Abstract
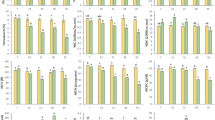
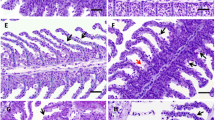
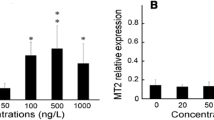
Pesticides are one of the main sources of pollution on the planet, affecting different environments. The aim of the study was to evaluate the chronic effect of atrazine (ATZ) on brain, gill, and liver histology and the clinical signs of intoxication in Hyphessobrycon eques fish and to determine the effect on the expression of proteins related to proliferation, damage, death, and cellular stress pathways. The chronic toxicity test was performed during 30 days of exposure to ATZ. Concentrations of 0.57, 1.14, 5.74, and 11.50 mg L−1 were applied and there was a control. Aquariums with a capacity of 5 L of water were used with aeration pumps containing 5 animals per replica, weighing between 1.0 ± 0.2 g per organism. At the end of the chronic toxicity tests of ATZ for H. eques, samples of the gills, brain, and liver were collected for histological analysis. The same organs were collected and stored in cryogen tubes in liquid nitrogen until the moment of extraction and then massaged mechanically for the Western-blot technique. In the histopathological analyses, the gills showed the greatest changes in relation to the other organs, such as the loss of support of the secondary lamellae, and the fish also showed a loss of swim bladder capacity. In conclusion, ATZ in the environment, in long-term exposure, can cause histological and biochemical effects, affecting the survival and proliferation of cell pathways.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data generated from the experiment.
References
Abarikwu, So. (2014). Protective effect of quercetin on atrazine-induced oxidative stress in the liver, kidney, brain, and heart of adult wistar rats. Toxicology International, 21, 148–155.
ABNT (Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas). (2007). NBR 15499 (1° ed. 21). Rio de Janeiro: Ecotoxicologia aquática – Toxicidade crônica de curta duração – Método de ensaio com peixes.
Alavanja, M. C., Ross, M. K., & Bonner, M. R. (2013). Increased cancer burden among pesticide applicators and others due to pesticide exposure. CA: Cancer Journal Clinicians, 63, 120–42.
Américo-Pinheiro, J. H. P., Machado, A. A., Cruz, C., Aguiar, M. M., Ferreira, L. F. R., Torres, N. H., & Machado-Neto, J. G. (2020). Histological changes in targeted organs of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to sublethal concentrations of the pesticide carbofuran. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 231, 1–8.
Andrade Vieira, J. A. R., & da Silva, G. S. (2019). Avaliação dos efeitos do Roundup® e da hipóxia sobre os parâmetros hematológicos e histologia branquial de Colossoma macropomum (Cuvier, 1818), Scientia Amazonia, v. 8, n.2, CAm16-CAm28.
ANVISA. Brazilian Health Surveillance Agency. (2016). Available at: http://portal.anvisa.gov.br/resultado-de-busca?p_p_id=101&p_p_lifecycle=0&p_p_state=maximized&p_p_mode=view&p_p_col_id=column-1&p_p_col_count=1&_101_struts_action=%2Fasset_publisher%2Fview_content&_101_assetEntryId=2838557&_101_type=document. Accessed 11 June 2021
Behmer, A. O., Talosa, C. M. E., & Neto, F. G. A. (1976). Manual De Técnicas Para Histologia Normal e Patológica (p. 239). São Paulo: Edart.
Brunet, A., Bonni, A., Zigmond, M. J., Lin, M. Z., Juo, P., Hu, L. S., Anderson, M. J., Arden, K. C., Bleins, J., & Grrenberg, M. E. (1999). Akt Promotes Cell Survival by Phosphorylating and Inhibiting a Forkhead Transcription Factor. Cell, 96, 857–868.
Carraschi, S. P., Cruz, C., Machado Neto, J. G., Ignácio, N. F., Barbuio, R., & Machado, M. R. F. (2012). Histopathological biomarkers in pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila and treated with antibiotics. Ecotoxicology Environmental Safety, 83, 115–120.
Cattani, D., Cavalli, V. L. L. O., Reig, C. E. H., Domingues, J. T., Dal-Cim, T., Tasca, C. I., Silva, F. R. M. B., & Zamoner, A. (2014). Mechanisms underlying the neurotoxicity induced by glyphosate-based herbicide in immature rat hippocampus: Involvement of glutamate excitotoxicity. Toxicology, 320, 34–45.
