Abstract
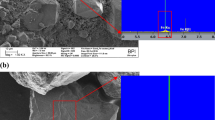
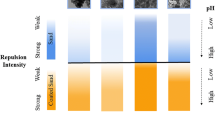
Nanoplastics (NPs) in the subsurface environment have received great attention recently. In this study, column experiments were conducted to investigate the individual effect of Fe and Al oxyhydroxide, and also the combined effects of the two oxyhydroxides and pH on the transport of polystyrene nanoplastics (PSNPs) in water-saturated Fe/Al oxyhydroxide-coating sand. The results showed that compared with Fe oxyhydroxide, Al oxyhydroxide exhibited a more profound impact to retain PSNPs because of its higher pHPZC (point of zero charge; Fe: 7.2, Al: 9.9). More interestingly, for pH values (Fe: 4.5–7.0, Al: 4.5–9.7) lower than Fe/Al oxyhydroxide pHPZC, Fe/Al oxyhydroxide coating dramatically enhanced the retention of negatively charged PSNPs, attributing to the less negatively charged surface and thus reduced electrostatic repulsion. In contrast, for pH values (Fe: 9.7, Al: 11.0) higher than Fe/Al oxyhydroxide pHPZC, Fe/Al oxyhydroxide coating had negligible influence on PSNP retention, because the electrostatic repulsion dominated the transport process. These results clearly demonstrate that pH strongly mediates the transport of PSNPs in Fe/Al oxyhydroxide-coated sand, and emphasize the dominant role of electrostatic interaction in PSNP transport. Findings of this study provide new insight into understanding and predicting the fate and transport of NPs in natural medias with complex physicochemical properties.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alimi, O. S., Farner Budarz, J., Hernandez, L. M., & Tufenkji, N. (2018). Microplastics and nanoplastics in aquatic environments: Aggregation, deposition, and enhanced contaminant transport. Environmental Science & Technology, 52, 1704–1724.
Dong, Z., Qiu, Y., Zhang, W., Yang, Z., & Wei, L. (2018). Size-dependent transport and retention of micron-sized plastic spheres in natural sand saturated with seawater. Water Research, 143, 518–526.
Fisher-Power, L. M., Cheng, T. (2018). Nanoscale titanium dioxide (nTiO2) transport in natural sediments: importance of soil organic matter and Fe/Al oxyhydroxides. Environmental Science & Technology, 52, 2668–2676.
Hurley, R. R., & Nizzetto, L. (2018). Fate and occurrence of micro(nano)plastics in soils: Knowledge gaps and possible risks. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 1, 6–11.
Jeong, C. B., Kang, H. M., Lee, Y. H., Kim, M. S., Lee, J. S., Seo, J. S., Wang, M., & Lee, J. S. (2018). Nanoplastic ingestion enhances toxicity of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the monogonont potifer brachionus koreanus via multixenobiotic resistance (MXR) disruption. Environmental Science & Technology, 52, 11411–11418.
Johnson, P. R., Sun, N., & Elimelech, M. (1996). Colloid transport in geochemically heterogeneous porous media: Modeling and measurements. Environmental Science & Technology, 30, 3284–3293.
Kang, J. K., Yi, I. G., Park, J. A., Kim, S. B., Kim, H., Han, Y., Kim, P. J., Eom, I. C., & Jo, E. (2015). Transport of carboxyl-functionalized carbon black nanoparticles in saturated porous media: Column experiments and model analyses. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 177–178, 194–205.
Kuan, W. H., Lo, S. L., Wang, M. K., & Lin, C. F. (1998). Removal of Se(IV) and Se(VI) from water by aluminum-oxide-coated sand. Water Research, 32, 915–923.
Li, M., He, L., Zhang, M., Liu, X., Tong, M., & Kim, H. (2019). Cotransport and deposition of iron oxides with different-sized plastic particles in saturated quartz sand. Environmental Science & Technology, 53, 3547–3557.
Liu, J., Zhang, T., Tian, L., Liu, X., Qi, Z., Ma, Y., Ji, R., & Chen, W. (2019). Aging significantly affects mobility and contaminant-mobilizing ability of nanoplastics in saturated loamy sand. Environmental Science & Technology, 53, 5805–5815.
Liu, Y., Shao, H., Liu, J., Cao, R., Shang, E., Liu, S., Li, Y., 2021. Transport and transformation of microplastics and nanoplastics in the soil environment: A critical review. Soil Use and Management.
Lu, T., Gilfedder, B. S., Peng, H., Peiffer, S., Papastavrou, G., Ottermann, K., & Frei, S. (2021). Relevance of iron oxyhydroxide and pore water chemistry on the mobility of nanoplastic particles in water-saturated porous media environments. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 232, 168.
Luo, Y., Zhang, Y., Xu, Y., Guo, X., & Zhu, L. (2020). Distribution characteristics and mechanism of microplastics mediated by soil physicochemical properties. Science of The Total Environment, 726, 138389.
