWRA-2020BLOCKWISE%20MASTERSHEET.pdf. Accessed 7 June 2022.
Chachadi, A. G. (2005). Seawater intrusion mapping using modified GALDIT indicator model: A case study in Goa.
Choudhury, K., Saha, D. K., & Chakraborty, P. (2001). Geophysical study for saline water intrusion in a coastal alluvial terrain. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 46(3), 189–200.
Dhiman, S. C. (2012). Aquifer systems of India. New Delhi: CGWB, Ministry of Water Resources, Gov of India.
Domenico, P. A., & Schwartz, F. W. (1990). Physical and chemical hydrogeology. Wiley.
Ferguson, G., & Gleeson, T. (2012). Vulnerability of coastal aquifers to groundwater use and climate change. Nature Climate Change, 2(5), 342–345.
Fetter, C. W. (2018). Applied hydrogeology. Waveland Press.
Gayathri, S., Krishnan, K. A., Krishnakumar, A., Maya, T. V., Dev, V. V., Antony, S., & Arun, V. (2021). Monitoring of heavy metal contamination in Netravati river basin: Overview of pollution indices and risk assessment. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 7(2), 20.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science, 170(3962), 1088–1090.
Gimenez, E., & Morell, I. (1997). Hydrogeochemical analysis of salinization processes in the coastal aquifer of Oropesa (Castellon, Spain). Environmental Geology, 29(1), 118–131.
Giménez-Forcada, E. (2010). Dynamic of sea water interface using hydrochemical facies evolution diagram. Groundwater, 48(2), 212–216.
Giménez-Forcada, E. (2019). Use of the hydrochemical facies diagram (HFE-D) for the evaluation of salinization by seawater intrusion in the coastal Oropesa Plain: Comparative analysis with the coastal Vinaroz Plain, Spain. HydroResearch, 2, 76–84.
Indian Meteorological Department. (n.d.). https://mausam.imd.gov.in, https://mausam.imd.gov.in/imd_latest/contents/smart_cities/MANGALURU.png. Accessed 27 Sept 2022.
India-WRIS, Water Resources Information System. (2022). Groundwater level data. https://indiawris.gov.in/wris/#/groundWater. Accessed 21 Sept 2022.
Kanagaraj, G., Elango, L., Sridhar, S. G. D., & Gowrisankar, G. (2018). Hydrogeochemical processes and influence of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers south of Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(9), 8989–9011.
Karnataka Rural Water Supply and Sanitation Agency. (2004). Groundwater quality scenario in Karnataka state - District-wise individual reports. https://www.indiawaterportal.org/sites/default/files/iwp2/11._Dakshina_kannada.pdf. Accessed 27 July 2022.
Keesari, T., Kulkarni, U. P., Jaryal, A., Mendhekar, G. N., Deshmukh, K. N., Hegde, A. G., & Kamble, S. N. (2014). Groundwater dynamics of a saline impacted coastal aquifer of western Maharashtra, India: Insights from a radiotracer study. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 300(1), 1–6.
Kelly, F. (2005). Seawater intrusion topic paper. Island Country Health Department.
Klassen, J., Allen, D. M., & Kirste, D. (2014). Chemical indicators of saltwater intrusion for the Gulf Islands. Final report, Department of Earth Sciences, Simon Rfaser University.
Klassen, J., & Allen, D. M. (2017). Assessing the risk of saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Journal of Hydrology, 551, 730–745.
Krishnan, A., Das, R., & Vimexen, V. (2020). Seasonal phytoplankton succession in Netravathi-Gurupura estuary, Karnataka, India: Study on a three tier hydrographic platform. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 242, 106830.
Kumar, C. P., Chachadi, A. G., Purandara, B. K., Kumar, S., & Juyal, R. (2007). Modelling of seawater intrusion in coastal area of North Goa. Water Digest, 2(3), 80–83.
Kumar, K. A., Priju, C. P., & Prasad, N. N. (2015). Study on saline water intrusion into the shallow coastal aquifers of Periyar River Basin, Kerala using hydrochemical and electrical resistivity methods. Aquatic Procedia, 4, 32–40.
Lagudu, S., Rao, V. V. S., Prasad, P. R., & Sarma, V. S. (2013). Use of geophysical and hydrochemical tools to investigate seawater intrusion in coastal alluvial aquifer, Andhra Pradesh, India. In Groundwater in the coastal zones of Asia-Pacific (pp. 49–65). Springer, Dordrecht.