Cavalli, V. L. L. O., Cattani, D., Reig, C. E. H., Pierozan, P., Zanatta, L., Parisotto, E. B., Filho, D. W., Silva, F. R. M. B., Pessoa-Pureur, R., & Zamoner, A. (2013). Roundup disrupts male reproductive functions by triggering calcium-mediated cell death in rat testis and Sertoli cells. Free Radical Biology and Medicine., 65, 335–346.
Cross, D. A. E., Alessi, D. R., Cohen, P., Andjelkovich, M., & Hemmings, B. A. (1995). Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature, 378, 785–789.
Dane, H., & Sisman, T. (2017). A histopathological study on the freshwater fish species chub (Squalius cephalus) in the Karasu River, Turkey. Turkish Journal of Zoology, 41(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.3906/zoo-1509-21
Destro, A. L. F., Silva, S. B., Gregório, K. P., Oliveira, J. M., Lozi, A. A., Zuanon, J. A., Salaro, A. L., Matta, S. L. P., Gonçanves, R. V., & Freitas, M. B. (2021). Effects of subchronic exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of the herbicide atrazine in the Neotropical fish Astyanax altiparanae. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 208, 111601.
EC, European Commission. Commission decision of 10 March 2004 concerning the non-inclusion of atrazina in Annex I to Council Directive 91/414/EEC and the withdrawal of authorisations for plant protection products containing this active substance, 2004/248/EC [displayed 10 March 2015]. Available at http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/protection/evaluation/existactive/oj_atrazina.pdf
Erlacher-Reid, C. D. (2018). Considerations for treatment of large zoologic collections: Fish. Vet Clin Exot Anim, 21, 311–325.
Ferrari, A., Venturino, A., & D’Angelo, A. M. P. (2007). Muscular and brain cholinesterase sensitivities to azinphos methyl and carbaryl in the juvenile rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 146C, 308–313.
Fillols, E., Davis, A. M., Lewis, S. E., & Ward, A. (2020). Combining weed efficacy, economics and environmental considerations for improved herbicide management in the Great Barrier Reef catchment area. Science of the Total Environment, 720, 137481.
Franke, T. F., Kaplan, D. R., & Cantley, L. C. (1997). PI3K: Downstream AKT ion blocks apoptosis. Cell, 88, 435–437.
Franke, T. F., Yang, S. I., Chan, T. O., Datta, K., Kazlauskas, A., Morrison, Kaplan, D. R., & Tsichlis, P. N. (1995). The protein kinase encoded by the Akt proto-oncogene is a target of the PDGF-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell, 81, 727–36.
Guyton, K. Z., Loomis, D., Grosse, Y., El Ghissassi, F., Benbrahim-Tallaa, L., Guha, N., Scoccianti, C., Mattock, H., & Straif, K. (2015). Carcinogenicity of tetrachlorvinphos, parathion, malathion, diazinon, and glyphosate. The Lancet Oncology, 16, 490–491.
Hajduch, E., Litherland, G. J., & Hundal, H. S. (2001). Protein kinase B (PKB/Akt)–a key regulator of glucose transport. FEBS Letters, 492, 199–203.
Hou, X., Huang, X., Ai, Z., Zhao, J., & Zhang, L. (2017). Ascorbic acid induced atrazina degradation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 327, 71–78.
Hu, K., Tian, Y., Du, Y., Huang, L., Chen, J., Li, N., & Liu, W. (2016). Atrazina promotes proliferation of prostate cancer cells. International Journal of Oncology., 48, 2166–2174.
Inoki, K., Li, Y., Zhu, T., Wu, J., & Guan, K. L. (2002). TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR signalling. Nature Cell Biology, 4, 648–657.
Instituto Brazileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis (IBAMA) – IBAMA. (2020). Relatórios de comercialização de agrotóxicos. 2019. Available at http://www.ibama.gov.br/relatorios/quimicos-e-biologicos/relatoriosdecomercializacao-de-agrotoxicos#historicodecomercializacao. Accessed 4 Jul 2021
Jin, Y., Wang, L., Chen, G., Lin, X., Miao, W., & Fu, Z. (2014). Exposure of mice to atrazina and its metabolite diaminochlorotriazine elicits oxidative stress and endocrine disruption. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology., 37, 782–790.
