Abstract
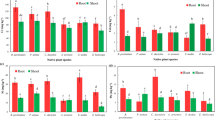
For plant growth, cadmium (Cd) is a toxic and easily accumulated element but silicon (Si) is beneficial. To explore the alleviating effect of Si on Cd toxicity to plants in Cd-contaminated calcareous soil, the effect of Si on Cd absorption was investigated for cucumber organs in pot experiments. The Cd concentration of cucumber organs using an atomic absorption spectrophotometer. The Si significantly inhibited Cd uptake by cucumber organs and was most effective for Si application of 100–200 mg kg−1. On the whole, the translocation factors of stems and leaves did not vary significantly, but substantially varied in fruit. The distribution pattern of Cd content in different cucumber organs follows: root > stem > leaf > > fruit. For Cd content in soil ≤ 3 mg kg−1, the Cd content in cucumber fruit was lower than the maximum limit of Cd content in fresh vegetables in China (GB2762-2017) for Si application of 100–300 mg kg−1. However, with the Cd treatment of 5 mg kg−1, the content of Cd in cucumber fruit exceeded this limit, even though Si alleviated Cd toxicity to some extent. Therefore, Si had a substantial alleviating effect on Cd uptake in cucumber, effectively reduced Cd toxicity to cucumber in calcareous soil. The study may help us understand the mechanism for silicon-mediated Cd tolerance in calcareous soil and provide theoretical basis for the application of silicon in the production of crops in alkaline soil polluted by Cd.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrees, M., Ali, S., Rizwan, M., Zia-Ur-Rehman, M., Ibrahim, M., Abbas, F., et al. (2015). Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: a review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 119(Complete), 186–197.
Asif, N., Saifullah, Zia ur Rehman, M., Tasneem, A., Hussan, Z. M., & Muhammad, A. (2018). Silicon nutrition lowers cadmium content of wheat cultivars by regulating transpiration rate and activity of antioxidant enzymes. Environmental Pollution, 242, 126–135.
Buchter, B., Davidoff, B., Amacher, M. C., Hinz, C., Iskandar, I. K., & Selim, H. M. (1989). Correlation of Freundlich Kd and n retention parameters with soils and elements. Soil Science, 148(5), 370–379.
Chen, H. M., Zheng, C. R., Tu, C., & Shen, Z. G. (2000). Chemical methods and phytoremediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals. Chemosphere, 41(1), 229–234.
Esposito, M., Picazio, G., Serpe, P., Lambiase, S., & Cerino, P. (2015). Content of cadmium and lead in vegetables and fruits grown in the Campania region of Italy. Journal of Food Protection, 78(9), 1760–1765.
Feng, J., Shi, Q., Wang, X., Wei, M., Yang, F., & Xu, H. (2010). Silicon supplementation ameliorated the inhibition of photosynthesis and nitrate metabolism by cadmium (Cd) toxicity in Cucumis sativus L. Scientia Horticulturae, 123(4), 521–530.
Gao, M., Zhou, J., Liu, H., Zhang, W., Hu, Y., Liang, J., et al. (2018). Foliar spraying with silicon and selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice. Science of the Total Environment, 631-632, 1100–1108.
GB2762-2017. (2017). The national food safety standard for maximum levels of contaminants in foods. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 30(3), 329–340.
Greger, M., Kabir, A. H., Landberg, T., Maity, P. J., & Lindberg, S. (2016). Silicate reduces cadmium uptake into cells of wheat. Environmental Pollution, 211, 90–97.
He, S., He, Z., Yang, X., Stoffella, P. J., & Baligar, V. C. (2015). Soil biogeochemistry, plant physiology, and phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soils. Advances in Agronomy, 134, 135–225.
Jia, X., Liu, F., & Fan, W. (2018). Effects of silicon on photosynthesis and antioxidant enzymes of cucumber seedling under cadmium stress. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 32(04), 321–326 In Chinese.
Jia, X., Liu, F., Fan, W., & Wang, S. (2019). Effect of silicon on cucumber yield and quality under cadmium stress. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2019, 50(1), 171–176 In Chinese.
Landberg, T., & Greger, M. (1996). Differences in uptake and tolerance to heavy metals in salix from unpolluted and polluted areas. Applied Geochemistry, 11(1–2), 175–180.
Liang, Y., Wong, J. W. C., & Wei, L. (2005). Silicon-mediated enhancement of cadmium tolerance in maize (Zea Mays L.) grown in cadmium contaminated soil. Chemosphere, 58(4), 475–483.
Liu, J., Ma, J., He, C., Li, X., Zhang, W., Xu, F., Lin, Y., & Wang, L. (2013a). Inhibition of cadmium ion uptake in rice (Oryza sativa) cells by a wall-bound form of silicon. New Phytologist, 200(3), 691–699.
Liu, J., Zhang, H., Zhang, Y., & Chai, T. (2013b). Silicon attenuates cadmium toxicity in Solanum nigrum L. by reducing cadmium uptake and oxidative stress. Plant Physiol Biochemistry, 68(68C), 1–7.
Liu, F., Liu, X., Ding, C., & Wu, L. (2015). The dynamic simulation of rice growth parameters under cadmium stress with the assimilation of multi-period spectral indices and crop model. Field Crops Research, 183, 225–234.
