Abstract
In this present work, the performance of a semifluidized bed adsorption column has been evaluated for the removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in a semi-continuous mode. The composite adsorbents have been synthesized from waste biomass–based biochar and alginate-based biopolymer. Synthesized adsorbent characterized and finally tested its effectiveness in the removal of both Pb2+ and Cd2+ metal ions by batch and semifluidized bed column adsorption studies. The adsorptive removal efficiencies were found to be dependent on solution pH, initial metal ion concentration, adsorbent dose or initial bed height, static bed height, system temperature and inlet flow rate of semifluidized bed operation. Pseudo-second-order kinetic model was fitted to the batch adsorption experimental data by non-linear and linear regression method and it was found that the non-linear method gives a better way of obtaining the various kinetic parameters and its applicability. A solute phase mass transfer–based dynamic model has been developed to explain the adsorptive behaviour of metal ions onto adsorbents during the semi-continuous mode of operation of a semifluidized bed system. Various mass transfer parameters and degree of dispersion coefficients for the individual packed and fluidized section were obtained from the developed model.
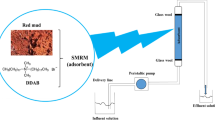
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Superficial area of the particle, m2
- C 0, C t, C ∗ :
-
Solute concentration at the initial time, any time and at equilibrium time respectively, mg/L
- D p, D f :
-
Axial dispersion coefficient for packed and fluidized section respectively, m2/s
- H p, H f, H sf :
-
Height of packed, fluidized and semifluidized bed, cm
- K l :
-
Mass transfer coefficient, m/s
- q e, q t :
-
Adsorption capacity at equilibrium and at any time, mg/g
- u :
-
Superficial liquid velocity, cm/s
- v :
-
Volume of effluent used, L
- w :
-
Weight of adsorbent, g
- ρ a :
-
Bulk density of the material, kg/m3
- ε :
-
Porosity of the bed
References
Afroze, S., & Sen, T. K. (2018). A Review on Heavy Metal Ions and Dye Adsorption from Water by Agricultural Solid Waste Adsorbents. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 229(7), 225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3869-z.
Afroze, S., Sen, T. K., & Ang, H. M. (2016). Adsorption performance of continuous fixed bed column for the removal of methylene blue (MB) dye using Eucalyptus sheathiana bark biomass. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 42(3), 2343–2364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-015-2153-8.
Ahmed Hared, I., Dirion, J.-L., Salvador, S., Lacroix, M., & Rio, S. (2007). Pyrolysis of wood impregnated with phosphoric acid for the production of activated carbon: kinetics and porosity development studies. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 79(1–2), 101–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2006.12.016.
Alade, A. O., Jameel, A. T., Muyibi, S. A., Abdul Karim, M. I., & Alam, M. Z. (2011). Application of semifluidized bed bioreactor as novel bioreactor system for the treatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME). African Journal of Biotechnology, 10(81), 18642–18648. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.2767.
Azouaou, N., Sadaoui, Z., Djaafri, A., & Mokaddem, H. (2010). Adsorption of cadmium from aqueous solution onto untreated coffee grounds: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 184(1–3), 126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.014.
Balkaya, N., & Cesur, H. (2008). Adsorption of cadmium from aqueous solution by phosphogypsum. Chemical Engineering Journal, 140(1–3), 247–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.10.002.
Basu, M., Guha, A. K., & Ray, L. (2019). Adsorption of lead on lentil husk in fixed bed column bioreactor. Bioresource Technology, 283(March), 86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.133.
Biswas, S., Meikap, B. C., & Sen, T. K. (2019a). Adsorptive removal of aqueous phase copper (Cu2+) and nickel (Ni2+) metal ions by synthesized biochar–biopolymeric hybrid adsorbents and process optimization by response surface methodology (RSM). Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 230(8), 197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4258-y.
Biswas, S., Sen, T. K., & Meikap, B. C. (2019b). Experimental hydrodynamic and bed characteristics of co-current gas-liquid-solid three phase semifluidization with liquid as the continuous phase. Particulate Science and Technology, 38, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2019.1651586.
Biswas, S., Sen, T. K., Yeneneh, A. M., & Meikap, B. C. (2019c). Synthesis and characterization of a novel Ca-alginate-biochar composite as efficient zinc (Zn 2+ ) adsorbent: thermodynamics, process design, mass transfer and isotherm modeling. Separation Science and Technology, 54(7), 1106–1124. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1527353.
