Abstract
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a synthetic monomer applied in the polymeric industry that can contaminate food and water, leading to serious health risks associated with human exposure. The consumption of food and water contaminated with this compound directly affects the endocrine system and increases the susceptibility to cancer. The purpose of this review is to present the main studies dedicated to detection and removal of BPA from aqueous media. The literature reports different ways of detecting BPA in different fluids, such as aqueous solutions, water matrix, and bottled drinks (water, juices, and soft drinks). In addition, the main treatment of these matrixes include adsorption or (photo)degradation processes. Detection techniques include high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), capillary electrophoresis (EC), immunochromatographic assay, and electrochemical sensors. The recent studies discourse about BPA removal includes techniques such as (photo)degradation Fenton, adsorption, peroxidation, oxidation and heterogeneous photocatalysis. For photo-degradation, many semiconductor oxides have been used, which can be active under visible or ultraviolet irradiation. Also, plant-based materials have been used as adsorbate to remove BPA. In general, all available techniques present advantages and disadvantages for determining and removing BPA in aqueous media. In this review, we will discuss the main contributions of recent studies related to the detection and treatment of systems contaminated with BPA.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
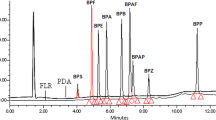
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article files. Source data for figure n° 01 is provided with the paper.
References
Ahsan, M. A., Jabbari, V., Md, T., Turley, R. S., Dominguez, N., Kim, H., Castro, E., Hernandez-Viezcas, J. A., Curry, M. L., Lopez, J., Gardea-Torresdey, J. L., & Noveron, J. C. (2019). Sustainable synthesis and remarkable adsorption capacity of MOF/graphene oxide and MOF/CNT based hybrid nanocomposites for the removal of bisphenol a from water. Science of the Total Environment, 673, 306–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.219
Aksu, Z. (2005). Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutants: A review. Process Biochemistry, 40(3–4), 997–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.04.008
Ali, H., Mukhopadhyay, S., & Jana, N. R. (2019). Selective electrochemical detection of bisphenol A using a molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposite. New Journal of Chemistry, 43(3), 1536–1543. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ05883K
Ana, K. M. S., & Espino, M. P. (2020). Occurrence and distribution of hormones and bisphenol A in Laguna Lake, Philippines. Chemosphere, 256, 127122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127122
Araújo, L. G., & Teixeira, A. C. S. C. (2016). Degradação foto-oxidativa de bisfenol A por meio de peroxidação fotoassistida. In Anais do Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia Química, Anais eletrônicos. Campinas, Galoá. 1, 1–8.
Cao, P., Zhong, H., Qiu, K., Li, D., Wu, G., Sui, H., & Song, Y. (2020). Exposure to bisphenol a and its substitutes, bisphenol F and bisphenol S from canned foods and beverages on Chinese market. Food Control, 120, 107502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107502
Chaves, F. P. (2018). Estudo da eficiência dos processos Cl/UV e H2O2/UV na degradação de bisfenol-A, 17 β estradiol e 17 α etinilestradiol: avaliação da atividade estrogênica e toxicidade. 2018. 137 f. Dissertação (Mestrado em Saneamento Ambiental: controle da poluição urbana e industrial) - Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro.
