Abstract
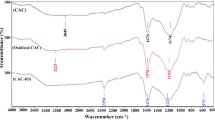
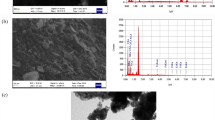
The presence of chromium in the discharge of textile industrial effluents has become a major public and environmental health problem in developing countries including Ethiopia. Consequently, this research work aimed to investigate the adsorptive capacity of manganese ferrite and nickel ferrite (Mn-Ni ferrite) nanocomposite for chromium removal from textile industrial wastewater. Wastewater samples were collected from textile wastewater which is located at the Bole Lemi industrial park. The co-precipitation method was used to synthesize the Mn-Ni ferrite nanocomposite, and characterization was done using the techniques of FTIR, SEM, XRD, and BET surface area. The adsorptive performance of the nanocomposite was evaluated under the influence of contact time, adsorbent dose, pH, and initial chromium concentration which was supported by the response surface methodology. The BET surface area of Mn-Ni ferrite composites was found to be 60 m2/g, whereas the XRD and FTIR analyses showed the crystalline structure and presence of functional group peaks, respectively. This can create a fertile condition to illustrate the expected interaction mechanisms between the adsorbate and adsorbent. The maximum chromium removal from aqueous solution was found to be 87.7% at the contact time of 60 min, pH of 9, the adsorbent dosage of 0.5 g/100 mL, and initial chromium concentration of 200 mg/L, whereas the corresponding predicted chromium removal of 75.6% was recorded through a regression model. Similarly, the maximum chromium adsorption from textile wastewater was 84.5%. Among the adsorption isotherms, the Langmuir isotherm model was the best fit with the experimental data at R2 0.98 which implies the adsorption process was chemical sorption and monolayer. Finally, the nanocomposite adsorbent appears to be promising for the removal of chromium from textile industrial effluent on an industrial scale.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data are fully available without restriction.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahmaruzzaman, M. (2021). Biochar based nanocomposites for photocatalytic degradation of emerging organic pollutants from water and wastewater. Materials Research Bulletin, 140, 111262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111262
Alaqarbeh, M., Khalili, F. I., & Kanoun, O. (2019). Manganese ferrite ( MnFe 2 O 4) as potential nanosorbent for adsorption of uranium ( VI ) and thorium ( IV ). Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-019-06953-4
Bedada, D., Angassa, K., Tiruneh, A., Kloos, H., & Fito, J. (2020). Chromium removal from tannery wastewater through activated carbon produced from Parthenium hysterophorus weed. Energy. Ecology and Environment, 5, 184–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-020-00160-8
Chen, Y., Xu, F., Li, H., Li, Y., Liu, Y., Chen, Y., Li, M., Li, L., Jiang, H., & Chen, L. (2021). Simple hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic MnFe2O4-sludge biochar composites for removal of aqueous Pb2+. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 156, 105173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105173
Cheng, R., Luo, S., Li, X., Zhang, S., Thang Nguyen, T., Guo, M., & Gao, X. (2021). Ultrasound-assisted heterogeneous Fenton-like process for methylene blue removal using magnetic MnFe2O4/biochar nanocomposite. Applied Surface Science, 566, 150654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150654
Czech, B., Shirvanimoghaddam, K., Trojanowska, E., & Naebe, M. (2020). Sorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) onto a sustainable cotton based adsorbent. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 18, 100324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2020.100324
Enaime, G., Baçaoui, A., Yaacoubi, A., Lübken, M., 2020. Biochar for wastewater treatment-conversion technologies and applications Applied Sciences 10https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103492
Fito, J., & Van Hulle, S. W. H. (2021). Wastewater reclamation and reuse potentials in agriculture: Towards environmental sustainability. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23, 2949–2972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00732-y
Fito, J., Tefera, N., Kloos, H., & Van Hulle, S. W. H. (2018). Anaerobic treatment of blended sugar industry and ethanol distillery wastewater through biphasic high rate reactor. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. - Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst. Environmental Engineering, 53, 676–685. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2018.1438826
Fito, J., Tefera, N., Kloos, H., & Van Hulle, S. W. H. (2019). Physicochemical properties of the sugar industry and ethanol distillery wastewater and their impact on the environment. Sugar Tech, 21, 265–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-018-0633-z