Biswas, S., Diwakar, R. K., Dipamitra, Behera, I., Meikap, B. C., Sen, T. K., & Khiadani, M. (2020a). Aqueous phase phenol removal from synthetic and real steel plant effluents through a batch and Semifluidized bed column operation: experimental and model analysis. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(August), 104441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104441.
Biswas, S., Mohapatra, S. S., Kumari, U., Meikap, B. C., & Sen, T. K. (2020b). Batch and continuous closed circuit semi-fluidized bed operation: removal of MB dye using sugarcane bagasse biochar and alginate composite adsorbents. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(1), 103637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103637.
Biswas, S., Sharma, S., Mukherjee, S., Meikap, B. C., & Sen, T. K. (2020c). Process modelling and optimization of a novel Semifluidized bed adsorption column operation for aqueous phase divalent heavy metal ions removal. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 37, 101406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101406.
Biswas, S., Siddiqi, H., Meikap, B. C., Sen, T. K., & Khiadani, M. (2020d). Preparation and characterization of raw and inorganic acid-activated pine cone biochar and its application in the removal of aqueous-phase Pb2+ metal ions by adsorption. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 231(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4375-7.
Corrêa, R. A., Calçada, L. A., & Peçanha, R. P. (2007). Development of a fluidized bed system for adsorption of phenol from aqueous solutions with commercial macroporous resins. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 24(1), 15–28. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-66322007000100002.
Daud, W. (2004). Comparison on pore development of activated carbon produced from palm shell and coconut shell. Bioresource Technology, 93(1), 63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2003.09.015.
Fan, L. T., & Hsu, E. H. (1981). Semifluidized bed bioreactor. In Scientific and engineering principles (pp. 663–669). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-025383-1.50109-0.
Freundlich, H. M. (1906). Over the adsorption in solution. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 57, 385–470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9030970.
Gharaibeh, S. H., Abu-el-sha’r, W. Y., & Al-Kofahi, M. M. (1998). Removal of selected heavy metals from aqueous solutions using processed solid residue of olive mill products. Water Research, 32(2), 498–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00221-2.
Hanra, M. S., & Ramachandhran, V. (1996). Trace level separation of zinc sulfate and lead nitrate from toxic effluent streams by reverse osmosis modular systems. Separation Science and Technology, 31(1), 49–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496399608000680.
Hashim, M. (2004). Biosorption of cadmium by brown, green, and red seaweeds. Chemical Engineering Journal, 97(2–3), 249–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1385-8947(03)00216-X.
Kannan, N., & Rengasamy, G. (2005). Comparison of cadmium ion adsorption on various activated carbons. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 163(1–4), 185–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-0277-y.
Karagöz, S., Tay, T., Ucar, S., & Erdem, M. (2008). Activated carbons from waste biomass by sulfuric acid activation and their use on methylene blue adsorption. Bioresource Technology, 99(14), 6214–6222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.12.019.
Katsumata, H., Kaneco, S., Inomata, K., Itoh, K., Funasaka, K., Masuyama, K., et al. (2003). Removal of heavy metals in rinsing wastewater from plating factory by adsorption with economical viable materials. Journal of Environmental Management, 69(2), 187–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4797(03)00145-2.
Kumagai, S., Noguchi, Y., Kurimoto, Y., & Takeda, K. (2007). Oil adsorbent produced by the carbonization of rice husks. Waste Management, 27(4), 554–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2006.04.006.
Lagergren, S. Y. (1898). Zur Theorie der sogenannten Adsorption gelöster Stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakad. Handlingar, 24(4), 1–39. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0167428.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40(9), 1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004.
Lee, S., & Davis, A. P. (2001). Removal of cu (II) and cd (II) from aqueous solution by seafood processing waste sludge. Water Research, 35(2), 534–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00284-0.
Lim, A. P., & Aris, A. Z. (2014). Continuous fixed-bed column study and adsorption modeling: Removal of cadmium (II) and lead (II) ions in aqueous solution by dead calcareous skeletons. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 87, 50–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2014.03.019.
Low, K., Lee, C., & Liew, S. (2000). Sorption of cadmium and lead from aqueous solutions by spent grain. Process Biochemistry, 36(1–2), 59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(00)00177-1.