Chen, M., Wang, N., & Zhu, L. (2020). Single-atom dispersed Co-N-C: A novel adsorption-catalysis bifunctional material for rapid removing bisphenol A. Catalysis Today, 348, 187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2019.08.059
Choong, C. E., Ibrahim, S., & Basirun, W. J. (2019). Mesoporous silica from batik sludge impregnated with aluminum hydroxide for the removal of bisphenol A and ibuprofen. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 541, 12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.01.071
Chu, Y., Miao, B., Zheng, X., & Su, H. (2021). Fabrication of flower-globular Bi2WO6/BiOI@Ag3PO4 photocatalyst for the degradation of bisphenol A and cefepime under sunlight: Photoelectric properties, degradation performance, mechanism and biodegradability enhancement. Separation and Purification Technology, 272, 118866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118866
Deng, Y., & Zhao, R. (2015). Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in Wastewater Treatment. Current Pollution Reports, 1, 167–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-015-0015-z
Dong, Y., Wu, D., Chen, X., & Lin, Y. (2010). Adsorption of bisphenol A from water by surfactant-modified zeolite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 348(2), 585–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.04.074
Du, J., Bao, J., Fu, X., Lu, C., & Kim, S. H. (2016). Mesoporous sulfur-modified iron oxide as an effective Fenton-like catalyst for degradation of bisphenol A. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 184, 132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.11.015
European Commission (EC). (2010). Joint Research Centre. Institute for Health and Consumer Protection. 4,4'-isopropylidenediphenol (Bisphenol-A) Part 1 Environment. JCR Scientific and Technical Reports. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities. VIII pp and 204 pp.
European Food Safety Authority. (2015). Scientific opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs. EFSA Journal, 13(Suppl 1), 3978. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2015.3978
EU-European Union (Commission Recommendation No. 794/2019 of 15 May 2019) on a coordinated control plan to determine the prevalence of species that migrate from basic materials and objects to come into contact with food [notified under number C (2019) 3519] (Text with EEA relevance.). oj: JOL_2019_129_R - Official Journal of the European Union, L 129.
Fowler, P. A. F., Bellingham, M., Sinclair, K. D., Evans, N. P., Pocar, P., Fischer, B., Schaedlich, K., Schmidt, J.-S., Amezaga, M. R., Bhattacharya, S., Rhind, S. M., & O’Shaughnessy, P. J. (2012). Impact of endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs) on female reproductive health. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 355(2), 231–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2011.10.021
Fujishima, A., & Honda, K. (1972). Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature, 0238, 37–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/238037a0
Gao, S., Guo, C., Lv, J., Wang, Q., Zhang, Y., Hou, S., Gao, J., & Xu, J. (2017). A novel 3D hollow magnetic Fe3O4/BiOI heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic performance for bisphenol A degradation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 307, 1055–1065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.032
Garg, A. S., Singhania, T., Singh, A., Sharma, S., Rani, S., Neogy, A., Yadav, S. R., Sangal, V. K., & Garg, N. (2019). Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol-A using N, Co codoped TiO2 catalyst under solar light. Science and Reports, 9, 765. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-38358-w
Geens, T., Aerts, D., Berthot, C., Bourguignon, J. P., Goeyens, L., Lecomte, P., Maghuin-Rogister, G., Pironnet, A. M., Pussemier, L., Scippo, M. L., Van Loco, J., & Covaci, A. (2012). A review of dietary and non-dietary exposure to bisphenol-A. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 50, 3725–3740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.032
Guo, C., Ge, M., Liu, L., Gao, G., Feng, Y., & Wang, Y. (2010). Directed synthesis of mesoporous TiO2 microspheres: Catalysts and their photocatalysis for bisphenol A degradation. Environmental Science and Technology, 44(1), 419–425. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9019854
Hak, C. H., Sim, L. C., Leong, K. H., Lim, P. F., Chin, Y. H., & Saravanan, P. (2018). M/g-C3N4 (M=Ag, Au, and Pd) composite: Synthesis via sunlight photodeposition and application towards the degradation of bisphenol A. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 25401–25412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2632-8