Kurien, B. T., & Scofield, R. H. (2006). Western blotting. Methods. San Diego. 38, 283-293.
Loomis, D., Guyton, K., Grosse, Y., El Ghissasi, F., Bouvard, V., Benbrahim-Tallaa, L., Guha, N., Mattock, H., & Straif, K. (2015). International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group, IARC, Lyon France. Lancet Oncology, 16, 891–892.
Mahmood, T., & Yang, P.-C. (2012). Western blot: Technique, theory, and trouble shooting. North American Journal of Medical Science, 4, 429–434.
Manning, B. D., Tee, A. R., Logsdon, M. N., Bleins, J., & Cantley, L. C. (2002). Identification of the tuberous sclerosis complex-2 tumor suppressor gene product tuberin as a target of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Molecular Cell, 10, 151–162.
Marques, M. B. L., Brunetti, I. A., Faleiros, C. A., Cruz, C., Iqbal, H. M. N., Bilal, M., & Américo-Pinheiro, J. H. P. (2021). Ecotoxicological assessment and environmental risk of the insecticide chlorpyrifos for aquatic neotropical indicators. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 232, 428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05369-9
Mattos, G.E. (2011). Vias de sinalização e efeito biológico da corticotropina (ACTH), do peptídeo NH2-terminal da próopiomelanocortina (N-POMC) e do fator de crescimento de fibroblastos (FGF2) em culturas primárias de células da suprarenal de ratos. Tese de doutorado, USP-SP.
Mcdonald, D. G. (1983). The effects of H+ upon the gill of fresh water fish. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 61, 691–703.
Melletti, P.C., Rocha, O., & Martinez, C. B. R. (2004) Avaliação da degradação ambiental na Bacia do Rio Mogi-Guaçu por meio de testes de toxicidade com sedimento e análises histopatológicas em peixes. In: Brigante J, Espíndola ELG. Limnologia fluvial: um estudo no rio Mogi-Guaçu. 1 ed. Editora Rima, p. 249–280.
Miron, D., Crestani, M., Schetinger, M. R., Morsch, V. M., Baldisserotto, B., & Tierno., M. A., Moraes, G., Vieira, V. L. P. (2005). Effects of the herbicides clomazone, quinclorac, and metsulfuron methyl on acetylcholinesterase activity in the silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) (Hepatapteridae). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 61, 398–403.
Modesto, K. A., & Martinez, C. B. R. (2010). Roundp® causes oxidative stress in liver and inhibits acetylcholinesterase in muscle and brain of the fish Prochilodus lineatus. Chemosphere, 78(3), 294–299.
Montiel-León, J. M., Munoz, G., Duy, S. V., Do, D. T., Vaudreuil, M. A., Goeury, K., Guillemette, F., Amyot, M., & Sauvé, S. (2019). Widespread occurrence and spatial distribution of glyphosate, atrazine, and neonicotinoids pesticides in the St Lawrence and Tributary Rivers. Environmental Pollution, 250, 29–39.
Murphy, L. O., & Blenis, J. (2006). MAPK signal specificity: The right place at the right time. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 31, 268–275.
Murty, A.S. (1988). Toxicology of pesticide to fish. Boca Raton, Editora: CRC Press.1, 129.
Navé, B. T., Ouwens, D. M., Withers, D. J., Alessi, D. R., & Shepherd, P. R. (1999). Mammalian target of rapamycin is a direct target for protein kinase B: Identification of a convergence point for opposing effects of insulin and amino-acid deficiency on protein translation. The Biochemical Journal, 344(2), 427–431.
Oliveira, S. E., Costa, P. M., Nascimento, S. B., Castro, W. V., Ribeiro, R. I. M. A., Santos, H. B., & Thomé, R. G. (2018). Atrazine promotes immunomodulation by melanomacrophage centre alterations in spleen and vascular disorders in gills from Oreochromis niloticus. Aquatic Toxicology, 202, 57–64.
Paiva, P. P., Delcorso, M. C., Matheus, V. A., Queiroz, S. C. do N., Collares-Buzato, C. B., & Arana, S. (2017). Acute toxicity of comercial atrazine in Piaractus mesopotamicus: histophatologival, ultrastructural, molecular and genotoxic evaluation. Veterinary World, 10(9), 1008–1019.
