Abstract
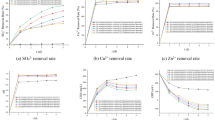
In response to the emergency treatment of trace Pb(II) pollution, taking cost and coordination with existing conventional processes into account, based on the lignite upgrading by-products (waste) as raw materials, a low cost adsorbent lignite-based activated carbon/polyacrylic acid (LAC/PAA) was developed by the in situ grafting of PAA on the surface of LAC. The declination of the pH from 8.71 for LAC to 4.83 for LAC/PAA and FT-IR analyses of LAC/PAA before and after Pb(II) adsorption confirmed the appearance of carboxyl groups on the surface of LAC/PAA. The adsorption experiments reveal that more than 90% of Pb(II) were removed by LAC/PAA within 20 min (only 31% for LAC). Its adsorption behavior obeys the Freundlich isotherm model (R2 = 0.973), and the adsorption kinetics agrees with the pseudo-second-order kinetic model (R2 = 0.961). The performances for the removal of Pb(II) in XJ River (South of China) were investigated for LAC/PAA and the conventional water treatment processes, respectively. Based on the results, a combination process (LAC/PAA adsorption + conventional water treatment) was developed, which achieved the best Pb(II) removal (99.8%) under a lower LAC/PAA and coagulant dosages (both 20 mg/L) at a pH of 10, 3 times better than that of the conventional water treatment processes (only 30%). Undoubtedly, the above results will provide significant technical support for the emergency treatment of trace Pb(II) pollution of drinking water. Moreover, converting the lignite upgrading by-products (waste) into LAC will add considerable economic value and reduce the costs of waste disposal.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM D2866-11. (2011). Standard test method for total ash content of activated carbon. West Conshohocken: ASTM International.
ASTM D3860-98. (2014). Standard practice for determination of adsorptive capacity of activated carbon by aqueous phase isotherm technique. West Conshohocken: ASTM International.
ASTM D3838-05. (2017). Standard test method for pH of activated carbon. West Conshohocken: ASTM International.
Adekunle, I. M., Adetunji, M. T., Gbadebo, A. M., & Banjoko, O. B. (2007). Assessment of groundwater quality in a typical rural settlement in Southwest Nigeria. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 4, 307–318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph200704040007.
Azimi, E., Karimipour, S., Rahman, M., Szymanski, J., & Gupta, R. (2013). Evaluation of the performance of air dense medium fluidized bed (ADMFB) for low-ash coal beneficiation. Part 2: characteristics of the beneficiated coal. Energy & Fuels, 27, 5595–5606. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef400456n.
Cao, X., Ma, L., Gao, B., & Harris, W. (2009). Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine. Environmental Science Technology, 43, 3285–3291. https://doi.org/10.1021/es803092k.
Charerntanyarak, L. (1999). Heavy metals removal by chemical coagulation and precipitation. Water Science Technology, 39(10-11), 135–138. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.1999.0642.
Dong, L., Liu, W., Jiang, R., & Wang, Z. (2014). Physicochemical and porosity characteristics of thermally regenerated activated carbon polluted with biological activated carbon process. Bioresource Technology, 171(1), 260–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.08.067.
Dong, L. H., Liu, W. J., Wang, Z. S., & Jiang, R. F. (2016). Study on the adsorption mechanism of activated carbon removing low concentrations of heavy metals. Desalination Water Treatment, 57, 7812–7822. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1100140.
Dong, L. H., Hou, L.’a., Wang, Z. S., Gu, P., Chen, G. Y., & Jiang, R. F. (2018). A new function of spent activated carbon in BAC process: removing heavy metals by ion exchange mechanism. Journal Hazardous Materials, 57, 7812–7822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.07.030.
de Freitas, F., Battirola, L. D., & de Andrade, R. L. T. (2018). Adsorption of Cu2+ and Pb2+ ions by Pontederia rotundifolia (L.f.) (Pontederiaceae) and Salvinia biloba Raddi (Salviniaceae) Biomass. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 229, 349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-4005-9.
El-Bayaa, A. A., Badawy, N. A., & AlKhalik, E. A. (2009). Effect of ionic strength on the adsorption of copper and chromium ions by vermiculite pure clay mineral. Journal Hazardous Materials, 170(2–3), 1204–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.100.
Fu, W., Wang, X. Y., & Huang, Z. Q. (2019). Remarkable reusability of magnetic Fe3O4-encapsulated C3N3S3 polymer/reduced graphene oxide composite: a highly effective adsorbent for Pb and Hg ions. Science of the Total Environment, 659, 895–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.303.