Heo, J., Yoon, Y., Lee, G., Kim, Y., Han, J., & Park, C. M. (2019). Enhanced adsorption of bisphenol A and sulfamethoxazole by a novel magnetic CuZnFe2O4–biochar composite. Bioresource Technology, 281, 179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.091
Herrmann, J. M. (1999). Heterogeneous photocatalysis: Fundamentals and applications to the removal of various types of aqueous pollutants. Catalysis Today, 53(1), 115–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-5861(99)00107-8
Huelsmann, R. D., & Martendal, E. (2020). A simple and effective liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction method with ultraviolet spectrophotometric detection for the determination of bisphenol A in aqueous matrices and plastic leachates. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 31(8), 1575–1584. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20200043
Ioan, I., Wilson, S., Lundanes, E., & Neculai, A. (2007). Comparison of Fenton and sono-Fenton bisphenol A degradation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 142(1–2), 559–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.08.015
Jemmeli, D., Marcoccio, E., Moscone, D., Dridi, C., & Arduimi, F. (2020). Highly sensitive paper-based electrochemical sensor for a reagent free detection of bisphenol A. Talanta, 216, 120924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120924
Jin, Q., Zhang, S., Wen, T., Wang, J., Gu, P., Zhao, G., Wang, X., Chen, Z., Hayat, T., & Wang, X. (2018). Simultaneous adsorption and oxidative degradation of Bisphenol A by zero-valent iron/iron carbide nanoparticles encapsulated in N-doped carbon matrix. Environmental Pollution, 243, 218–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.061
Joseph, L., Heo, J., Park, Y.-G., Flora, J. R. V., & Yoon, Y. (2011). Adsorption of bisphenol A and 17α-ethinyl estradiol on single walled carbon nanotubes from seawater and brackish water. Desalination, 281(17), 68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.07.044
Kim, J. G. (2020). Chemical recycling of poly (bisphenol A carbonate). Polymer Chemistry, 11(30), 4830–4849. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9PY01927H
Kondrakov, A. O., Ignatev, A. N., Frimmel, F. H., Bräse, S., Horn, H., & Revelsky, A. I. (2014). Formation of genotoxic quinones during bisphenol A degradation by TiO2 photocatalysis and UV photolysis: A comparative study. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 160–161, 106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.05.007
Koyun, Ö., Gorduk, S., Gencten, M., & Sahin, Y. (2019). A novel copper (II) Phthalocyanine modified multiwalled carbon nanotube-based electrode for sensitive electrochemical detection of bisphenol A. New Journal of Chemistry, 34, 85–92. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ03721C
Koo, M. S., Cho, K., Yoon, J., & Choi, W. (2017). Photoelectrochemical degradation of organic compounds coupled with molecular hydrogen generation using electrochromic TiO2 nanotube arrays. Environmental Science and Technology, 51, 6590–6598. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00774
Lalwani, D., Ruan, Y., Taniyasu, S., Yamazaki, E., Kumar, N. J. I., Lam, P. K. S., Wang, X., & Yamashita, N. (2020). Nationwide distribution and potential risk of bisphenol analogues in Indian waters. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 200, 110718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110718
Legrini, O., Liveros, E., & Braun, A. M. (1993). Photochemical processes for water treatment. Chemical Reviews, 93, 671–698. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00018a003
Liu, J., Lu, W., Liu, H., Wu, X., Li, J., & Chen, L. (2016). Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for four phenolic environmental estrogens in water samples followed by determination using capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis, 37(19), 2502–2508. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201500519
Locatelli, M., Sciascia, F., Cifelli, R., Malatesta, L., Brunia, P., & Croce, F. (2016). Analytical methods for the endocrine disruptor compounds determination in environmental water samples. Journal of Chromatography A, 1434, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.01.034
Luo, Z., Chen, H., Wu, S., Yang, C., & Cheng, J. (2019). Enhanced removal of bisphenol A from aqueous solution by aluminum-based MOF/sodium alginate-chitosan composite beads. Chemosphere, 237(1), 24493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124493
Machado, C. R. de A., Saggioro, E. M., Silva, Y. G. L., Pereira, L. P. S., & Campos, J. C. (2015). Avaliação da adsorção de Fenol e Bisfenol A em carvões ativados comerciais de diferentes matrizes carbonáceas. Revista Ambiente & Água, 10(4). https://doi.org/10.4136/ambi-agua.1698
