Abstract
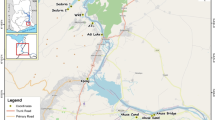
Rivers are influenced by surrounding environmental factors, especially land use and occupation type in their watersheds, which affect the integrity of the communities. This study aimed to evaluate the benthic macroinvertebrate community (BMIC) in a river passing through rural (Rur) and urban (Urb) areas and its correlation with various physical–chemical parameters, nutrients, and heavy metals in the water and sediment. The BMIC samples from five sites (three Rur and two Urb) were collected bimonthly between July 2015 and July 2016. The physical–chemical parameters of water (electrical conductivity, biochemical oxygen demand, dissolved oxygen, pH, total solids turbidity, and temperature), heavy metal (Cd, Pb, Fe, Mn, and Zn), and nutrient (N and P) contents in the water and sediment were measured. We compared the BMIC in different areas using principal coordinate analysis and permutational multivariate analysis of variance. These analyses were performed considering the Euclidean distance to which the Hellinger transformation was applied for determining abundance. We performed partial canonical redundancy analysis using the forward selection method, followed by variance partitioning techniques to evaluate the effect of these factors on BMIC. The BMIC varied between Rur and Urb areas. Taxa tolerant to high N and P contents were predominant in the Urb area, which indicates a high degree of contamination by organic pollutants. In the Rur area, Zn contamination, possibly from agricultural activities, was evident. Thus, although BMIC complete part or all of their life cycle close to the substrate, the physicochemical parameters of water, mainly pH and total dissolved phosphorus, had the highest influence on its composition.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within this published article.
References
Addo-Bediako, A., & Malakane, K. (2020). Preliminary assessment of chemical elements in sediments and larvae of gomphidae (Odonata) from the blyde river of the olifants river system, South Africa. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 17(21), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17218135
ANA – Agência Nacional das Águas (2011) Guia nacional de coleta e preservação de amostras: Água, sedimento, comunidades aquáticas e efluentes líquidos. Cetesb, São Paulo.
Andreoli, C. V., & Carneiro, C. (Eds.). (2005). Gestão integrada de mananciais de abastecimento eutrofizados (p. 500). Curitiba: Sanepar.
AOAC. (2005). Official methods of analysis of the Association Analytical Chemists, Maryland: AOAC.
Aparecida, K., Tonani, D. A., Nikaido, M., & Cardoso, O. D. O. (2010). Avaliação das concentrações de metais pesados em águas superficiais e sedimentos do Córrego Monte Alegre e afluentes , Ribeirão Preto , SP , Brasil, Ri. Ambiente & Água, 5(3), 122–132. https://doi.org/10.4136/ambi-agua.157
APHA—American Public Health Association. (2012). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 22th ed. Washington.
Baptista, D.F., Buss, D.F., & Egler, M. (2003). Macroinvertebrados como bioindicadores de ecossistemas aquáticos contaminados por agrotóxicos. p. 157–176. In Peres F, Moreira JC, orgs. É veneno ou é remédio?: agrotóxicos, saúde e ambiente [online]. Rio de Janeiro: Editora FIOCRUZ, 2003. 384 p. ISBN 85–7541–031–8. Available from SciELO Books.
Blanchet, F. G., Legendre, P., & Borcard, D. (2008). Forward selection of explanatory variables. Ecology, 89(9), 2623–2632. https://doi.org/10.1890/07-0986.1
Callisto, M., Goulart, M., & Moretti, M. (2001). Macroinvertebrados bentônicos como ferramenta para avaliar a saúde de riachos. Revista Brasileira de Recursos Hídricos, 6(1), 71–82. https://doi.org/10.21168/rbrh.v6n1.p71-82
CETESB. (2010). Qualidade das águas superficiais no estado de São Paulo. Relatórios apontam tendências dos índices de qualidade ambiental registradas em 2009. Access in 2021, April 26 from https://cetesb.sp.gov.br/blog/2010/07/23/relatorios-da-cetesb-apontam-tendencias-dos-indices-de-qualidade-ambiental-registradas-em-2009/
CONAMA—Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente. (2005). Resolution 420. Available in: http://conama.mma.gov.br/?option=com_sisconama&task=arquivo.download&id=450. Access April/2022.
