Abstract
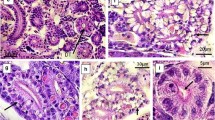
This study aimed to evaluate histological changes in targeted tilapia organs exposed to sublethal concentrations of carbofuran. Fishes with an average weight of 67.5 ± 2.0 g were exposed to sublethal concentrations (0.0044, 0.0088, 0.0440, and 0.0880 mg L−1) of carbofuran for 7 days. In the end of the experiment, the gill, the liver, and the kidney samples were collected for histological evaluation. In gills exposed to 0.0044 mg L−1 of carbofuran, an increase in interlayer epithelium and disruption of the secondary lamella was observed, while in other concentrations (0.0088, 0.0440, and 0.0880 mg L−1), only blood congestion in the secondary lamellae occurred. In the liver samples of exposed tilapias, all carbofuran concentrations caused hepatocyte hypertrophy with the nuclei displaced to the cell periphery, stasis within the sinusoid capillaries, and necrosis points. All sublethal concentrations tested caused detachment of the glomerular capsule, necrosis in the proximal and distal tubules, and absence of intercellular space in the kidney of exposed tilapia. The presence of carbofuran in aquatic environments at concentrations from 0.0044 mg L−1 and exposure periods longer than 7 days alters the gill, the liver, and the kidney histology and consequently compromising the fish’s health.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Khalek, A. A., Badran, S. R., & Marie, M. S. (2020). The efficient role of rice husk in reducing the toxicity of iron and aluminum oxides nanoparticles in Oreochromis niloticus: hematological, bioaccumulation, and histological endpoints. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 231, 1–10.
Abe, F. R., Machado, A. A., Coleone, A. C., Cruz, C., & Machado-Neto, J. G. (2019). Toxicity of diflubenzuron and temephos on freshwater fishes: ecotoxicological assays with Oreochromis niloticus and Hyphessobrycon eques. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 230, 1–10.
ABNT (Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas). (2007). NBR 15499 (1st ed.p. 21). Rio de Janeiro: Ecotoxicologia aquática – Toxicidade crônica de curta duração – Método de ensaio com peixes.
Altinok, I., Capkin, E., Karaham, S., & Boran, M. (2006). Effects of water quality and fish size on toxicity of methiocarb, a carbamate pesticide, to rainbow trout. Envrionmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 22, 20–26.
Behmer, A. O., Tolosa, E. M. C., & Freitas-Neto, A. G. (1976). Manual de técnicas para histologia normal e patológica (239p). São Paulo: Edart.
Bernet, D., Schmidt, H., Meier, W., Burkhardt-Holm, P., & Wahli, T. (1999). Histopath-ology in fish: proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. Journal of Fish Diseases, 22, 25–34.
Boran, H., Altinok, I., & Capkin, E. (2010). Histopathological changes induced by maneb and carbaril on some tissues of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Tissue & Cell, 42, 158–164.
Bretaud, S., Toutant, J. E., & Saglio, E. (2000). Effects of carbofuran, diuron and nicosulfuron on acetylcholinestarase activity in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 47, 117–124.
Campos-Garcia, J., Martinez, D. S. T., Alvez, O. L., Leonardo, A. F. G., & Barbieri, E. (2015). Ecotoxicological effects of carbofuran and oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes on the freshwater fish Nile tilapia: nanotubes enhance pesticide ecotoxicity. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 111, 131–137.
Capkin, E., Terzl, E., Boran, H., Yandi, I., & Altinok, I. (2010). Effects of some pesticides on the vital organs of juvenile raiwbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Tissue & Cell, 42, 376–382.
Dutta, H. M. (1996) A composite approach for evaluation of the effects of pesticides on fish. In: Munshi JSD, Dutta HM. Fish Morphology. Horizon of New Research, Lebanon. New Hampshire Science Publishers, Oxford IBH, p. 249–269.
Fanta, E., Rios, F. S., Romão, S., Vianna, A. C. C., & Freiberger, S. (2003). Histopathology of the fish Corydoras paleatus contaminated with sublethal levels of organophosphorus in water and food. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 54, 119–130.
Guimarães, A. T. B., Silva De Assis, H. C., & Boeger, W. (2007). The effect of trichlorfon on acetylcholinesterase activity and histopathology of cultivated fish Oreochromis niloticus. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 68, 57–62.
