Abstract
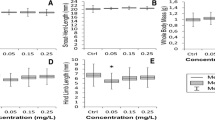
Tamoxifen is used to treat breast cancer and infertility. It acts as an estrogen antagonist or agonist, depending on the target species. Tamoxifen has been detected in aquatic environments, which causes sexual distortion in aquatic animals by affecting their hormone balance in the body. The influence of tamoxifen on golden apple snail Pomacea canaliculata Lamarck (Caenogastropoda: Ampullariidae), a freshwater mollusk, is still unclear. The purpose of this study was to determine whether tamoxifen had an estrogenic effect on P. canaliculata, and to evaluate the extent of tamoxifen’s influence on their reproductive and hormonal responses. The results showed that tamoxifen significantly decreased the contents of various hormones in the snails. The contents of estradiol, progesterone, testosterone, and 5-hydroxytryptamine were decreased to trace levels. The number of laying eggs by female snails was greatly reduced by tamoxifen, and the lowest fecundity was only 42.28. The hatching rate was reduced to 15.8% by tamoxifen treatment. Tamoxifen was ecotoxicity to the golden apple snail by disrupting the dynamic balance of key hormones, affecting social and mating behaviors of the snails. Therefore, it is important to prevent tamoxifen from being discharged into the aquatic ecosystem, to prevent residual tamoxifen from causing aquatic ecotoxicity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abderrahman, B., & Jordan, V. C. (2017). Long-term adjuvant tamoxifen therapy and decreases in contralateral breast cancer. JAMA Oncology, 3, 163–164.
Amal, K. A., & Aqeel, H. Q. (2020). Effect of tamoxifen drug on testes of Albino male rats. Medico-legal Update, 20: No. 4.
Baglan, H., Lazzari, C. R., & Guerrieri, F. J. (2018). Glyphosate impairs learning in mosquito larvae (Aedes aegypti) at field-realistic doses. Journal of Experimental Biology, 221, jeb187518.
Balasinor, N., Gill-Sharma, M. K., Parte, P., et al. (2002). Effect of paternal administration of an antiestrogen, tamoxifen on embryo development in rats. Molecular & Cellular Endocrinology, 190(1–2), 159–166.
Bois, C., Delalande, C., Nurmio, M., et al. (2010). Age- and cell-related gene expression of aromatase and estrogen receptors in the rat testis. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 45, 147–159.
Borgatta, M., Waridel, P., Decosterd, L. A., et al. (2016). Multigenerational effects of the anticancer drug tamoxifen and its metabolite 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen on Daphnia pulex. Science of the Total Environment, 545–546(Mar.1), 21–29.
Buckley, M. M., & Goa, K. L. (1989). Tamoxifen. A reappraisal of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use. Drugs, 37(4), 451–90. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198937040-00004
Canesi, L., Lorusso, L. C., Ciacci, C., et al. (2007). Immunomodulation of Mytilus hemocytes by individual estrogenic chemicals and environmentally relevant mixtures of estrogens: In vitro and in vivo studies. Aquatic Toxicology, 81(1), 36–44.
Carreau, S., & Hess, R. A. (2010). Oestrogens and spermatogenesis. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 365(1546), 1517–1535. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0235
Chaichana, R., Sumpan., et al. (2015). Environmental tolerance of invasive golden apple snails (Pomacea canaliculata (Lamarck, 1822)) and Thai native apple snails (Pila scutata, (Mousson, 1848)). Tropical Ecology, 56(3), 347–355.
Clotfelter, E. D., Bell, A. M., & Levering, K. R. (2004). The role of animal behaviour in the study of endocrine-disrupting chemicals-ScienceDirect. Animal Behaviour, 68(4), 665–676.
Cuvillier-Hot, V., & Lenoir, A. (2020). Invertebrates facing environmental contamination by endocrine disruptors: Novel evidences and recent insights. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2020.110712
Dominika, W., & Anna, H. (2020). Tamoxifen-induced alterations in the expression of selected matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, -9, -10, and -13) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMP-2 and -3) in the chicken ovary. Theriogenology, 148, 208–215.
Dumasia, K., Kumar, A., Kadam, L., et al. (2015). Effect of estrogen receptor-subtype-specific ligands on fertility in adult male rats. Journal of Endocrinology, 225(3), 169.
