Abstract
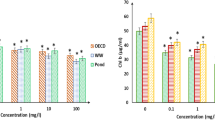
Laponite nanoparticles have been proposed for soil densification to reduce the negative impacts of seismic hazards. However, the effects of laponite on the aquatic ecosystem are lacking. In this study, different concentrations (0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5%) of laponite were used to investigate the growth and total chlorophyll content of microalgae: Chlorella sp. This study examined the potential toxic effects of laponite on the growth characteristics of freshwater green algae Chlorella sp. isolated from northern Ontario. The experiments were carried out in a 500-ml glass flask with 300 ml working volume and placed under white fluorescent lights for 16 h: 8 h day-night cultivation cycle in a constant orbital shaker. The results revealed that the lower concentration of laponite can enhance microalgae growth, while the higher laponite concentration had a growth inhibitory effect. The total chlorophyll content increased by 33% at 0.1% treatment group than that of the control group. Based on the SEM images, aggregation of microalgae was significantly noticeable at the lower concentration of laponite (0.1% treatment) whereas, in the higher laponite concentration (0.4 and 0.5% treatment), algal cells were embedded in laponite gel and also noticed some physical impairment.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Agapoulaki, G., & Papadimitriou, A. (2018). Rheological properties of colloidal silica grout for passive stabilization against liquefaction. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 30, 04018251. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002377
Aruja, V., Pokhrel, S., Sihtmae, M., Mortimer, M., Madler, L., & Kahru, A. (2015). Toxicity of 12 metal-based nanoparticles to algae, bacteria and protozoa. Environmental. Science Nano, 2, 630–644. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EN00057B
Bellinger, E., & Sigee, D. (2015). Freshwater algae: Identification, enumeration and use as bioindicators. 2nd Edition. Akademiai Kiado, John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Bhuvaneshwari, M., Iswarya, V., Vishnu, S., Chandrasekaran, N., & Mukherjee, A. (2018). Dietary transfer of zinc oxide particles from algae (Scenedesmus obliquus) to daphnia (Ceriodaphniadubia). Environmental Research, 164, 395–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.03.015
BYK. (2014). Technical Information B-RI 21: Laponite performance. BYK Additive and Instruments.
Cao, W. (2004). Nanostructures and nanomaterials—Synthesis, properties and applications. Imperial College Press.
Cardinale, B., Bier, R., & Kwan, C. (2012). Effects of TiO2 nanoparticles on the growth and metabolism of three species of freshwater algae. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 14, 913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0913-6
Cattaneo, A. (2018). Nanotoxicological evaluation in marine water ecosystem: A detailed review, in: Environment Toxicity of Nanomaterials. Book Title: Environmental Toxicity of Nanomaterials, 1st Edition, CRC Press-Francis and Taylor Group, pp. 61– 90.
Chen, P., Powell, B., Mortimer, M., & Ke, P. (2012). Adaptive interactions between zinc oxide nanoparticles and Chlorella sp. Env. Sci. Technol., 16, 12178–12185. https://doi.org/10.1021/es303303g
Cheng, J., Ye, Q., Li, K., Liu, J., & Zhou, J. (2017). Removing ethinylestradiol from wastewater by microalgae mutant Chlorella PY-ZU1 with CO2 fixation. Bioresource Technology, 249, 284–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.036
da Silva Rodrigues, D., da Cunha, C., Freitas, M., de Barros, A., Castro, P., Pereira, A., de Queiroz Silva, S., da Fonseca Santiago, A., & de Cássia Franco Afonso, R. (2020). Biodegradation of sulfamethoxazole by microalgae-bacteria consortium in wastewater treatment plant effluents. Science of the Total Environment. 749. https://10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141441
Demir, V., Ates, M., Arslan, Z., Camas, M., Celik, F., Bogatu, C., & Can, S. (2015). Influence of alpha and gamma-iron oxide nanoparticles on marine microalgae species. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination Toxicology, 95, 752–757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1633-2
Dhawan, V., Dhoat, S., Williams, A., Dimarco, A., Pal, S., Forbes, A., Tobías, A., Martinez-Martin, P., & Chaudhuri, K. (2006). The range and nature of sleep dysfunction in untreated Parkinson’s disease (PD). A comparative controlled clinical study using the Parkinson’s disease sleep scale and selective polysomnography. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 25, 158–162.
El Mohtar, C., Bobet, A., Santagata, M., Drnevich, V., & Johnston, C. (2013). Liquefaction mitigation using bentonite suspensions. ASCE Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 139, 1369–1380. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000865
El-Howayek, A. (2011). Characterization, rheology and microstructure of laponite suspensions (MSc thesis). Department of Civil Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, USA. https://docs.lib.purdue.edu/dissertations/AAI1501215/
El-Sheekh, M., Abomohra, A., & Hanelt, D. (2013). Optimization of biomass and fatty acid productivity of Scenedesmus obliquus as a promising microalga for biodiesel production. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 29, 915–922.