CONAMA—Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente. (2012). Resolution 454. Available in: http://conama.mma.gov.br/?option=com_sisconama&task=arquivo.download&id=667. Access April/2022.
Copatti, C. E., Ross, M., Copatti, B. R., & Seibel, L. F. (2013). Bioassessment using benthic macroinvertebrates of the water quality in the Tigreiro river Jacuí Basin. Acta Scientiarum. Biol Sci, 35(4), 521–529. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascibiolsci.v35i4.18934
Cordeiro, G. G., Guedes, N. D. M., Kisaka, T. B., & Nardoto, G. B. (2016). Avaliação rápida da integridade ecológica em riachos urbanos na bacia do rio Corumbá no Centro-Oeste do Brasil. Ambiente e Agua—An Interdisciplinary Journal of Applied Science, 11(3), 702. https://doi.org/10.4136/ambi-agua.1857
Corrêa, M.S.G., Sanches, P.V. Baumgartner, D., Sebastién, N.Y. (2020). A qualidade dos sedimentos do rio Toledo (PR): Biomonitoramento da qualidade da água do rio Toledo utilizando a comunidade de macroinvertebrados bentônicos. In C. A. Lindino (Ed.), Eu, rio Toledo : Qualidade Ambiental e perspectivas futuras (p. 107,126). Cascavel: Edunioeste.
Dala-Corte, R. B., Melo, A. S., Siqueira, T., Bini, L. M., Martins, R. T., Cunico, A. M., et al. (2020). Thresholds of freshwater biodiversity in response to riparian vegetation loss in the Neotropical region. Journal of Applied Ecology, 57(7), 1391–1402. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.13657
Deliberalli, W., Cansian, R. L., Pereira, A. A., Loureiro, R. C., Hepp, L. U., & Restello, R. M. (2018). The effects of heavy metals on the incidence of morphological deformities in Chironomidae (Diptera). Zoologia (Curitiba), 35. https://doi.org/10.3897/zoologia.35.e12947
Esteves, F. A. (1998). Fundamentos de limnologia (2a ed.). Interciência.
Frentiu, T., Ponta, M., Levei, E., Gheorghiu, E., Kasler, I., & Cordos, E. (2008). Validation of the Tessier scheme for speciation of metals in soil using the Bland and Altman test. Chemical Papers, 62(1), 114–122. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-007-0087-3
Gao, Q. F., Cheung, K. L., Cheung, S. G., & Shin, P. K. S. (2005). Effects of nutrient enrichment derived from fish farming activities on macroinvertebrate assemblages in a subtropical region of Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 51(8–12), 994–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.01.009
Guagliardi, I., Apollaro, C., Scarciglia, F., & Rosa, R. (2013). Influence of particle-size on geochemical distribution of stream sediments in the Lese river catchment, southern Italy. Biotechnologie, Agronomie, Société Et Environnement, 17(1), 43–55.
Hamada, N., Nessimian, J.L., & Querino, R.B. (Eds.). (2014). Insetos aquáticos na Amazônia brasileira: taxonomia, biologia e ecologia. Manaus: Editora do INPA. Access: 2021, April 26 from https://www.embrapa.br/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/1000609/insetos-aquaticos-na-amazonia-brasileira-taxonomia-biologia-e-ecologia
IAT - Instituto Água e Terra. (2020). Relatório de Conjuntura dos Recursos Hídricos do Estado do Paraná. Instituto Água e Terra. http://www.iat.pr.gov.br/Pagina/Relatorio-de-Conjuntura-dos-Recursos-Hidricos-do-Estado-do-Parana
Khan, S., Cao, Q., Zheng, Y. M., Huang, Y. Z., & Zhu, Y. G. (2008). Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution, 152(3), 686–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.056
Legendre, P. (2008). Studying beta diversity: Ecological variation partitioning by multiple regression and canonical analysis. Journal of Plant Ecology, 1(1), 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpe/rtm001
Legendre, P., & Gallagher, E. D. (2001). Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia, 129(2), 271–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420100716
Legendre, P., & Legendre, L. (2012). Numerical ecology. Elsevier.