Harabawy, A. S. A., & Ibrahim, A. T. A. (2014). Sublethal toxicity of carbofuran pesticide on the African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822): hematological, biochemical and cytogenetic response. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 103, 61–67.
Henares, M. N. P., Cruz, C., Gomes, G. R., Pitelli, R. A., & Machado, M. R. F. (2008). Toxicidade aguda e efeitos histopatológicos do herbicida diquat na brânquia e no fígado da tilápia nilótica (Oreochromis niloticus). Acta Scientiarum Biological Sciences, 30, 77–82.
Iqbal, F., Qureshi, I. Z., & Ali, M. (2004). Histopathological changes on the kidney of common carp, Cyprinus carpio following nitrate exposure. Journal of Research in Science, 15, 411–418.
Jimenez, B. D., & Stegman, J. (1990). Detoxification enzymes as indicators of environmental stress on fish. In M. S. Adams (Ed.), Biological Indicators of Stress in Fish (pp. 67–79). Bestheda: American Fisheries Symposium, American Fisheries Society.
Kuzmanovíc, M., Ginebreda, A., Petrovíc, M., & Barceló, D. (2015). Risk assessment based prioritization of 200 organic micropollutants in 4 Iberian rivers. Science of the Total Environment, 503/504, 289–299.
Mcdonald, D. G. (1983). The effects of H+ upon the gill of fresh water fish. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 61, 691–703.
Melletti, P.C., Rocha, O., & Martinez, C. B. R. (2004) Avaliação da degradação ambiental na Bacia do Rio Mogi-Guaçu por meio de testes de toxicidade com sedimento e análises histopatológicas em peixes. In: Brigante J, Espíndola ELG. Limnologia fluvial: um estudo no rio Mogi-Guaçu. 1 ed. Editora Rima, p. 249–280.
Miller, D. S. (2002). Xenobiotic export pumps, endothelin signaling, and tubular nephrotoxicants – a case of molecular hijacking. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 16, 121–127.
Nandan, S. B., & Nimila, P. J. (2012). Lindane toxicity: histopathological, behavioural and biochemical changes in Etroplus maculatus (Bloch, 1795). Marine Environmental Research, 76, 63–70.
Pawert, M., Muller, E., & Triebskor, N. R. (1998). Ultrastructural changes in fish gills as biomarker to assess small stream pollution. Tissue & Cell, 30, 617–626.
Roberts, R. J. (2001). Fish pathology (p. 472). London: W.B. Saunders.
Santos, E. L., Winterle, W. M. C., Ludke, M. C. M. M., & Barbosa, J. M. (2008). Digestibilidade de ingredientes alternativos para tilápia-do-nilo (Oreochromis niloticus): revisão. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia de Pesca., 3, 135–149.
Tang, Z., Huang, Q., Yang, Y., Zhu, X., & Haihui, F. (2013). Organochlorine pesticides in the lower reaches of Yangtze River: occurrence, ecological risk and temporal trends. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 87, 89–97.
Teh, S. J., Adams, S. M., & Hinton, D. E. (1997). Histopathologic biomarkers in feral freshwater fish populations exposed to different types of contaminant stress. Aquatic Toxicology, 37, 51–70.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), (2006) Interim reregistration eligibility decision – carbofuran. Disponível em: <http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/reregistration/carbofuran/carbofuran_noic.htm> Accessed 15 Jan 2016
Vaz, B. S., Lopes, P. R. S., Enke, D. B. S., & Pouey, J. L. F. O. (2007). Aspectos sobre bem-estar em peixes cultivados. Revista Brasileira de Agrociência, 13, 419–422.
Veiga, M. M., Silva, D. M., Veiga, L. B. E., & Faria, M. V. C. (2006). Análise da contaminação dos sistemas hídricos por agrotóxicos numa pequena comunidade rural do Sudeste do Brasil. Cadernos de Saúde Pública., 22, 2391–2399.
Velmurugan, B., Selvanayagam, M., Cengiz, E. I., & Unlu, E. (2007). Histopathology of lambda-cyhalothrin on tissues (gill, kidney, liver and intestine) of Cirrhinus mrigala. Envrionmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 24, 286–291.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the UNESP Aquaculture Center for the supply of fish required for this work.
Funding
This study is funded by the the Brazilian Higher Level Education Council (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P., Machado, A.A., da Cruz, C. et al. Histological Changes in Targeted Organs of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Exposed to Sublethal Concentrations of the Pesticide Carbofuran. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 228 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04628-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04628-5