Flament, S. (2016). Sex reversal in amphibians. Sexual Development, 10(5–6), 267–278. https://doi.org/10.1159/000448797
Frédéric, O., Laurent, S., Gladys, M., et al. (2015). Bioconcentration of 15N-tamoxifen at environmental concentration in liver, gonad and muscle of Danio rerio. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 120, 457–462.
Gagné, F., André, C., Cejka, P., et al. (2008). Immunotoxic effects on freshwater mussels of a primary-treated wastewater before and after ozonation: a pilot plant study. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 69(3), 366–373.
Giraudo, M., Dubé, M., Lepine, M., et al. (2017). Multigenerational effects evaluation of the flame retardant tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate (TBOEP) using Daphnia magnae. Aquatic Toxicology, 190, 142–149.
Gu, H. L., Chen, C. F., Lin, Z. H., et al. (2013). Application of vitellogenin in aquatic organisms in the detection of endocrine disruptors. Journal of Ningbo University (Science and Technology Edition), 02, 12–16.
Gust, M., Gagne, F., Berlioz-Barbier, A., et al. (2014). Caged mudsnail Potamopyrgus antipodarum (Gray) as an integrated field biomonitoring tool: exposure assessment and reprotoxic effects of water column contamination. Water Research, 54(may 1), 222–236.
Han, J., & Fang, Z. (2010). Estrogenic effects, reproductive impairment and developmental toxicity in ovoviparous swordtail fish (Xiphophorus helleri) exposed to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Aquatic Toxicology, 99(2), 281–290.
Hernandez-Hernandez, O. T., Martinez-Mota, L., Herrera-Perez, J. J., et al. (2018). Role of estradiol in the expression of genes involved in serotonin neurotransmission: implications for female depression. Current Neuropharmacology, 16(5)
Horiguchi, T., & Ohta, Y. (2020). Chapter 8, A critical review of sex steroid hormones and the induction mechanisms of imposex in gastropod mollusks. In: Advances in Invertebrate (Neuro)Endocrinology: A Collection of Reviews in the Post-Genomic Era (2-volume set). (eds. Saleuddin, S., Lange, A.B., Orchard, I.) Apple Academic Press Inc., Ontario, Canada, Volume 1: Phyla Other Than Arthropoda, pp. 255–283.
Huh, W. J., Khurana, S. S., Geahlen, J. H., et al. (2012). Tamoxifen induces rapid, reversible atrophy, and metaplasia in mouse stomach. Gastroenterology, 142(1), 21-24.e7. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.09.050
Isidori, M., Bellotta, M., Cangiano, M., et al. (2009). Estrogenic activity of pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment. Environment International, 35, 826–829.
Ito, K. (2002). Environmental factors influencing overwintering success of the golden apple snail, Pomacea canaliculata (Gastropoda: Ampullariidae), in the northernmost population of Japan. Applied Entomology & Zoology, 37(4), 655–661.
Jo, A., Ji, K., & Choi, K. (2014). Endocrine disruption effects of long-term exposure to perfluorodecanoic acid (PFDA) and perfluorotridecanoic acid (PFTrDA) in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and related mechanisms. Chemosphere, 108(aug.), 360–366.
Liu, J., He, Y. J., Tan, J. C., et al. (2012). Characteristics of Pomacea canaliculata reproduction under natural conditions. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23(2), 559–565.
Kaur, S., Jobling, S., Jones, C. S., et al. (2015). The nuclear receptors of Biomphalaria glabrata and Lottia gigantea: implications for developing new model organisms. PLOS One, 10(4), e0121259. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121259
Keeley, T. M., Horita, N., & Samuelson, L. C. (2019). Tamoxifen-induced gastric injury: Effects of dose and method of administration. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 8(3), 365–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.06.007.
Kumar, A., Dumasia, K., Deshpande, S., et al. (2018). Delineating the regulation of estrogen and androgen receptor expression by sex steroids during rat spermatogenesis. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 127–136.
Lam, C., Neumann, R., Shin, P. K. S., et al. (2010). Polybrominated diphenylethers (PBDEs) alter larval settlement of marine benthic polychaetes. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(18), 7130.
Lee, Jin Wuk, Lee, Jae-Woo., Shin, Yu-Jin., et al. (2017). Multi-generational xenoestrogenic effects of Perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) mixture on Oryzias latipes using a flow-through exposure system. Chemosphere, 169(FEB.), 212–223.
Lee, S. B., Lee, S. M., Park, C. B., et al. (2019). The environmental adaptability of Pomacea canaliculata used for weed control in wet rice paddies and crop damage caused by overwintered golden apple snails. Korean Journal of Environmental Agriculture, 38(1), 23–33.