Liu, J., Cao, L., & Dou, S. (2017). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and health risk assessment in three benthic bivalves along the coast of Laizhou Bay, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 117(1–2), 98–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.01.062
Malik, N., Fareed, I., & Irshad, M. (2017). Reducing the leachability of nitrate, phosphorus and heavy metals from soil using waste material. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 34, 715–726. https://doi.org/10.1590/0104-6632.20170343s20150617
Manfrin, J., Schwantes, D., Gonçalves, A.C., Ferronato, M.C., Aleixo, V., & Schiller, A.P. (2018). Contamination by lead in sediments at Toledo River, hydrographic basin of PARANÁ III. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190(4). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6611-9
Marins, A. T., Cerezer, C., Leitemperger, J. W., Severo, E. S., Costa, M. D., Fontoura, D. O., et al. (2021). A mixture of pesticides at environmental concentrations induces oxidative stress and cholinergic effects in the neotropical fish Rhamdia quelen. Ecotoxicology, 30(1), 164–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02300-6
Marmontel, C. V. F., & Rodrigues, V. A. (2015). Parâmetros indicativos para qualidade da água em nascentes com diferentes coberturas de terra e conservação da vegetação ciliar. Floresta e Ambiente, 22(2), 171–181. https://doi.org/10.1590/2179-8087.082014
Masson, S., Desrosiers, M., Pinel-Alloul, B., & Martel, L. (2010). Relating macroinvertebrate community structure to environmental characteristics and sediment contamination at the scale of the St. Lawrence River. Hydrobiologia, 647(1), 35–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9915-5
Merten, G. H., & Minella, J. P. (2002). Qualidade da agua em bacias hidrograficas rurais: Um desafio atual para a sobrevivencia futura. Agroecologia e Desenvolvimento Rural Sustentavel, 3(4), 33–38.
Mudroch, A., & MacKnight, S.D. (1994). Handbook of techniques for aquatic sediments sampling (2°.). CRC Press.
Mugnai, R., Nessimian, J.L., & Baptista, D.F. (2010). Manual de identificação dos macroinvertebrados aquáticos do Rio de Janeiro (1a Ed.). Rio de Janeiro: Technical Books Ed.
Nascimento, L. P., Reis, D. A., Roeser, H. M. P., & Santiago, A. F. (2018). Avaliação geoquímica de metais em sistemas fluviais afetados por atividades antrópicas no Quadrilátero Ferrífero. Engenharia Sanitaria e Ambiental, 23(4), 767–778. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1413-41522018165852
Negrão, G. N., & Cunha, M. C. (2019). Diversidade de macroinvertebrados bentônicos na avaliação do uso do solo e qualidade ambiental da bacia do Guabiroba. Guarapuava, Pr, Brasil. Revista Geografar, 14(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.5380/geografar.v14i1.53497
Nunes, M. V., Rocha, O., & Verani, J. R. (2014). Trophic interactions between the fish Geophagus brasiliensis (Cichlidae) and the benthic macroinvertebrate community. Studies on Neotropical Fauna and Environment, 49(1), 11–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/01650521.2014.904551
Pereira, E.A., Lindino, C.A., Pozzobon, G.M.G., & Fornari, M.M.T. (2020). A qualidade dos sedimentos do rio Toledo (PR): Biomonitoramento da qualidade da água do rio Toledo utilizando a comunidade de macroinvertebrados bentônicos. In C. A. Lindino (Ed.), Eu, rio Toledo : Qualidade ambiental e perspectivas futuras (pp. 21–50). Cascavel: Edunioeste.