Mahmound, A. E. D. (2020). Graphene-based nanomaterials for the removal of organic pollutants: Insights into linear versus nonlinear mathematical models. Journal of Environmental Management, 270, 110911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110911
Meng, A., Chaihu, L.-X., Chen, H.-H., & Gu, Z.-Y. (2017). Ultrahigh adsorption and singlet-oxygen mediated degradation for efficient synergetic removal of bisphenol A by a stable zirconium-porphyrin metal-organic framework. Science and Reports, 7, 6297. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06194-z
Michałowicz, J. (2014). Bisphenol A - sources, toxicity and biotransformation. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 37(2), 738–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2014.02.003
Mu, C., Zhang, Y., Cui, W., Liang, Y., & Zhu, Y. (2017). Removal of bisphenol A over a separation free 3D Ag3PO4 -graphene hydrogel via an adsorption-photocatalysis synergy. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 212, 41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.04.018
Ndagijimana, P., Liu, X., Yu, G., & Wang, Y. (2019a). Synthesis of a novel core-shell-structure activated carbon material and its application in sulfamethoxazole adsorption. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 368, 602–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.01.093
Ndagijimana, P., Liu, X., Li, Z., Yu, G., & Wang, Y. (2019b). Optimized synthesis of a core-shell structure activated carbon and its adsorption performance for bisphenol A. Science of The Total Environment. Science of the Total Environment, 689, 457–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.235
Nguyen, T. B., Huang, C. P., & Doong, R. (2019). Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A over a ZnFe2O4/TiO2 nanocomposite under visible light. Science of the Total Environment, 646, 745–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.352
Oh, W., Lok, L.-W., Veksha, A., Giannis, A., & Lim, T. (2018). Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A with Ag–decorated S–doped g–C3N4 under solar irradiation: Performance and mechanistic studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 333, 739–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.182
Oshita, D., & Jardim, I. (2015). Csf. Comparação de métodos por cromatografia líquida na determinação de multirresíduos de agrotóxicos em morangos. Química Nova, 38(10), 1273–1281.
Peñalver, R., Arroyo-Manzanares, N., Campillo, N., & Viñas, P. (2020). Targeted and untargeted gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of honey samples for determination of migrants from plastic packages. Food Chemistry, 334, 127547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127547
Peng, T. Y., Zhao, D., Dai, K., Shi, W., & Hirao, K. (2005). Synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with mesoporous anatase wall and high photocatalytic activity. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 109(11), 4947–4952. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp044771r
Peng, X., Wang, H., Yang, B., Zhan, X., & Wu, Y. (2016). Field-amplified sample injection-capillary electrophoresis for the determination of bisphenol A, α-naphthol and β-naphthol in drinks and lake water. Chromatographia, 79(5–6), 327–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-016-3028-x
Plasticseurope. (2018). – Association of plastics manufactures. Plastics – the Facts 2018. PlasticsEurope.
Polydorou, O., Schmidt, O.-C., Spraula, M., Vach, K., Schulz, S. D., König, A., Hellwig, E., & Gminski, R. (2020). Detection of bisphenol A in dental wastewater after grinding of dental resin composites. Dental Materials, 36(8), 1009–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2020.04.025
Reddy, P. V. L., Kim, K.-H., Kavitha, B., Kumar, V., Raza, N., & Kalagara, S. (2017). Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A in aqueous media: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 213, 189–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.02.059
Repousi, V., Petala, A., Frontistis, Z., Antonopoulou, M., Konstantinou, I., Kondarides, D. I., & Mantzavinos, D. (2017). Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A over Rh/TiO2 suspensions in different water matrices. Catalysis Today, 284, 59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2016.10.021
Rochester, J. R. (2013). Bisphenol A and human health: A review of the literature. Reproductive Toxicology, 42, 132–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2013.08.008
Rosenfeldt, E. J., & Linden, K. G. (2004). Degradation of endocrine disrupting chemicals bisphenol, ethinyl estradiol, and estradiol during UV photolysis and advanced oxidation processes. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 5476–5483. https://doi.org/10.1021/es035413p