Gao, T. T., Yu, J. Q., Zhou, Y., & Jiang, X. Y. (2017). Performance of xanthate-modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes on adsorption of lead ions. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 228, 172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3359-8.
Ge, H., & Wang, J. (2017). Ear-like poly (acrylic acid)-activated carbon nanocomposite: a highly efficient adsorbent for removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere, 169, 443–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.069.
Goovaerts, P. (2017). The drinking water contamination crisis in flint: modeling temporal trends of lead level since returning to Detroit water system. Science of the Total Environment, 581, 66–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/jscitotenv.2016.09.207.
Grigoropoulou, G., Stathi, P., Karakassides, M. A., Louloudi, M., & Deligiannakis, Y. (2008). Functionalized Sio2, with N-, S-containing ligands for Pb(II) and Cd(II) adsorption. Colloids Surfaces A- Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 320(1), 25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.01.007.
Kraus, U., & Wiegand, J. (2006). Long-term effects of the aznalcóllar mine spill-heavy metal content and mobility in soils and sediments of the guadiamar river valley (SW Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 367(2–3), 855–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.12.027.
Kikuchi, Y., Qian, Q. R., Machida, & Tatsumoto, M. H. (2006). Effect of ZnO loading to activated carbon on Pb(II) adsorption from aqueous solution. Carbon, 44, 195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2005.07.040.
Lan, Y., Liang, R., Zhao, X., Ma, Q., Xu, Z., Gou, T., Wang, L., & Zhuo, Q. (2017). Impacts of environmental pollution incident of cadmium and thallium and their emergency disposal on ecological risk of Hejiang River. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 37, 3602–3612. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2017.0175.
Lange, & Adolph, N. (1999). Lange’s handbook of chemistry. Mcgraw-Hill Book Company.
Le, V. T., Doan, V. D., Nguyen, D. D., Nguyen, H. T., Ngo, Q. P., Tran, T. K. N., & Le, H. S. (2018). A novel cross-linked magnetic hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite: preparation, characterization, and application for Ni(II) ion removal from aqueous solution. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 229, 101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3762-9.
Lee, C. G., Hong, S. H., Hong, S. G., Choi, J. W., & Park, S. J. (2019). Production of biochar from food waste and its application for phenol removal from aqueous solution. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 230, 70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4125-x.
Li, C., Liu, M., Hu, Y., Gong, J., Sun, F., & Xu, Y. (2014). Characterization and first flush analysis in road and roof runoff in Shenyang, China. Water Science Technology, 70(3), 397–406. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2014.203.
Li, G. G., Fu, Q., & Lv, Y. B. (2010). Emergency monitoring cases of sudden environmental pollution. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press.
Li, Z., Chang, X., Hu, Z., Huang, X., Zou, X., Wu, Q., & Nie, R. (2009). Zincon-modified activated carbon for solid-phase extraction and preconcentration of trace lead and chromium from environmental samples. Journal Hazardous Materials, 166, 133–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.006.
Liu, W. R., Guo, Q. W., Yang, R. B., Xu, Z. C., & Zeng, D. (2013). Experimental studies on stability of flocs from cadmium pollution emergency treatment. Environmental Science, 34, 1797–1801. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9030635.
Mancinelli, E., Baltrėnaitė, E., Baltrėnas, P., Paliulis, D., & Passerini, G. (2016). Trace metals in biochars from biodegradable by-products of industrial processes. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 227, 198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2892-1.
Mohan, D., Pittman, C. U., Bricka, M., Smith, F., Yancey, B., Mohammad, J., Steele, P. H., Alexandre-Franco, M. F., Gómez-Serrano, V., & Gong, H. (2007). Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production. Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 310(1), 57–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.01.020.
Motta, F. V., Marques, A. P. A., Escote, M. T., Melo, D. M. A., Ferreira, A. G., Longo, E., Leitea, E. R., & Varela, J. A. (2008). Preparation and characterizations of Ba0.8Ca0.2Tio3, by complex polymerization method (CPM). Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 465, 452–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.10.107.
Moharram, M. A., & Allam, M. A. (2007). Application of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy to study the interactions of poly (acrylic acid) and mixtures of poly (acrylic acid) and polyacrylamide with bone powders and hydroxyapatites. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 105(6), 3228–3234. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.26581.
Nyairo, W. N., Eker, Y. R., Kowenje, C., Zor, E., Bingol, H., Tor, A., & Ongeri, D. M. (2017). Efficient removal of Lead(II) ions from aqueous solutions using methyl-β-cyclodextrin modified graphene oxide. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 228, 406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3589-9.