Peres-Neto, P. R., Legendre, P., Dray, S., & Borcard, D. (2006). Variation partitioning of species data matrices: Estimation and comparison of fractions. Ecology, 87(10), 2614–2625. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[2614:VPOSDM]2.0.CO;2
Piedras, S. R. N., Bager, A., Moraes, P. R. R., Isoldi, L. A., Ferreira, O. G. L., & Heemann, C. (2006). Macroinvertebrados bentônicos como indicadores de qualidade de água na Barragem Santa Bárbara, Pelotas, RS, Brasil. Ciência Rural, 36(2), 494–500. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-84782006000200020
R Core Team. (2019) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Acess: 2021, July 12. URL https://www.R-project.org/
Ruaro, R., Gubiani, E. A., Cunico, A. M., Moretto, Y., & Piana, P. A. (2016). Comparison of fish and macroinvertebrates as bioindicators of Neotropical streams. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5046-9
Sanches, P.V., Sebastién, N.Y., Baumgartner, D (2020) Metodologia de amostragens e análises no estudo da situação atual das águas do rio Toledo In C. A. Lindino (Ed.), Eu, rio Toledo : Qualidade Ambiental e perspectivas futuras (pp. 89–1005). Cascavel: Edunioeste.
Severo, E.S., Marins, A.T., Cerezer, C., Costa, D., Nunes, M., Prestes, O.D., … & Loro, V.L. (2020). Ecological risk of pesticide contamination in a Brazilian river located near a rural area: A study of biomarkers using zebrafish embryos. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 190, 110071 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110071
Scherer, E. E. (1997). Micronutrientes no esterco de suínos: Diagnose e uso na adubação. Agropecuária Catarinense, 10(1), 48–50.
Sitati, A., Raburu, P. O., Yegon, M. J., & Masese, F. O. (2021). Land-use influence on the functional organization of Afrotropical macroinvertebrate assemblages. Limnologica, 88, 125875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2021.125875
Soares, J.A.C., Sebastién, N.Y., Baumgartner, D., & Sanches, P.V. (2020). A qualidade dos sedimentos do rio Toledo (PR): Análises físico-químicas e ecotoxicológicas. In C. A. Lindino (Ed.), Eu, rio Toledo : Qualidade Ambiental e perspectivas futuras (pp. 89–1005). Cascavel: Edunioeste.
Song, Y., Ji, J., Mao, C., Yang, Z., Yuan, X., Ayoko, G. A., & Frost, R. L. (2010). Heavy metal contamination in suspended solids of Changjiang River environmental implications. Geoderma, 159(3–4), 286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.07.020
Souto, R. D. M. G., Facure, K. G., Pavanin, L. A., & Jacobucci, G. B. (2011). Influence of environmental factors on benthic macroinvertebrate communities of urban streams in Vereda habitats, Central Brazil. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia, 23(3), 293–306. https://doi.org/10.1590/S2179-975X2012005000008
Taborda, J., Sebastién, N.Y., Baumgartner, D., Sanches, P.V, & Johann, A.S.T. (2020). A qualidade dos sedimentos do rio Toledo (PR): Diagnóstico da qualidade da água do rio Toledo (PR) por meio de análises físico-químicas e microbiológicas. In C. A. Lindino (Ed.), Eu, rio Toledo : Qualidade Ambiental e perspectivas futuras (pp. 67–78). Cascavel: Edunioeste.
Tundisi, J. G. (2008). Recursos hídricos no futuro: Problemas e soluções. Estudos Avançados, 22(63), 7–16. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-40142008000200002
Uechi, D. A., Gabas, S. G., & Lastoria, G. (2017). Análise de metais pesados no Sistema Aquífero Bauru em Mato Grosso do Sul. Engenharia Sanitaria e Ambiental, 22(1), 155–167. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-41522016142430
Valente, J. P. S., Padilha, P. M., & Silva, A. M. M. (1997). Contribution of Botucatu - SP with nutrients (phosphorus and nitrogen) to the eutrophication of the Barra Bonita dam. Eclética Química, 22, 31–48. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-46701997000100004
Woodward, G., Perkins, D. M., & Brown, L. E. (2010). Climate change and freshwater ecosystems: Impacts across multiple levels of organization. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 365(1549), 2093–2106. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2010.0055
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JT: Data collection, analysis, and manuscript preparation, JACS, MSGC: Data collection and analysis; JCN: Text review, help with physical-chemical analysis; PAP: Analysis and statistical of data treatment; PVS: Data collection and analysis and manuscript review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors agree with the publication of the article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Taborda, J., Soares, J.A.C., Correa, M.S.G. et al. Influences of water and sediment quality on benthic macroinvertebrates in a river with different land use types. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 388 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05842-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05842-z