Momčilović, M., Purenović, M., Bojić, A., Zarubica, A., & Randelovid, M. (2011). Removal of lead (II) ions from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto pine cone activated carbon. Desalination, 276(1–3), 53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.03.013.
Mondal, M., Mukherjee, R., Sinha, A., Sarkar, S., & De, S. (2019). Removal of cyanide from steel plant effluent using coke breeze, a waste product of steel industry. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 28, 135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.01.013.
Muhamad, H., Doan, H., & Lohi, A. (2010). Batch and continuous fixed-bed column biosorption of Cd2+ and Cu2+. Chemical Engineering Journal, 158(3), 369–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.12.042.
Mullick, A., & Neogi, S. (2016). Synthesis of potential biosorbent from used stevia leaves and its application for malachite green removal from aqueous solution: kinetics, isotherm and regeneration studies. RSC Advances, 6(70), 65960–65975. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA15225B.
Narayanan, C. M. (2019). Performance and applications of semifluidized bioreactors – a review. International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering, 17(1), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2017-0178.
Narayanan, C. M., & Biswas, S. (2016). Studies on waste water treatment in three phase semifluidized bed bioreactors : computer aided analysis and software development. Journal of Miodern Chemistry and Chemical Technology, 7(1), 1–21.
Oswald, W. J. (2003). My sixty years in algology. Journal of Applied Phycology, 15(99), 99–106. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023871903434.
Sabry, R., Hafez, A., Khedr, M., & El-Hassanin, A. (2007). Removal of lead by an emulsion liquid membrane. Desalination, 212(1–3), 165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.11.006.
Sreejalekshmi, K. G., Krishnan, K. A., & Anirudhan, T. S. (2009). Adsorption of Pb (II) and Pb (II)-citric acid on sawdust activated carbon: Kinetic and equilibrium isotherm studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(2–3), 1506–1513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.002.
Srivastava, V. C., Mall, I. D., & Mishra, I. M. (2006). Equilibrium modelling of single and binary adsorption of cadmium and nickel onto bagasse fly ash. Chemical Engineering Journal, 117(1), 79–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2005.11.021.
Tan, K. L., & Hameed, B. H. (2017). Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 74, 25–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.01.024
Tsibranska, I., & Hristova, E. (2010). Modelling of heavy metal adsorption into activated carbon from apricot stones in fluidized bed. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 49(10), 1122–1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2010.08.003.
Vázquez, G., González-Álvarez, J., Freire, S., López-Lorenzo, M., & Antorrena, G. (2002). Removal of cadmium and mercury ions from aqueous solution by sorption on treated Pinus pinaster bark: kinetics and isotherms. Bioresource Technology, 82(3), 247–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00186-9.
Vinodhini, V., & Das, N. (2010). Packed bed column studies on Cr (VI) removal from tannery wastewater by neem sawdust. Desalination, 264(1–2), 9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.06.073.
Volesky, B. (2007). Biosorption and me. Water Research, 41(18), 4017–4029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.05.062.
Weber, W. J., & Morris, J. C. (1965). Kinetics of adsorption in columns of fluidized media. Journal - Water Pollution Control Federation, 37(4), 425–443 http://www.jstor.org/stable/25035275.
Yaghoobi-Khankhajeh, S., Alizadeh, R., & Zarghami, R. (2018). Adsorption modeling of CO2 in fluidized bed reactor. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 129, 111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.10.037.
Zulfadhly, Z., Mashitah, M. D., & Bhatia, S. (2001). Heavy metals removal in fixed-bed column by the macro fungus Pycnoporus sanguineus. Environmental Pollution, 112(3), 463–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00136-6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Performance of a semifluidized bed adsorption column has been analyzed.
• Mass transfer–based dynamic model system has been developed and validated.
• Fast removal of heavy metals has been achieved in SFBR.
• Maximum bed capacity found 54.4 mg/g for Pb2+and 36.8 mg/g for Cd2+.
• Mass transfer parameters and dispersion coefficients have been evaluated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biswas, S., Sharma, S., Siddiqi, H. et al. Semifluidized Bed Adsorption Column Studies for Simultaneous Removal of Aqueous Phase Pb2+ and Cd2+ by Composite Adsorbents: an Experimental and Mass Transfer Dynamic Model–Based Approach. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 8 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04951-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04951-x