McBride, M. B., Shayler, H. A., Spliethoff, H. M., Mitchell, R. G., Marquez-Bravo, L. G., Ferenz, G. S., et al. (2014). Concentrations of lead, cadmium and barium in urban garden-grown vegetables: the impact of soil variables. Environmental Pollution, 194, 254–261.
Ministry of Environmental Protection and Ministry of Land and Resources Issued the Bulletin of National Soil Pollution Investigation (2014). Resources and human settlements, 184, 28–29.
Norton, G. J., Deacon, C. M., Mestrot, A., Feldmann, J., Jenkins, P., Baskaran, C., et al. (2015). Cadmium and lead in vegetable and fruit produce selected from specific regional areas of the UK. Science of the Total Environment, 533, 520–527.
Sandalio, L. M. (2001). Cadmium-induced changes in the growth and oxidative metabolism of pea plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 52, 2115–2126.
Santillan-Medrano, J., & Jurinak, J. J. (1975). The chemistry of lead and cadmium in soil: solid phase formation. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 39(5), 851–856.
Shi, G., Cai, Q., Liu, C., & Wu, L. (2010). Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in peanut plants in relation to cadmium distribution and stimulation of antioxidative enzymes. Plant Growth Regulation, 61(1), 45–52.
Song, A., Li, Z., Zhang, J., Xue, G., Fan, F., & Liang, Y. (2009). Silicon-enhanced resistance to cadmium toxicity in Brassica chinensis L. is attributed to Si-suppressed cadmium uptake and transport and Si-enhanced antioxidant defense capacity. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(1), 74–83.
Song, W., Chen, S., Liu, J., Chen, L., Song, N., Li, N., & Liu, B. (2015). Variation of Cd concentration in various rice cultivars and derivation of cadmium toxicity thresholds for paddy soil by species-sensitivity distribution. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 14(9), 1845–1854.
Song, Y., Wang, Y., Mao, W., Sui, H., Yong, L., Yang, D., et al. (2017). Dietary cadmium exposure assessment among the Chinese population. PLoS One, 12(5), e0177978.
Tripathi, D. K., Singh, V. P., Kumar, D., & Chauhan, D. K. (2012). Rice seedlings under cadmium stress: effect of silicon on growth, cadmium uptake, oxidative stress, antioxidant capacity and root and leaf structures. Chemistry and Ecology, 28(3), 281–291.
Ueno, D., Koyama, E., Yamaji, N., & Ma, J. F. (2010). Physiological, genetic, and molecular characterization of a high-Cd-accumulation rice cultivar, Jarjan. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62(7), 2265–2272.
Vaculík, M., Lux, A., Luxová, M., Tanimoto, E., & Lichtscheidl, I. (2009). Silicon mitigates cadmium inhibitory effects in young maize plants. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 67(1), 52–58.
Vaculík, M., Landberg, T., Greger, M., Luxová, M., Stolariková, M., & Lux, A. (2012). Silicon modifies root anatomy, and uptake and subcellular distribution of cadmium in young maize plants. Annals of Botany, 110(2), 433–443.
Van Assche, F., & Clijsters, H. (1990). Effects of heavy metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell & Environment, 13, 195–206.
Wang, M., Nie, L., Xu, R., & Wang, S. (2018). Effects of foliar application of silicon on accumulation of sugar and vitamin C and related enzymes in cucumber fruits. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 45(02), 351–358.
Wu, J., Guo, J., Hu, Y., & Gong, H. (2015). Distinct physiological responses of tomato and cucumber plants in silicon-mediated alleviation of cadmium stress. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6.
Xia, H. (1997). Studies on cadmium in soil-plant system. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology., 3(03), 289–298 In Chinese.
Xue, S., Shi, L., Wu, C., Wu, H., Qin, Y., Pan, W., et al. (2017). Cadmium, lead, and arsenic contamination in paddy soils of a mining area and their exposure effects on human HEPG2 and keratinocyte cell-lines. Environmental Research, 156, 23–30.
Yang, Y., Zhang, F. S., Li, H. F., & Jiang, R. F. (2009). Accumulation of cadmium in the edible parts of six vegetable species grown in Cd-contaminated soil soils. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(2), 1117–1122.
Zahoor, Sun, D., Li, Y., Wang, J., Tu, Y., Wang, Y., Hu, Z., Zhou, S., Wang, L., Xie, G., Huang, J., Alam, A., & Peng, L. (2017). Biomass saccharification is largely enhanced by altering wall polymer features and reducing silicon accumulation in rice cultivars harvested from nitrogen fertilizer supply. Bioresource Technology, 243, 957–965.
Zhang, C., Wang, L., Nie, Q., Zhang, W., & Zhang, F. (2008). Long-term effects of exogenous silicon on cadmium translocation and toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environmental and Experimental Botany, 62(3), 300–307.
Zhang, S., Yang, Y., Zhai, W., Tong, Z., & Ding, F. (2019). Controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer improved lodging resistance and potassium and silicon uptake of direct-seeded rice. Crop ence, 59(6), 2733–2740.
Zhu, Y., Yin, J., Liang, Y., Liu, J., Jia, J., & Huo, H. (2019). Transcriptomic dynamics provide an insight into the mechanism for silicon- mediated alleviation of salt stress in cucumber plants. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 174(6), 245–254.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, J., Liu, F., Fan, W. et al. Effect of Silicon on Cadmium Absorption of Cucumber Organs in Calcareous Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 380 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04747-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04747-z