Fito, J., Abrham, S., & Angassa, K. (2020). Adsorption of methylene blue from textile industrial wastewater onto activated carbon of Parthenium hysterophorus. International Journal of Environmental Research, 14, 501–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-020-00273-2
Fito, J., Kefeni, K. K., & Nkambule, T. T. I. (2022). The potential of biochar-photocatalytic nanocomposites for removal of organic micropollutants from wastewater. Science of the Total Environment, 829, 154648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154648
Guo, Z., Chen, R., Yang, R., Yang, F., Chen, J., Li, Y., Zhou, R., & Xu, J. (2020). Synthesis of amino-functionalized biochar/spinel ferrite magnetic composites for low-cost and efficient elimination of Ni(II) from wastewater. Science of the Total Environment, 722, 137822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137822
Hegazy, A. K., Abdel-Ghani, N. T., & El-Chaghaby, G. A. (2014). Adsorption of phenol onto activated carbon from Rhazya stricta: Determination of the optimal experimental parameters using factorial design. Applied Water Science, 4, 273–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0143-9
Iqbal, M. B. T. T., & Snobia, A. H. (2017). Wet chemical co-precipitation synthesis of nickel ferrite nanoparticles and their characterization. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 27, 1430–1438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-017-0598-5
Kaynar, U. H., Çam Kaynar, S., Ekdal Karali, E., Ayvacıklı, M., & Can, N. (2021). Adsorption of thorium (IV) ions by metal ion doped ZnO nanomaterial prepared with combustion synthesis: Empirical modelling and process optimization by response surface methodology (RSM). Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 178, 109955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2021.109955
Kefeni, K. K., Mamba, B. B., & Msagati, T. A. M. (2017). Application of spinel ferrite nanoparticles in water and wastewater treatment: A review. Separation and Purification Technology, 188, 399–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.07.015
Kumar, R., Bhattacharya, S., & Sharma, P. (2021). Novel insights into adsorption of heavy metal ions using magnetic graphene composites. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9, 106212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106212
Lee, J.E., Park, Y.K., 2020. Applications of modified biochar-based materials for the removal of environment pollutants: A mini review. Sustain. 12https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156112
Lingamdinne, L. P., Koduru, J. R., & Karri, R. R. (2019). A comprehensive review of applications of magnetic graphene oxide based nanocomposites for sustainable water purification. Journal of Environmental Management, 231, 622–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.063
Mallik, A. K., Moktadir, M. A., Rahman, M. A., Shahruzzaman, M., & Rahman, M. M. (2021). Progress in surface-modified silicas for Cr(VI) adsorption: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 423, 127041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127041
Miao, J., Wang, F., Chen, Y., Zhu, Y., Zhou, Y., & Zhang, S. (2019). The adsorption performance of tetracyclines on magnetic graphene oxide: A novel antibiotics absorbent. Applied Surface Science, 475, 549–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.036
Moges, A., Nkambule, T. T. I., & Fito, J. (2022). The application of GO-Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposite for chromium adsorption from tannery industry wastewater. Journal of Environmental Management, 305, 114369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114369
Neolaka, Y. A. B., Lawa, Y., Naat, J. N., Riwu, A. A. P., Iqbal, M., Darmokoesoemo, H., & Kusuma, H. S. (2020). The adsorption of Cr(VI) from water samples using graphene oxide-magnetic (GO-Fe3O4) synthesized from natural cellulose-based graphite (kusambi wood or Schleichera oleosa): Study of kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. J. Mater. Res. Technol., 9, 6544–6556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.04.040
Niu, Z., Feng, W., Huang, H., Wang, B., Chen, L., Miao, Y., & Su, S. (2020). Green synthesis of a novel Mn–Zn ferrite/biochar composite from waste batteries and pine sawdust for Pb2+ removal. Chemosphere, 252, 126529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126529
Nure, J. F., Shibeshi, N. T., Asfaw, S. L., Audenaer, W., & Van Hulle, S. W. H. (2017). COD and colour removal from molasses spent wash using activated carbon produced from bagasse fly ash of matahara sugar factory, Oromiya region, Ethiopia. Water SA, 43, 470–479. https://doi.org/10.4314/wsa.v43i3.12
Reguyal, F., Sarmah, A.K., Gao, W., 2017. Synthesis of magnetic biochar from pine sawdust via oxidative hydrolysis of FeCl2 for the removal sulfamethoxazole from aqueous solution Journal of Hazardous Materials 321https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.006