Seachrist, D. D., Bonk, K. W., Ho, S.-M., Prins, G. S., Soto, A. M., & Keri, R. A. (2016). A review of the carcinogenic potential of bisphenol A. Reproductive Toxicology, 59, 167–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2015.09.006
Selvakumara, K., Raja, A., Arunpandian, M., Stalindurai, K., Rajasekaran, P., Sami, P., Nagarajan, E. R., & Swaminathan, M. (2019). Efficient photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin and bisphenol A under visible light using Gd2WO6 loaded ZnO/bentonite nanocomposite. Applied Surface Science, 481(1), 1109–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.178
Shao, H., Wang, Y., Zeng, H., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Sillanpää, M., & Zha, X. (2019). Enhanced photoelectrocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A by BiVO4 photoanode coupling with peroxymonosulfate. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 394, 121105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121105
Sheng, W., Liu, Y., Li, S., Lu, Y., Chang, Q., Zhang, Y., & Wang, S. (2018a). Lateral flow quantum-dot-based immunochromatographic assay and fluorescence quenching immunochromatographic assay with quantum dots as fluorescence donors to visually detect bisphenol a in food and water samples. Food Analytical Methods, 11(3), 675–685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-1039-3
Sheng, W., Duan, W., Shi, Y., Chang, Q., Zhang, Y., Lu, Y., & Wang, S. (2018b). Sensitive detection of bisphenol A in drinking water and river water using an upconversion nanoparticles-based fluorescence immunoassay in combination with magnetic separation. Analytical Methods, 10(44), 5313–5320. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AY01260A
Staples, C. A., Dorn, P. B., Klecka, G. M., O’Block, S. T., & Harris, L. R. (1998). A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A. Chemosphere, 36(10), 2149–2173. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0045-6535(97)10133-3
Sun, F., Kang, L., Xiang, X., Li, H., Luo, X., Luo, R., Lu, C., & Peng, X. (2016). Recent advances and progress in the detection of bisphenol A. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 408(25), 6913–6927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9791-6
Tarafdar, A., Sirohi, R., Balakumaran, P. A., Reshmy, R., Madhavan, A., Sindhu, R., Bino, P., Kumar, Y., Kumar, D., & Sim, S. J. (2022). The hazardous threat of bisphenol A: Toxicity, detection and remediation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 423(A), 127097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127097
Torres, R. A., Abdelmalek, F., Combet, E., Pétrier, C., & Pulgarin, C. (2007). A comparative study of ultrasonic cavitation and Fenton’s reagent for bisphenol A degradation in deionised and natural waters. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 146(3), 546–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.056
Vandenberg, L. N., Chahoud, I., Heindel, J. J., Padmanabhan, V., Paumgartten, F. J. R., & Schoenfelder, G. (2010). Urinary, circulating, and tissue biomonitoring studies indicate widespread exposure to bisphenol A. Environmental Health Perspectives, 118(8), 1055–1070. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901716
Wang, X., & Lim, T.-T. (2010). Solvothermal synthesis of C-N codoped TiO2 and photocatalytic evaluation for bisphenol A degradation using a visible-light irradiated LED photoreactor. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 100(1–2), 355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.08.012
Wang, B., Wang, L., Zhu, J., Chen, S., & Sun, H. (2013). Condensation of phenol and acetone on a modified macroreticular ion exchange resin catalyst. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering., 7(2), 218–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-013-1330-9
Wang, C. Y., Zhang, Y.-J., Wang, W.-K., Pei, D.-N., Huang, G.-X., Chen, J.-J., Zhang, X., & Yu, H.-Q. (2018a). Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A by Co-doped BiOCl nanosheets under visible light irradiation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 221, 320–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.09.036
Wang, Z., Zhu, Y., Chen, H., Wu, H., & Ye, C. (2018b). Fabrication of three functionalized silica adsorbents: Impact of co-immobilization of imidazole, phenyl and long-chain alkyl groups on bisphenol A adsorption from high salt aqueous solutions. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 86, 120–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.02.025
Wang, H., Zhang, N., Cheng, G., Guo, H., Shen, Z., Yang, L., Zhao, Y., Alsaedi, A., Hayat, T., & Wang, X. (2020a). Preparing a photocatalytic Fe doped TiO2 /rGO for enhanced bisphenol A and its analogues degradation in water sample. Applied Surface Science, 505, 144640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144640