Li, C. L. (1995). Experiment on growth rate and fecundity of Pomacea canaliculata. Plant Protection, 21(4), 12–14.
Li, J. F., Li, W. H., Yang, J., et al. (2006). 17-α effects of ethinylestradiol on vitellogenin and gonadal development of zebrafish. Journal of Toxicology, 20(1), 9–13. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-3127.2006.01.004
Li, S. W., How, C. M., & Liao, H. C. (2018). Prolonged exposure of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate induces multigenerational toxic effects in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science of The Total Environment, 634(SEP.1), 260–266.
Li, X., Du, Z., Chen, M., Chen, J., & Gao, T. (2019). The effects of tamoxifen on mouse behavior. Genes Brain and Behavior, 19(4).
Li, Z. J., Yang, L. J., Wang, J., et al. (2010). Research progress of vitellogenin. Life Sciences, 3, 7.
Liu, Q., Guo, X., Jiang, G., et al. (2020). NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase Ccr1 is a target of tamoxifen and participates in its antifungal activity via regulating cell wall integrity in fission yeast. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 64(9). https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00079-20
Luque, G. M., Bellard, C., Bertelsmeier, C., et al. (2014). The 100th of the world’s worst invasive alien species. Biological Invasions, 16(5), 981–985.
Lu, Y., Zhang, P., Li, C., et al. (2013). Characterisation of immune-related gene expression in clam (Venerupis philippinarum) under exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 34(1), 142–146.
Lv, X. F. (2007). Application of vitellogenin in the research of environmental endocrine disruptors. Research Center for Ecological Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Marchi, T. D., Kuhn, E., Dekker, L., et al. (2016). Targeted ms assay predicting tamoxifen resistance in estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer tissues and sera. Journal of Proteome Research, 15, 1230–1242.
Mccallum, M. L., Matlock, M., Treas, J., et al. (2013). Endocrine disruption of sexual selection by an estrogenic herbicide in the mealworm beetle (Tenebrio molitor). Ecotoxicology, 22(10), 1461–1466.
Niranjan, M. K., Koiri, R. K., & Srivastava, R. (2020). Expression of estrogen receptor alpha in response to stress and estrogen antagonist tamoxifen in the shell gland of Gallus gallus domesticus: involvement of anti-oxidant system and estrogen. Stress, 1(16).
Nussey, S. S., & Whitehead, S. A. (2001). Endocrinology: An Integrated Approach.
O’Donnell, L., Robertson, K. M., Jones, M. E., & Simpson, E. R. (2001). Estrogen and spermatogenesis. Endocrine Reviews, 22, 289–318. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.22.3.289
Olfati, A., & Khamisabadi, H. (2020). Ellagic acid improves testicular dysfunction via autophagy in a tamoxifen-injured rat model. Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology, 56, 265–276.
Olfati, A., Moghaddam, G. H., Baradaran, B., et al. (2018). The effect of estradiol benzoate and FSH on hormonal levels and stereology structure of testis in Ghezel lambs treated with tamoxifen citrate. Revue De Médecine Vétérinaire, 1–3, 58–64.
Oliveira-Filho, E. C., Grisolia, C. K., & Paumgartten, F. (2009). Trans-generation study of the effects of nonylphenol ethoxylate on the reproduction of the snail Biomphalaria tenagophila. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72(2), 458–465.
Orias, F., Bony, S., Devaux, A., et al. (2015a). Tamoxifen ecotoxicity and resulting risks for aquatic eco-systems. Chemosphere, 128, 79–84.
Orias, F., Simon, L., Mialdea, G., et al. (2015b). Bio-concentration of (15)N-tamoxifen at environmental concentration in liver, gonad and muscle of Danio rerio. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 120, 457–462.