Rocha, L.S., Pereira, D., Sousa, É., Otero, M., Esteves, V.I., Calisto, V., 2020. Recent advances on the development and application of magnetic activated carbon and char for the removal of pharmaceutical compounds from waters: A review. Science of the Total Environment 718https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137272
Shan, H., Zeng, C., Zhao, C., & Zhan, H. (2021). Iron oxides decorated graphene oxide/chitosan composite beads for enhanced Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 172, 197–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.060
Tebeje, A., Worku, Z., Nkambule, T. T. I., & Fito, J. (2022). Adsorption of chemical oxygen demand from textile industrial wastewater through locally prepared bentonite adsorbent. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 19, 1893–1906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03230-4
Tefera, N., Mulualem, Y., & Fito, J. (2020). Adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution and groundwater onto activated carbon of avocado seeds. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng., 5, 187–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41101-020-00093-7
UN-Water. (2020). Water and climate change, The United Nations World Water Development Report 2020, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization 7, Place de Fontenoy, 75352 Paris 07 SP. France. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118786352.wbieg0793.pub2
UN-water, 2021. Valuing water,The United Nations World Water Development Report 2021,the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, 7, place de Fontenoy, 75352 Paris 07 SP, France.
WEF, A.A., 1999. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Washington, DC: American Public Health Associ- ation; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation.
Xiao, Y., Lyu, H., Yang, C., Zhao, B., Wang, L., & Tang, J. (2021). Graphitic carbon nitride/biochar composite synthesized by a facile ball-milling method for the adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of enrofloxacin. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 103, 93–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.10.006
Xinchun, C., Mengyang, W., Xiangping, G., Yalian, Z., Yan, G., Nan, W., & Weiguang, W. (2017). Assessing water scarcity in agricultural production system based on the generalized water resources and water footprint framework. Science of the Total Environment, 609, 587–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.191
Xu, Z., Xiang, Y., Zhou, H., Yang, J., He, Y., Zhu, Z., & Zhou, Y. (2021). Manganese ferrite modified biochar from vinasse for enhanced adsorption of levofloxacin: Effects and mechanisms. Environmental Pollution, 272, 115968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115968
Zhao, D., Gao, X., Wu, C., Xie, R., Feng, S., & Chen, C. (2016). Facile preparation of amino functionalized graphene oxide decorated with Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles for the adsorption of Cr(VI). Applied Surface Science, 384, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.05.022
Zheng, C., Wu, Q., Hu, X., Wang, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, S., & Zheng, H. (2021). Adsorption behavior of heavy metal ions on a polymer-immobilized amphoteric biosorbent: Surface interaction assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 403, 123801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123801
Zhou, Y., Liu, G., Liu, J., Xiao, Y., Wang, T., & Xue, Y. (2021). Magnetic biochar prepared by electromagnetic induction pyrolysis of cellulose: Biochar characterization, mechanism of magnetization and adsorption removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution. Bioresource Technology, 337, 125429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125429
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the University of South Africa, the Institute for Nanotechnology and Water Sustainability, and Addis Ababa Science and Technology University for the support and provision of laboratory facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Jemal Fito and Oudum Ebrahim; methodology, Jemal Fito, Oudum Ebrahim; software, Jemal Fito and Oudum Ebrahim; validation, Jemal Fito, Oudum Ebrahim, and Thabo Nkambule; formal analysis, Jemal Fito, and Thabo Nkambule; investigation, Oudum Ebrahim; data curation, Jemal Fito, and Thabo Nkambule; writing—original draft preparation, Jemal Fito, and Thabo Nkambule; writing—review and editing, Jemal Fito, and Thabo Nkambule; and; visualization and supervision, Jemal Fito, and Thabo Nkambule. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fito, J., Ebrahim, O. & Nkambule, T.T.I. The Application Mn-Ni Ferrite Nanocomposite for Adsorption of Chromium from Textile Industrial Wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 37 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-06058-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-06058-x