Wang, Y., Yin, C., & Zhuang, Q. (2020b). An electrochemical sensor modified with nickel nanoparticle/nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheet nanocomposite for bisphenol A detection. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 827, 154335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154335
Wang, N., Zhang, J., Zhou, P., Zhang, Y., Li, W., Cheng, F., Pan, Z., Liu, Y., & La, B. (2021). Iron molydate catalyzed activation of peroxymonosulfate for bisphenol AF degradation via synergetic non-radical and radical pathways. Science of the Total Environment, 797, 149151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149151
Wirasnita, R., Mori, K., & Toyama, T. (2018). Effect of activated carbon on removal of four phenolic endocrine-disrupting compounds, bisphenol A, bisphenol F, bisphenol S, and 4-tert-butylphenol in constructed wetlands. Chemosphere, 210, 717–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.060
Xiao, Z., Wang, R., Suo, D., Li, T., & Su, X. (2020). Trace analysis of bisphenol A and its analogues in eggs by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chemistry, 327, 126882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126882
Xu, J., Wang, L., & Zhu, Y. (2012). Decontamination of bisphenol A from aqueous solution by graphene adsorption. Langmuir, 28(22), 8418–8425. https://doi.org/10.1021/la301476p
Yang, S.-F., Niu, C. G., Huang, D.-W., Zhang, H., Liang, C., & Zeng, G.-M. (2017). SrTiO3 nanocubes decorated with Ag/AgCl nanoparticles as photocatalysts with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity towards the degradation of dyes, phenol and bisphenol A. Environmental Science: Nano, 4, 585–595. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EN00597G
Yang, X., Blagodatsky, S., Lippe, M., Liu, F., Hammond, J., Xu, J., & Cadisch, G. (2016). Land-use change impact on time-averaged carbon balances: Rubber expansion and reforestation in a biosphere reserve, South-West China. Forest Ecology and Management, 372, 149–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.04.009
Ye, Y., Bruning, H., Li, X., Yntema, D., & Rijnaarts, H. (2018). Significant enhancement of micropollutant photocatalytic degradation using a TiO2 nanotube array photoanode based photocatalytic fuel cell. Chemical Engineering Journal, 354, 553–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.064
Yu, J. C., Zhang, L. Z., & Yu, J. G. (2002). Direct sonochemical preparation and characterization of highly active mesoporous TiO2 with a bicrystalline framework. Chemistry of Materials, 14(11), 4647–4653. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0203924
Zhang, Y., Cui, W., An, W., Liu, L., Liang, Y., & Zhu, Y. (2018a). Combination of photoelectrocatalysis and adsorption for removal of bisphenol A over TiO2 -graphene hydrogel with 3D network structure. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 221, 36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.08.076
Zhang, Y., Wang, F., Ou, P., Zhu, H., Lai, Y., Zhao, Y., Shi, W., Chen, Z., Li, S., & Wang, T. (2018b). High efficiency and rapid degradation of bisphenol A by the synergy between adsorption and oxidization on the MnO2@nano hollow carbon sphere. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 360, 223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.003
Zhong, P., Yu, Q., Zhao, J., Xu, S., Qiu, X., & Chen, J. (2019). Degradation of bisphenol A by Fe-Al layered double hydroxides: A new synergy of homo- and heterogeneous Fenton systems. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science., 552, 122–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.05.040
Zhou, X. Q., Xing, A., Li, J., Zhao, D. C., Zhao, K. F., & Lei, M. (2016). Synergistic enhancement in photoelectrocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A by CeO2 and reduced graphene oxide co-modified TiO2 nanotube arrays in combination with Fenton oxidation. Electrochimica Acta, 209, 379–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.05.094
Zhu, H., Li, Z., & Yang, J. (2018). A novel composite hydrogel for adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A by visible light irradiation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 334, 1679–1690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.148
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank to Federal University of Piauí and State University of Piauí by partnership.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos Costa, M.J., Araújo, J.V.S., Moura, J.K.L. et al. A Brief Review of Detection and Removal of Bisphenol A in Aqueous Media. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 362 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05834-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05834-z