Lyu, X., Liu, X., Wu, X., Sun, Y., Gao, B., & Wu, J. (2020). Importance of Al/Fe oxyhydroxide coating and ionic strength in perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) transport in saturated porous media. Water Research, 175, 115685.
Mofijur, M., Ahmed, S. F., Rahman, S. M. A., Arafat Siddiki, S. K. Y., Islam, A. B. M. S., Shahabuddin, M., Ong, H. C., Mahlia, T. M. I., Djavanroodi, F., & Show, P. L. (2021). Source, distribution and emerging threat of micro- and nanoplastics to marine organism and human health: socio-economic impact and management strategies. Environmental Research, 195, 110857.
Qi, R., Jones, D. L., Li, Z., Liu, Q., & Yan, C. (2020). Behavior of microplastics and plastic film residues in the soil environment: A critical review. Science of The Total Environment, 703, 134722.
Qu, M., Kong, Y., Yuan, Y. J., & Wang, D. Y. (2019). Neuronal damage induced by nanopolystyrene particles in nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Environmental Science: Nano, 6, 2591–2601.
Rillig, M. C., Ingraffia, R., & Machado, A. A. (2017). Microplastic incorporation into soil in agroecosystems. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 1805.
Schwaferts, C., Niessner, R., Elsner, M., & Ivleva, N. P. (2019). Methods for the analysis of submicrometer- and nanoplastic particles in the environment. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 112, 52–65.
Song, Z., Yang, X., Chen, F., Zhao, F., Zhao, Y., Ruan, L., Wang, Y., & Yang, Y. (2019). Fate and transport of nanoplastics in complex natural aquifer media: Effect of particle size and surface functionalization. Science of the Total Environment, 669, 120–128.
Stahl, R. S., & James, B. R. (1991). Zinc sorption by iron-oxide-coated sand as a function of pH. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 55, 1287–1290.
Tian, Y., Gao, B., Silvera-Batista, C., & Ziegler, K. J. (2010). Transport of engineered nanoparticles in saturated porous media. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 12, 2371–2380.
Torkzaban, S., & Bradford, S. A. (2016). Critical role of surface roughness on colloid retention and release in porous media. Water Research, 88, 274–284.
Wang, D., Bradford, S. A., Harvey, R. W., Gao, B., Cang, L., & Zhou, D. (2012). Humic acid facilitates the transport of ARS-labeled hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in iron oxyhydroxide-coated sand. Environmental Science & Technology, 46, 2738–2745.
Wang, D., Zhang, W., & Zhou, D. (2013). Antagonistic effects of humic acid and iron oxyhydroxide grain-coating on biochar nanoparticle transport in saturated sand. Environmental Science & Technology, 47, 5154–5161.
Wang, F., Wong, C. S., Chen, D., Lu, X. W., Wang, F., & Zeng, E. Y. (2018). Interaction of toxic chemicals with microplastics: A critical review. Water Research, 139, 208–219.
Wu, X., Lyu, X., Li, Z., Gao, B., Zeng, X., Wu, J., & Sun, Y. (2020). Transport of polystyrene nanoplastics in natural soils: effect of soil properties, ionic strength and cation type. Science of The Total Environment, 707, 136065.
Xu, B., Liu, F., Cryder, Z., Huang, D., Lu, Z., He, Y., Wang, H., Lu, Z., Brookes, P. C., Tang, C., Gan, J., & Xu, J. (2020). Microplastics in the soil environment: Occurrence, risks, interactions and fate — a review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 50, 2175–2222.
Yang, X., Flynn, R., von der Kammer, F., & Hofmann, T. (2011). Influence of ionic strength and pH on the limitation of latex microsphere deposition sites on iron-oxide coated sand by humic acid. Environmental Pollution, 159, 1896–1904.
Yuan, R., Zhang, W., Tao, X., Wang, S., & Zhang, L. (2020). Coupled effects of high pH and chemical heterogeneity on colloid retention and release in saturated porous media. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 586, 124285.
Zhang, W., Isaacson, C. W., Rattanaudompol, U. S., Powell, T. B., & Bouchard, D. (2012). Fullerene nanoparticles exhibit greater retention in freshwater sediment than in model porous media. Water Research, 46, 2992–3004.
Zhang, Y., Luo, Y., Guo, X., Xia, T., Wang, T., Jia, H., & Zhu, L. (2020). Charge mediated interaction of polystyrene nanoplastic (PSNP) with minerals in aqueous phase. Water Research, 178, 115861.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018 YFC1800604), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42007114), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20200817).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Zeng, X., Lyu, X. et al. Combined Effects of Fe/Al Oxyhydroxide Coating and pH on Polystyrene Nanoplastic Transport in Saturated Sand Media. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 2 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05469-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05469-6