Espinasse, B., Geitzer, N., Schierz, A., Therezien, M., Richardson, C., Lowry, G., Ferguson, L., & Wiesne, M. (2018). Comparative persistence of engineered nanoparticles in a complex aquatic ecosystem. Environmental Science and Technology, 52, 4072–4078. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06142
Franklin, N., Rogers, N., Apte, S., Batley, G., Gadd, G., & Casey, P. (2007). Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate ZnO, bulk ZnO, and ZnCl2 to a freshwater microalga (Pseudokirchneriellasubcapitata): The importance of particle solubility. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 8484–8490. https://doi.org/10.1021/es071445r
Gallagher, P. (2000). Passive site remediation for mitigation of liquefaction risk (Ph.D. Dissertation). Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Virginia. http://hdl.handle.net/10919/29610
Hazeem, L., Bououdina, M., Rashdan, S., Brunet, L., Slomianny, C., & Boukherroub, R. (2016). Cumulative effect of zinc oxide and titanium oxide nanoparticles on growth and chlorophyll content of Picochlorum sp. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 2821–2830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5493-4
He, M., Yan, Y., Pei, F., Wu, M., Gebreluel, T., Zou, S., & Wang, C. (2017). Improvement on lipid production by Senedesmus obliquus triggered by low dose exposure to nanoparticles. Science and Reports, 7, 15526.
Huang, Y., & Wang, L. (2016). Laboratory investigation of liquefaction mitigation in silty sand using nanoparticles. Engineering Geology, 204, 23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.01.015
Ji, J., Long, Z., & Lin, D. (2011). Toxicity of oxide nanoparticles to the green algae Chlorella sp. Chemical Engineering Journal, 170, 525–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.11.026
Kadar, E., Rooks, P., Lakey, C., & White, D. (2012). The effect of engineered iron nanoparticles on growth and metabolic status of narine microalgae cultures. The Science of the Total Environment, 439, 8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.09.010
Klaine, S., Alvarez, P., Batley, G., Fernandes, T., Handy, R., Lyon, D., Mahendra, S., McLaughlin, M., & Lead, R. (2008). Nanomaterials in the environment: Behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27, 1825–1851. https://doi.org/10.1897/08-090.110.1002/etc.340
Kroon, M., Vos, G., & Wegdem, G. (1998). Structure and formation of a gel of colloidal disks. Physical Review E, 57, 1962–1970. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.57.1962
Lei, C., Zhang, L., Yang, K., Zhu, L., & Lin, D. (2016). Toxicity of iron-based nanoparticles to green algae: Effects of particle size, crystal phase, oxidaton state and environmental aging. Environmental Pollution, 218, 505–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.07.030
Li, J., Schiavo, S., Rametta, G., Miglietta, M., La Ferrara, V., Wu, C., & Manzo, S. (2017). Comparative toxicity of nano ZnO and bulk ZnO towards marine algae Tetraselmissuecica and Phaeodactylumtricornutum. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 6543–6553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8343-0
Ma, H., Williams, P., & Diamond, S. (2013). Ecotoxicity of manufactured ZnO nanoparticles—A review. Environmental Pollution, 172, 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.08.011
Miao, A., Zhang, X., Luo, Z., Chen, C., Chin, W., Santschi, P., & Quigg, A. (2010). Zinc oxide-engineered nanoparticles: Dissolution and toxicity to marine phytoplankton. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 29, 2814–2822. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.340
Navarro, E., Baun, A., Behra, R., Hatmann, N., Filser, J., Miao, A., Quigg, A., Santschi, P., & Sigg, L. (2008). Environmental behaviour and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants and fungi. Ecotoxicology, 17, 372–386.
Nazos, T., Mavroudakis, L., & Pergantis, S. (2020). Biodegradation of phenol by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Photosynthesis Research, 144, 383–395.
Nowack, B., & Bucheli, T. (2007). Occurrence, behaviour and effects of nanoparticles in the environment. Environmental Pollution, 150, 5–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.006
Ochao-Cornejo, F., Bobet, A., Johnston, C., Santagata, M., & Sinfield, J. (2016). Cyclic behavior and pore pressure generation in sands with laponite, a super-plastic nanoparticle. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 88, 265–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2016.06.008
Ochoa-Cornejo, F. (2015). Cyclic behaviour of sands with superplastic fines (a dissertation submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy). Purdue University.
