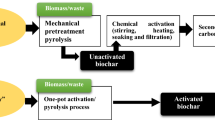
Abstract
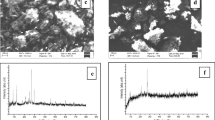
In this study, environmentally friendly activated biochar was produced from the wastes of the algal biodiesel industry (Gongolaria barbata (Stackhouse) Kuntze) using a microwave-assisted method. It was used as an adsorbent to remove hazardous aniline green dye from wastewater. The biochar, activated with phosphoric acid (BCH) was prepared in one step by a microwave-assisted method. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), pHpzc (pH at point of zero charges), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) techniques were used for the characterization of the adsorbent. The activated biochar presented a micropore volume of 0.181 cm3 g−1 and SBET of 1089 m2 g−1. The effects of contact time, pH, and adsorbent amount on the adsorption were investigated. The optimal condition for the maximum adsorption of aniline green (AG) was found as pH (7.0), adsorbent amount (1 g L−1), equilibrium time (40 min), and pollutant concentration (50 mg L−1). The maximum removal percentage was proved to be 99.9% of AG removal. Analyses of experimental data were discussed using nonlinear model equations. The isotherm model can be well described by the Freundlich model. The pseudo-second-order model was suitable for the adsorption kinetics. The reusability ability of BCH for AG dye uptake was found to be 88.3% and 71.6%, for the 50 and 100 mg L−1 pollutant concentrations, respectively, after the third cycle. Three cycles of adsorption and desorption showed that activated biochar is reusable. The economic analysis based on electricity consumption proved that the prepared adsorbent is suitable for large-scale use.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abbas, M. (2020). Experimental investigation of activated carbon prepared from apricot stones material (ASM) adsorbent for removal of malachite green (MG) from aqueous solution. Adsorption Science & Technology, 38(1–2), 24–45. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617420904476
Ahmad, M. A., Ahmad, N., & Bello, O. S. (2014). Adsorptive removal of malachite green dye using durian seed-based activated carbon. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 225(8), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2057-z
Ahmed, M. J., & Theydan, S. K. (2013). Microwave assisted preparation of microporous activated carbon from Siris seed pods for adsorption of metronidazole antibiotic. Chemical Engineering Journal, 214, 310–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.10.101
Aichour, A., Zaghouane-Boudiaf, H., & Khodja, H. D. (2022). Highly removal of anionic dye from aqueous medium using a promising biochar derived from date palm petioles: Characterization, adsorption properties and reuse studies. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 15(1), 103542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103542
Akhouairi, S., Ouachtak, H., Addi, A. A., Jada, A., & Douch, J. (2019). Natural sawdust as adsorbent for the eriochrome black T dye removal from aqueous solution. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 230(8), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4234-6
Al-Musawi, T.J., Arghavan S.M.A., Allahyari E., Arghavan F.S., Othmani A & Nasseh, N. (2022). Adsorption of malachite green dye onto almond peel waste: a study focusing on application of the ANN approach for optimization of the effect of environmental parameters. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-02174-6
Arivoli, S., Sundaravadivelu, M., & Elango, K. P. (2008). Removal of basic and acidic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption on a low cost activated carbon: Kinetic and thermodynamic study. Indian Journal of Chemical Technology, 15, 130–139.
Baird, R., & Bridgewater, L. (2017). edition 23. Washington, DC. American Public Health Association.
Boakye, P., Tran, H. N., Lee, D. S., & Woo, S. H. (2019). Effect of water washing pretreatment on property and adsorption capacity of macroalgae-derived biochar. Journal of Environmental Management, 233, 165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.12.031
Chen, Y. D., Liu, F., Ren, N. Q., & Ho, S. H. (2020). Revolutions in algal biochar for different applications: State-of-the-art techniques and future scenarios. Chinese Chemical Letters, 31(10), 2591–2602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2020.08.019
Daneshvar, E., Kousha, M., Jokar, M., Koutahzadeh, N., & Guibal, E. (2012). Acidic dye biosorption onto marine brown macroalgae: Isotherms, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 204, 225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.090
Daneshvar, E., Vazirzadeh, A., Niazi, A., Kousha, M., Naushad, M., & Bhatnagar, A. (2017). Desorption of methylene blue dye from brown macroalga: Effects of operating parameters, isotherm study and kinetic modeling. Journal of Cleaner Production, 152, 443–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.119
Daneshvar, E., Vazirzadeh, A., & Bhatnagar, A. (2019). Biosorption of methylene blue dye onto three different marine macroalgae: Effects of different parameters on isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions a: Science, 43(6), 2743–2754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-019-00764-8
Dil, E. A., Ghaedi, M., Asfaram, A., Hajati, S., Mehrabi, F., & Goudarzi, A. (2017). Preparation of nanomaterials for the ultrasound-enhanced removal of Pb2+ ions and malachite green dye: Chemometric optimization and modeling. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 34, 677–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.07.001
Esmaeli, A., Jokar, M., Kousha, M., Daneshvar, E., Zilouei, H., & Karimi, K. (2013). Acidic dye wastewater treatment onto a marine macroalga, Nizamuddina zanardini (Phylum: Ochrophyta). Chemical Engineering Journal, 217, 329–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.038
Fan, S., Wang, Y., Wang, Z., Tang, J., Tang, J., & Li, X. (2017). Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by sewage sludge-derived biochar: Adsorption kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics and mechanism. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5(1), 601–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.12.019
Farhan, S., Wang, R. M., & Li, K. Z. (2018). Physical and electromagnetic shielding properties of green carbon foam prepared from biomaterials. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 28(1), 103–113.