Lathashri, U. A., & Mahesha, A. (2015). Simulation of saltwater intrusion in a coastal aquifer in Karnataka, India. Aquatic Procedia, 4, 700–705.
Lyles, J. R. (Ed.). (2000). Is seawater intrusion affecting ground water on Lopez Island, Washington?. US Geological Survey.
Mahadevan, H., Krishnan, K. A., Pillai, R. R., & Sudhakaran, S. (2020). Assessment of urban river water quality and developing strategies for phosphate removal from water and wastewaters: Integrated monitoring and mitigation studies. SN Applied Sciences, 2, 1–14.
Mahesha, A., Vyshali, A., Lathashri, U. A., & Ramesh, H. (2012). Parameter estimation and vulnerability assessment of coastal unconfined aquifer to saltwater intrusion. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 17(8), 933–943.
Majumdar, R. K., Kar, S., Panda, A., & Samanta, S. K. (2016). Hydrological characterization of Budge Budge and Dum Dum areas of south and north 24 Parganas districts, West Bengal using geoelectric and geochemical methods. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 88(3), 330–338.
Maurya, P., Kumari, R., & Mukherjee, S. (2019). Hydrochemistry in integration with stable isotopes (δ18O and δD) to assess seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers of Kachchh district, Gujarat, India. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 196, 42–56.
Mohanty, A. K., & Rao, V. G. (2019). Hydrogeochemical, seawater intrusion and oxygen isotope studies on a coastal region in the Puri District of Odisha, India. CATENA, 172, 558–571.
Moujabber, M. E., Samra, B. B., Darwish, T., & Atallah, T. (2006). Comparison of different indicators for groundwater contamination by seawater intrusion on the Lebanese coast. Water Resources Management, 20(2), 161–180.
Omprakash, M. D., & Gadikar, N. (2018). Salt water intrusion and water security issues of coastal community: Case of Thane District (Maharashtra). In Water resources management (pp. 167–177). Springer, Singapore.
Palaiah, O. (2016). Working plan for the Mangalore division 2012–13 to 2023–24, report by Karnataka Forest Department, Govt. of Karnataka. http://aranya.gov.in/new/newdownloads/WP/Mangalore%20Working%20Plan.pdf. Accessed 27 Sept 2022.
Piper, A. M. (1944). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 25(6), 914–928.
Priya, K., & Jhariya, D. C. (2020, December). An integrated electrical resistivity and geochemical approach to delineate groundwater contamination due to seawater intrusion in the southern part of Mangalore, Karnataka, India. In IOP conference series: Earth and environmental science (Vol. 597, No. 1, p. 012012). IOP Publishing.
Priyanka, B. N., & Mahesha, A. (2015). Parametric studies on saltwater intrusion into coastal aquifers for anticipate sea level rise. Aquatic Procedia, 4, 103–108.
Prusty, P., & Farooq, S. H. (2020). Seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifers of India-A review. HydroResearch, 3, 61–74.
Prusty, P., Farooq, S. H., Swain, D., & Chandrasekharam, D. (2020). Association of geomorphic features with groundwater quality and freshwater availability in coastal regions. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 17(6), 3313–3328.
Rao, K. N., Subraelu, P., Venkateswara Rao, T., HemaMalini, B., Ratheesh, R., Bhattacharya, S., & Rajawat, A. S. (2008). Sea-level rise and coastal vulnerability: An assessment of Andhra Pradesh coast, India through remote sensing and GIS. Journal of Coastal Conservation, 12(4), 195–207.
Ravikumar, P., & Somashekar, R. K. (2017). Principal component analysis and hydrochemical facies characterization to evaluate groundwater quality in Varahi river basin, Karnataka state. India. Applied Water Science, 7(2), 745–755.
Rasmussen, P., Sonnenborg, T. O., Goncear, G., & Hinsby, K. (2013). Assessing impacts of climate change, sea level rise, and drainage canals on saltwater intrusion to coastal aquifer. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 17(1), 421–443.
Sangadi, P., Kuppan, C., & Ravinathan, P. (2022). Effect of hydro-geochemical processes and saltwater intrusion on groundwater quality and irrigational suitability assessed by geo-statistical techniques in coastal region of eastern Andhra Pradesh. India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 175, 113390.