Özacar, M., Şengil, İ. A., & Türkmenler, H. (2008). Equilibrium and kinetic data, and adsorption mechanism for adsorption of lead onto valonia tannin resin. Chemical Engineer Journal, 143, 32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.12.005.
Qu, J., Meng, X., Ye, X., & You, H. (2016). Characteristic variation and original analysis of emergent water source pollution accidents in China between 1985 and 2013. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 19675–19685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7164-5.
Rwiza, M. J., Oh, S. Y., Kim, K. W., & Sang, D. K. (2018). Comparative sorption isotherms and removal studies for Pb(II) by physical and thermochemical modification of low-cost agro-wastes from Tanzania. Chemosphere, 195, 135–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.043.
Samsuri, A. W., Sadegh-Zadeh, F., & Seh-Bardan, B. J. (2014). Characterization of biochars produced from oil palm and rice husks and their adsorption capacities for heavy metals. International Journal of Environmental Science Technology, 11(4), 967–976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0291-3.
Sheng, C., Duan, C. L., Zhao, Y. M., Zhang, P. P., & Dong, L. (2018). Separation and upgrading of fine lignite in a pulsed fluidized bed. 2. Experimental study on lignite separation characteristics and improvement of separation efficiency. Energy & Fuels, 32, 936–995. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b02941.
Sone, H., Fugetsu, B., & Tanaka, S. (2009). Selective elimination of Pb(II) ions by alginate/polyurethane composite foams. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 162(1), 423–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.093.
Van, H. T., Bui, T. T. P., & Nguyen, L. H. (2018). Residual organic compound removal from aqueous solution using commercial coconut shell activated carbon modified by a mixture of seven metal salts. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 229, 292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3953-4.
Wang, C., Zhao, J. L., & Wang, S. X. (2019). Selective capture models and mechanisms of Pb(II) from wastewater using tannic-functionalized nickel-iron oxide nanoparticles. Colloids Surfaces A- Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 570, 265–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.03.042.
Xiao, R., Bai, J., Huang, L., Zhang, H., Cui, B., & Liu, X. (2013). Distribution and pollution, toxicity and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from urban and rural rivers of the pearl river delta in southern China. Ecotoxicology, 22, 1564–1575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1142-1.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2017). Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edition, incorporating the 1st addendum.
Xu, Z. H., Tian, D. Q., & Sun, Z. H. (2019). Highly porous activated carbon synthesized by pyrolysis of polyester fabric wastes with different iron salts: pore development and adsorption behavior. Colloids Surfaces A- Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 320, 565,180–565,187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.01.007.
Yin, S., Feng, C., Li, Y., Yin, L., & Shen, Z. (2015). Heavy metal pollution in the surface water of the Yangtze estuary: a 5-year follow-up study. Chemosphere, 138, 718–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.060.
Zaini, M. A., Amano, Y., & Machida, M. (2010). Adsorption of heavy metals onto activated carbons derived from polyacrylonitrilefiber. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 180(1–3), 552–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.04.069.
Zhang, X. J., Chen, C., Lin, P. F., Hou, A. X., Niu, Z. B., & Wang, J. (2011). Emergency drinking water treatment during source water pollution accidents in China: origin analysis, framework and technologies. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 161–167. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101987e.
Zhang, X. J., Zhang, Y., Chen, C., Wang, H., & Zhang, S. X. (2009). Guidelines of emergency drinking water treatment technologies for urban water supply industry. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press.
Zhao, P., Zhao, Y., Luo, Z., Chen, Z., Duan, C., Song, S., & Dong, L. (2014). Feasibility studies of the sequential dewatering/dry separation of Chinese lignite in a vibration fluidized-bed dryer: effect of physical parameters and operation conditions. Energy & Fuels, 28, 4383–4391. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef5005418.
Zhao, X. M., Yao, L. A., Ma, Q. L., Zhou, G. J., Wang, L., Fang, Q. L., & Xu, Z. C. (2018). Distribution and ecological risk assessment of cadmium in water and sediment in Longjiang River, China: implication on water quality management after pollution accident. Chemosphere, 194, 107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.127.
Funding
This work was supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Management in China (2015ZX07406006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 40 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, L., Pan, S., Wang, Z. et al. Lignite-Activated Carbon Grafted PAA Combined with Conventional Drinking Water Treatment Processes for the Emergency Removal of Trace Pb(II) Pollution. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 230 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04607-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04607-w