Fazal, T., Faisal, A., Mushtaq, A., Hafeez, A., Javed, F., Alaud Din, A., ... & Rehman, F. (2021). Macroalgae and coal-based biochar as a sustainable bioresource reuse for treatment of textile wastewater. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 11(5), 1491-1506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-019-00555-6
Fdez-Sanromán, A., Pazos, M., Rosales, E., & Sanromán, M. A. (2020). Unravelling the environmental application of biochar as low-cost biosorbent: A review. Applied Sciences, 10(21), 7810. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217810
Freundlich, H. M. F. (1906). Over the adsorption in solution. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 57(385471), 1100–1107.
Gokulan, R., Prabhu, G. G., & Jegan, J. (2019). Remediation of complex remazol effluent using biochar derived from green seaweed biomass. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 21(12), 1179–1189. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2019.1612845
Gümüş, D. (2019). Biosorptive application of defatted Laurus nobilis leaves as a waste material for treatment of water contaminated with heavy metal. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 21(6), 556–563. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2018.1537254
Gümüş, D., & Gümüş, F. (2021). Removal of hydroxychloroquine using engineered biochar from algal biodiesel industry waste: Characterization and design of experiment (DoE). Arabian journal for science and engineering, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06235-w
Gurav, R., Bhatia, S. K., Choi, T. R., Choi, Y. K., Kim, H. J., Song, H. S., ... & Yang, Y. H. (2021). Application of macroalgal biomass derived biochar and bioelectrochemical system with Shewanella for the adsorptive removal and biodegradation of toxic azo dye. Chemosphere, 264, 128539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128539
Heidarinejad, Z., Dehghani, M. H., Heidari, M., Javedan, G., Ali, I., & Sillanpää, M. (2020). Methods for preparation and activation of activated carbon: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 18(2), 393–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-019-00955-0
Hidalgo, P., Ciudad, G., & Navia, R. (2016). Evaluation of different solvent mixtures in esterifiable lipids extraction from microalgae Botryococcus braunii for biodiesel production. Bioresource Technology, 201, 360–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.11.031
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34(5), 451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Jabar, J. M., Odusote, Y. A., Ayinde, Y. T., & Yılmaz, M. (2022). African almond (Terminalia catappa L) leaves biochar prepared through pyrolysis using H3PO4 as chemical activator for sequestration of methylene blue dye. Results in Engineering, 14, 100385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100385
Jawad, A. H., Ramlah, A. R., Khudzir, I., & Sabar, S. (2017). High surface area mesoporous activated carbon developed from coconut leaf by chemical activation with H3PO4 for adsorption of methylene blue. Desalination and Water Treatment, 74, 326–335.
Jeong, G. T., & Park, D. H. (2015). Optimization of lipid extraction from marine green macro-algae as biofuel resources. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 32(12), 2463–2467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-015-0083-1
Jerold, M., & Sivasubramanian, V. (2016). Biosorption of malachite green from aqueous solution using brown marine macro algae Sargassum swartzii. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(52), 25288–25300. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1156582
Khataee, A. R., Dehghan, G., Ebadi, E., & Pourhassan, M. (2010). Central composite design optimization of biological dye removal in the presence of macroalgae Chara sp. Clean-Soil Air Water, 38(8), 750–757. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.200900295
Lagergren, S. K. (1898). About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handingarl, 24, 1–39.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40(9), 1361–1403.