Ochoa-Cornejo, F. (2017). Dynamic behavior of sand with nanoparticles, in: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference. Presented at the Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Eng., Seoul. https://repositorio.uchile.cl/bitstream/handle/2250/169107/Dynamic-Behavior-of-Sand-with-NanoParticles.pdf?sequence=1
Padrova, K., Lukavsky, J., Nedbalova, L., Cejkova, A., Cajthaml, T., Sigler, K., Vitova, M., & Rezanka, T. (2015). Trace concentrations of iron nanoparticles cause overproduction of biomass and lipids during cultivation of cyanobacteria and microalgae. Journal of Applied Phycology, 27, 1443–1451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0477-1
Persoff, P., Apps, J., Moridis, G., & Whang, J. (1999). Effect of dilution and contaminants on sand grouted with colloidal silica. Journal of Geotechnical Geoenvironmental Engineering, 125, 461–469. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1999)125:6(461)
R Development Core Team. (2019). A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Rana, M., Bhushan, S., Sudhakar, D., & Prajapati, S. (2020). Effect of iron oxide nanoparticles on growth and biofuel potential of Chlorella spp. Algal Research, 49, 101942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2020.101942
Rawat, I., Kumar, R., Mutanda, T., & Bux, F. (2013). Biodiesel from microalgae: A critical evaluation from laboratory to large scale production. Applied Energy, 103, 444–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.10.004
Rugg, D., Yoon, J., Hwang, H., & El Mohtar CS, C. (2011). Undrained shearing properties of sand permeated with a bentonite suspension for static liquefaction mitigation. Geofrontiers Congress 2011, March 13-16, 2011, Dallas, Texas, United States. Advance Geotechnical Engineering Geotechnical Special Publication 211, 677686 (CD-ROM), American Society of Civil Engineers. https://doi.org/10.1061/41165(397)70
SaxenaHarish, P. (2019). Toxicity assessment of ZnO nanoparticles to freshwater microalgae Coelastrellaterrestris. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 26991–27001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05844-1
Seo, J., Lee, K., Praveenkumar, R., Kim, B., Lee, S., Oh, Y., & Park, S. (2015). Tri-functionality of Fe3O4-embedded carbon microparticles in microalgae harvesting. Chemical Engineering Journal, 280, 206–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.122
Sibi, G., Kumar, A., Gopal, T., Harinath, K., Banupriya, S., & Chiatra, S. (2017). Metal nanoparticle triggered growth and lipid production in Chlorella vulgaris. International Journal of Scientific Research in Environmental Science and Toxicology, 2(1), 1–8.
Song, C., Liu, Z., Wang, C., Li, S., & Kitamura, Y. (2020). Different interaction performance between microplastics and microalgae: The bio-elimination potential of Chlorella sp. L38 and Phaeodactylum tricornutum MASCC-0025. Science of the Total Environment, 723, 138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138146
Song, C., Wei, Y., Sun, J., Song, Y., Li, S., & Kitamura, Y. (2020). Biodegradation and metabolic fate of thiamphenicol via Chlorella sp UTEX1602 and L38. Bioresource Technology, 296, 122320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122320
Stanier, R., Kunisawa, R., Mandel, M., & Cohen-Bazire, G. (1971). Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriological Reviews, 35, 171. https://doi.org/10.1128/br.35.2.171-205.1971
Vannini, C., Domingo, G., Marsoni, M., Mattia, F., Labra, M., Castiglioni, S., & Bracale, M. (2011). Effects of a complex mixture of therapeutic drugs on unicellular algae Pseudokirchneriellasubcapitata. Aquatic Toxicology, 101, 459–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.10.011
Wang, S., Wang, Y., Liang, Y., Cao, W., Sun, C., Ju, P., & Zheng, L. (2020). The interaction between microplastic polyvinyl chloride and marine diatoms: Physiological, morphological, and growth effects. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 203, 111000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111000
Xu, X., Wang, S., Gao, F., Li, J., Zheng, L., Sun, C., He, C., Wang, Z., & Qu, L. (2019). Marine microplastic-associated bacterial community succession in response to geography, exposure time, and plastic type in China’s coastal seawaters. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 145, 278–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.05.036
Yonekura, R., & Kaga, M. (1992). Current chemical grout engineering in Japan, Proc., Grouting. Soil Improvement and Geosynthetics, ASCE, New York. https://cedb.asce.org/CEDBsearch/chapter.jsp?isbn=978-0-87262-865-6
Yoo, C., Jun, S., Lee, J., Ahn, C., & Oh, H. (2010). Selection of microalgae for lipid production under high levels carbon dioxide. Bioresource Technology, 101, S71–S74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.03.030
Zhao, T., Tan, L., Huang, W., & Wang, J. (2019). The interactions between micro polyvinyl chloride (mPVC) and marine dinoflagellate Kareniamikimotoi: The inhibition of growth, chlorophyll and photosynthetic efficiency. Environmental Pollution, 247, 883–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.114
Funding
This research was supported, in part, by the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) (Grant No. RGPIN-2017–05366 to W.Qin).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SNS and JRK were responsible for experimental design, performed laboratory works, data acquisition, processing of information, and writing the manuscript; SS participated in reviewing and editing; CC participated in reviewing and editing; XC participated in reviewing and editing; EM participated in reviewing and editing; JD participated in reviewing and editing; WQ participated in reviewing, editing, and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The authors declare that this manuscript is the authors’ own original work, that it has never been previously published, and is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. The paper reflects the authors’ own research and analysis in a truthful and complete manner. All sources used are properly disclosed (correct citation). There are no other persons, who meet the authorship criteria but are not included. The order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by the authors. The corresponding author is the sole contact for the editorial process, who is responsible for communicating with the other authors about progress, submissions of revisions, and final approval of proofs.
Statement of Informed Consent, Human/Animal Rights
No conflicts, informed consent, human or animal rights are applicable to this study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddique, S.N., Khatiwada, J.R., Shrestha, S. et al. Effect of Laponite Nanoparticles on Growth Characteristics and Chlorophyll Content of Chlorella sp.. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 308 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05792-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05792-6