Petrie, B., Barden, R., & Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. (2015). A review on emerging contaminants in wastewaters and the environment: current knowledge, understudied areas and recommendations for future monitoring. Water Research, 72,
Phuge, S. (2020). Tamoxifen stimulates gonad development and somatic growth in the tadpoles of indian skipper frog, euphlyctis cyanophlyctis. The Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology, 81 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41936-020-00161-3
Pn, A., Cw. B., & Rw. C. (2019). Effect of gonadotropin releasing hormone on the expression of luteinizing hormone and estrogen in the nerve ganglia and ovary of a tropical abalone, Haliotis asinina Linnaeus. Acta Histochemica, 122(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2019.151454
Pottoo, F. H., Javed, M. N., Barkat, M. A., et al. (2019). Estrogen and serotonin: complexity of interactions and implications for epileptic seizures and epileptogenesis. Current Neuropharmacology, 17(3), 214–231. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X16666180628164432
Ramaswamy, S., & Weinbauer, G. F. (2014). Endocrine control of spermatogenesis: Role of FSH and LH/ testosterone. Spermatogenesis, 4(2), e996025. https://doi.org/10.1080/21565562.2014.996025
Roberts, P., & Thomas, K. (2006). The occurrence of selected pharmaceuticals in wastewater effluent and surface waters of the lower Tyne catchment. Science of the Total Environment, 356(1–3), 143–153.
Scott, A. P. (2012). Do mollusks use vertebrate sex steroids as reproductive hormones? Part I: Critical appraisal of the evidence for the presence, biosynthesis and uptake of steroids. Steroids, 77, 1450–1468.
Solomon, K. R., Carr, J. A., Preez, L., et al. (2008). Effects of atrazine on fish, amphibians, and aquatic reptiles: A critical review. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 38(9), 721–772.
Sumner, B. E. H., Grant, K. E., Rosie, R., et al. (1999). Effects of tamoxifen on serotonin transporter and 5-hydroxytryptamine(2a) receptor binding sites and mrna levels in the brain of ovariectomized rats with or without acute estradiol replacement. Molecular Brain Research, 73(1–2), 119–128.
Taha, S. M., Shatha, M. H., Fahem, M. M., et al. (2016). Hormonal and histopathological changes in male reproductive system of albino mice after Tamoxifen administration. Journal of Genetic Environmental Resources Conservation, 4(1), 51–56.
Thibeault, A. H., Sanderson, J. T., & Vaillancourt, C. (2019). Serotonin-estrogen interactions: what can we learn from pregnancy? Biochimie. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2019.03.023
Tsutsui, K. (2009). A new key neurohormone controlling reproduction, gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH): Biosynthesis, mode of action and functional significance. Progress in Neurobiology, 88(1), 76–88.
Tsutsui, K., Bentley, G. E., Bedecarrats, G., et al. (2010). Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH) and its control of central and peripheral reproductive function. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 31(3), 284–295.
Verma, R., & Krishna, A. (2017). Effect of tamoxifen on spermatogenesis and testicular steroidogenesis. Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications, 486(1), 36–42.
Vogeler, S., Galloway, T. S., Lyons, B. P., et al. (2014). The nuclear receptor gene family in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas, contains a novel subfamily group. BMC Genomics, 15, 369. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-369
Wahli, W., Dawid, I., Ryffel, G., et al. (1981). Vitellogenesis and the vitellogenin gene family. Science, 212(4492), 298–304.
Yang, Y., Fu, J., Peng, H., et al. (2011). Occurrence and phase distribution of selected pharmaceuticals in the Yangtze Estuary and its coastal zone. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 190(1–3), 588–596.
Yan, B. L., Wei, H., & Zhen, H. X. (2010). Effects of temperature on growth and reproduction of Pomacea canaliculata. National Biological Invasion Conference.
Yu, Q., Huo, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, K., & Zhang, L. (2020). Tamoxifen-induced hepatotoxicity via lipid accumulation and inflammation in zebrafish. Chemosphere, 239, 124705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124705
Zhang, C. F., & Cai, S. L. (2003). Research progress on the biochemical properties of shrimp vitellogenin and the synthesis site of vitellogenin. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 12(2), 168–173.
Zhou, Z. L., Li, K., & Zhou, J. et al. (2004). Study on the estrogenic effect of nonylphenol on crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Environmental Science Research, (3):60–61. http://159.226.240.226/handle/311016/440
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Professor Yu Peng, Professor Zhenyu Wang and Dr. Pei Hu for their help in our work.
In addition, we are also very grateful for the suggestions of the two anonymous reviewers.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural of China’s Project “Hubei Province Major Invasive Alien Pests Survey and Monitoring and Integrated Control Project” (125A0609).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The research project was approved by the ethics committee of Hubei University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, J., Zhao, L., Fan, D. et al. Effects of Environmental-Related Concentration of Tamoxifen on Hormonal Balance and Reproduction of the Golden Apple Snail, Pomacea canaliculata (Caenogastropoda: Ampullariidae). Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 517 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05472-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05472-x