Payne, J. F., Mathieu, A., Melvin, W., & Fancey, L. L. (1996). Acetylcholinesterase, an old biomarker with a new future? Field trials in association with two urban rivers and a paper mill in Newfoundlan. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 32, 225–231.
Phyu, Y. L., Palmer, C. G., Warne, M. J., Hose, G. C., Chapman, J. C., & Lim, R. P. (2011). A comparison of mixture toxicity assessment: Examining the chronic toxicity of atrazine, permethrin and chlorothalonil in mixtures to Ceriodaphnia cf. dubia. Chemosphere, 85, 1568–1573.
Roux, P.P., & Blenis, J. (2004). ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: A family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews, June, 320–344.
Santos, E. A., Cruz, C., Carraschi, S. P., Silva, J. R. M., Botelho, R. G., Velini, E. D., & Pitelli, R. A. (2015). Atrazina levels in the Jaboticabal water stream (São Paulo State, Brazil) and its toxicological effects on the pacu fish Piaractus mesopotamicus. Archives of Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology, 66, 73–82.
Santos, T. G. (2010). Biomarcadores bioquímicos e genéticos para a detecção dos efeitos do herbicida atrazina no peixe neotropical Prochilodus lineatus. Universidade Estadual de Londrina.
Shiogiri, N. S., et al. (2016). Effects of azithromycin on tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): health status evaluation using biochemical, physiological and morphological biomarkers. Aquaculture Research, p. 1–15.
Talmi-Frank, D., Strauss-Ayali, D., Jaffe, C. L., & Baneth, G. (2006). Kinetics and diagnostic and prognostic potential of quantitative Western Blot analysis and antigenspecific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in experimental canine leishmaniasis. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology. Oxford., 3, 271–276.
Van Dyk, J. C., Cochrane, M. J., & Wagenaar, G. M. (2012). Liver histopathology of the sharptooth catfish Clarias gariepinus as a biomarker of aquatic pollution. Chemosphere, 87(4), 301–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.Chemosphere.2011.12.002
Velmurugan, B., Selvanayagam, M., Cengiz, E. I., & Unlu, E. (2007). Histopathology of lambda-cyhalothrin on tissues (gill, kidney, liver and intestine) of Cirrhinus mrigala. Envrionmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 24, 286–291.
Zajc, A., Neuefeind, T., Prade, L., Reinemer, P., Huber, R., & Bieseler, B. (1998). Herbicide detoxification by glutathione S-transferases as implicated from X-ray structures. Pesticide Sciences., 55, 248–252.
Zhao, F., Li, K., Zhao, L., Liu, J., Suo, Q., Zhao, J., Wang, H., & Zhao, S. (2014). Effect of Nrf2 on rat ovarian tissues against atrazina-induced anti-oxidative response. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology., 7, 2780–2789.
Zhao, X., Wang, L., Ma, F., Bai, S., Yang, J., & Qi, S. (2017). Pseudomonas sp, ZXY-1 a nwly isolated and highly afficient atrazina-degrading bacterium and optimization of biodegradation using response surface methodology. Journal Environmental Science., 54, 152–159.
Zhou, B. P., Liao, Y., Xia, W., Spohn, B., Lee, M. H., & Hung, M. C. (2001). Cytoplasmic localization of p21Cip1/WAF1 by Akt-induced phosphorylation in HER-2/neu-overexpressing cells. Nature Cell Biology., 3, 245–252.
Zimmermann, S., & Moelling, K. (1999). Phosphorylation and regulation of Raf by Akt (protein kinase B). Science, 286, 1741–1744.
Funding
Isabella Alves Brunetti received grants from the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) (Proc. 2015/03420–6). This work is funded by the Laboratory of Ecotoxicology and Pesticide Efficacy of the Barretos—Brazil. Juliana Heloisa Pinê Américo-Pinheiro thanks Brazil University for the Institutional Research Development and Support Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Isabella Alves Brunetti: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, visualization, funding acquisition. Pâmela Castro Pereira: methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft. Danilo Sagrillos Oliveira: methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft. Viviane Aline Oliveira Silva: methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, writing—original draft. Rui Manuel Reis: methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, writing—original draft. Juliana Heloisa Pinê Américo-Pinheiro: formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration. Claudinei da Cruz: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brunetti, I.A., Pereira, P.C., Oliveira, D.S. et al. Histological Biomarkers and Protein Expression in Hyphessobrycon eques Fish Exposed to Atrazine. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 97 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05569-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05569-x