Sarkar, B., Islam, A., & Majumder, A. (2021). Seawater intrusion into groundwater and its impact on irrigation and agriculture: Evidence from the coastal region of West Bengal, India. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 44, 101751.
Satheeskumar, V., Subramani, T., Lakshumanan, C., Roy, P. D., & Karunanidhi, D. (2021). Groundwater chemistry and demarcation of seawater intrusion zones in the Thamirabarani delta of south India based on geochemical signatures. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43(2), 757–770.
Selvakumar, S., Chandrasekar, N., Srinivas, Y., Selvam, S., Kaliraj, S., Magesh, N. S., & Venkatramanan, S. (2022). Hydrogeochemical processes controlling the groundwater salinity in the coastal aquifers of Southern Tamil Nadu, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 174, 113264.
Shaji, E., Vinayachandran, N., & Thambi, D. S. (2009). Hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in coastal phreatic aquifers of Alleppey district, Kerala. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 74(5), 585–590.
Sivakkumar, S. N., Mangottiri, V., Narayanan, N., & Saragur, S. K. (2020). Evolution of strategic planning for water sustainability in coastal cities of India–Contemporary issues and way forward. In IOP conference series: Materials science and engineering (Vol. 955, No. 1, p. 012103). IOP Publishing.
Sylus, K. J., & Ramesh, H. (2018). Geo-statistical analysis of groundwater quality in an unconfined aquifer of Nethravathi and Gurpur river confluence, India. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 4(4), 1555–1575.
Stuyfzand, P. J. (1989). A new hydrochemical classification of water types. IAHS Publication, 182, 89–98.
Stuyfzand, P. J. (2008). Base exchange indices as indicators of salinization or freshening of (coastal) aquifers. In 20th salt water intrusion meeting, Naples, Florida, USA.
Sudhakaran, S., Mahadevan, H., Arun, V., Krishnakumar, A. P., & Krishnan, K. A. (2020). A multivariate statistical approach in assessing the quality of potable and irrigation water environs of the Netravati River basin (India). Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 11, 100462.
Thangamani, R., Radhakrishnan, K., & Sindhu, K. V. (2021). Hydrogeochemical evaluation for developmental activity in part of Belma microwatershed, Dakshina Kannada District, Karnataka. Trends in Civil Engineering and Challenges for Sustainability: Select Proceedings of CTCS, 2019, 853–864.
Todd, D. K., & Mays, L. W. (2004). Groundwater hydrology. Wiley.
United Nations. (2016). The first global integrated marine assessment (world ocean assessment I). New York: United Nations. https://www.un.org/regularprocess/sites/www.un.org.regularprocess/files/woacompilation.pdf. Accessed 12 Aug 2022.
United Nations. (2017). People and oceans factsheet. The UN ocean conference. New York: United Nations. https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Ocean-fact-sheet-package.pdf. Accessed 12 Aug 2022.
Upendra, B., Ciba, M., Arun, V., Sreelesh, R., & Anoop Krishnan, K. (2023). Appraisal of coastal water quality of two hot spots on southwest coast of India: A case study of multi-year biogeochemical observations. Coasts, estuaries and lakes: Implications for sustainable development (pp. 41–62). Springer International Publishing.
Vengosh, A., & Rosenthal, E. (1994). Saline groundwater in Israel: Its bearing on the water crisis in the country. Journal of Hydrology, 156(1–4), 389–430.
VyshaliPalchaudhury, M., & Mahesha, A. (2008). Simulation of saltwater intrusion in the Pavanje-Gurpur basins of Karnataka. ISH Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 14(2), 49–60.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Department of Atomic Energy (DAE)—Board of Research in Nuclear Science (BRNS), Mumbai, for funding this research under the grant number 36(4)/14/21/2017-BRNS/36198.
Funding
This study was funded by the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE)—Board of Research in Nuclear Science (BRNS), Mumbai, under the project grant number 36(4)/14/21/2017-BRNS/36198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Thabrez M involved in sampling, data collection and analysis, original draft preparation, and editing. Parimalarenganayaki S carried out data curation and reviewing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thabrez, M., Parimalarenganayaki, S. Assessment of Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Parts of Mangaluru City, Karnataka, India. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 251 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06246-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06246-3