Leng, L., Yuan, X., Zeng, G., Shao, J., Chen, X., Wu, Z., ... & Peng, X. (2015). Surface characterization of rice husk bio-char produced by liquefaction and application for cationic dye (Malachite green) adsorption. Fuel, 155, 77-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.04.019
Li, B., Gan, L., Owens, G., & Chen, Z. (2018). New nano-biomaterials for the removal of malachite green from aqueous solution via a response surface methodology. Water Research, 146, 55–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.09.006
Lima, D. R., Klein, L., & Dotto, G. L. (2017). Application of ultrasound modified corn straw as adsorbent for malachite green removal from synthetic and real effluents. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(26), 21484–21495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9802-y
Lin, Y. C., Ho, S. H., Zhou, Y., & Ren, N. Q. (2018). Highly efficient adsorption of dyes by biochar derived from pigments-extracted macroalgae pyrolyzed at different temperature. Bioresource Technology, 259, 104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.02.094
Lu, P. J., Lin, H. C., Yu, W. T., & Chern, J. M. (2011). Chemical regeneration of activated carbon used for dye adsorption. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 42(2), 305–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2010.06.001
Mahadevan, H., Nimina, P. V. M., & Krishnan, K. A. (2022). An environmental green approach for the effective removal of malachite green from estuarine waters using Pistacia vera L shell-based active carbon. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 8(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00612-5
Mohammad, M., Maitra, S., & Dutta, B. K. (2018). Comparison of activated carbon and physic seed hull for the removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 229(2), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3686-4
Mokrzycki, J., Michalak, I., & Rutkowski, P. (2021). Biochars obtained from freshwater biomass—green macroalga and hornwort as Cr (III) ions sorbents. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 11(2), 301–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00649-6
Mullerova, S., Baldikova, E., Prochazkova, J., Pospiskova, K., & Safarik, I. (2019). Magnetically modified macroalgae Cymopolia barbata biomass as an adsorbent for safranin O removal. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 225, 174–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.12.074
Namazi, A. B., Allen, D. G., & Jia, C. Q. (2016). Benefits of microwave heating method in production of activated carbon. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 94(7), 1262–1268. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.22521
Nazemi, F., Karimi, K., Denayer, J. F., & Shafiei, M. (2021). Techno-economic aspects of different process approaches based on brown macroalgae feedstock: A step toward commercialization of seaweed-based biorefineries. Algal Research, 58, 102366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2021.102366
Nethaji, S., Sivasamy, A., & Mandal, A. B. (2013). Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and mechanism for the adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes onto carbonaceous particles prepared from Juglans regia shell biomass. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 10(2), 231–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0112-0
Paramasivan, B. (2022). Microwave assisted carbonization and activation of biochar for energy-environment nexus: A review. Chemosphere, 286, 131631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131631
Paunovic, O., Pap, S., Maletic, S., Taggart, M. A., Boskovic, N., & Sekulic, M. T. (2019). Ionisable emerging pharmaceutical adsorption onto microwave functionalised biochar derived from novel lignocellulosic waste biomass. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 547, 350–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.04.011
Qu, W., Yuan, T., Yin, G., Xu, S., Zhang, Q., & Su, H. (2019). Effect of properties of activated carbon on malachite green adsorption. Fuel, 249, 45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.03.058
Raval, N. P., Shah, P. U., & Shah, N. K. (2017). Malachite green “a cationic dye” and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption. Applied Water Science, 7(7), 3407–3445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0512-2
Ruangrit, K., Chaipoot, S., Phongphisutthinant, R., Duangjan, K., Phinyo, K., Jeerapan, I., ... & Srinuanpan, S. (2021). A successful biorefinery approach of macroalgal biomass as a promising sustainable source to produce bioactive nutraceutical and biodiesel. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01310-6
Sangeetha Piriya, R., Jayabalakrishnan, R. M., Maheswari, M., Boomiraj, K., & Oumabady, S. (2021). Coconut shell derived ZnCl2 activated carbon for malachite green dye removal. Water Science and Technology, 83(5), 1167–1182. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.050
Taqui, S. N., Mohan, C. S., Khatoon, B. A., Soudagar, M. E. M., Khan, T. M., Mujtaba, M. A., ... & Pruncu, C. I. (2021). Sustainable adsorption method for the remediation of malachite green dye using nutraceutical industrial fenugreek seed spent. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01827-w
Temkin, M. I. (1941). Adsorption equilibrium and the kinetics of processes on nonhomogeneous surfaces and in the interaction between adsorbed molecules. Zh Fiz Chim, 15, 296–332.
Thommes, M., Kaneko, K., Neimark, A. V., Olivier, J. P., Rodriguez-Reinoso, F., Rouquerol, J., & Sing, K. S. (2015). Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 87(9–10), 1051–1069. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Villota, E. M., Lei, H., Qian, M., Yang, Z., Villota, S. M. A., Zhang, Y., & Yadavalli, G. (2018). Optimizing microwave-assisted pyrolysis of phosphoric acid-activated biomass: Impact of concentration on heating rate and carbonization time. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 6(1), 1318–1326. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03669
Wang, J., & Wang, S. (2019). Preparation, modification and environmental application of biochar: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 227, 1002–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.282
Zhang, J., Li, Y., Zhang, C., & Jing, Y. (2008). Adsorption of malachite green from aqueous solution onto carbon prepared from Arundo donax root. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 150(3), 774–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.05.036
Zhang, J., Tian, Y., Yin, L., Zhang, J., & Drewes, J. E. (2018a). Insight into the effects of biochar as adsorbent and microwave receptor from one-step microwave pyrolysis of sewage sludge. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(19), 18424–18433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.10.101
Zhang, X., Lin, Q., Luo, S., Ruan, K., & Peng, K. (2018b). Preparation of novel oxidized mesoporous carbon with excellent adsorption performance for removal of malachite green and lead ion. Applied Surface Science, 442, 322–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.148
Zhang, X., Xiang, W., Miao, X., Li, F., Qi, G., Cao, C., ... & Gao, B. (2022). Microwave biochars produced with activated carbon catalyst: Characterization and sorption of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Science of The Total Environment, 827, 153996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gümüş, F. Utilization of Algal Waste Biomass-Derived Biochar Prepared by a Microwave-Assisted Method for Aniline Green Adsorption. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 364 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05833-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05833-0