Abstract
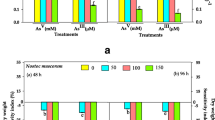
Long-term (20 days: 5 days interval) responses of Sarcodia suiae to high-tested As(V) concentration (125 and 250 μg L−1) under optimized condition significantly inhibited growth rate (GR) and caused noticeable depigmentation in algal morphology. Interestingly, S. suiae appears to have positive growth-promoting effects to 62.5 μg L−1 concentration exposure suggesting that S. suiae may have developed a coping strategy (i.e., adaptation, detoxification, and possibility on the analogous nature of arsenate and phosphate) resulting to tolerance noted by the obtained higher GR. Moreover, uptake of As(V), as confirmed by reduced concentrations, caused intracellular arsenic speciation in S. suiae, resulting in As(III) becoming the relatively dominant arsenic species and producing small amounts of methylated species (DMA > MMA) and arsenoribosides ((AsB); (AsC)), and results implied that long-term data lead to higher As accumulation with elevated concentration of major As species. The high levels of As(III) accumulated by S. suiae indicate a high tolerance of the alga to the more toxic iAs (As(III)) suggesting S. suiae may warrant its use as an As(III) phytoremediator. Similarly, the As(V) biotransformation of S. suiae in the present study was intracellular arsenate bioreduction and subsequent intracellular biomethylation in either short-term or long-term duration which can be regarded as a survival strategy over toxicity. The long-term data provide an improved understanding of the shortcomings of short-term studies and better interpretation of macroalgal cumulative behavior and As patterns.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- As:
-
Arsenic
- As(V):
-
Arsenate
- As(III):
-
Arsenite
- DMA:
-
Dimethylarsenic
- MMA:
-
Monomethylarsonic
- AsB:
-
Arsenobetaine
- AsC:
-
Arsenocholine
- iAs:
-
Inorganic arsenic
- TAs:
-
Total arsenic
References
Abdullah Al Mamun, M., Omori, Y., Miki, O., Rahman, I. M. M., Mashio, A. S., Maki, T., & Hasegawa, H. (2019a). Comparative biotransformation and detoxification potential of arsenic by three macroalgae species in seawater: evidence from laboratory culture studies. Chemosphere, 228, 117–127.
Abdullah Al Mamun, M., Rahman, I. M. M., Datta, R. R., Kosugi, C., Mashio, A. S., Maki, T., & Hasegawa, H. (2019b). Arsenic speciation and biotransformation by the marine macroalga Undaria pinnatifida in seawater: a culture medium study. Chemosphere, 222, 705–713.
Abtahi, M., Mesdaghinia, A., Saeedi, R., & Nazmara, S. (2013). Biosorption of As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solutions by brown macroalga Colpomenia sinuosa biomass: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Desalination and Water Treatment, 51, 3224–3232.
Ackley, K. L., B’Hymer, C., Sutton, K. L., & Caruso, J. A. (1999). Speciation of arsenic in fish tissue using microwave–assisted extraction followed by HPLC–ICP–MS. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 14, 845–850.
Aina, R., Labra, M., Fumagalli, P., Vannini, C., Marsoni, M., Cucchi, U., Bracale, M., Sgorbatia, S., & Citterio, S. (2007). Thiol–peptide level and proteomic changes in response to cadmium toxicity in Oryza sativa L. roots. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 59, 381–392.
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2012). Assessment of heavy metal accumulation in urban soil around potash industrial site in the east of the Dead Sea and their environmental risks. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 21, 276–290.
Anjum, S. A., Tanveer, M., Hussain, S., Ashraf, U., Khan, I., & Wang, L. (2017). Alteration in growth, leaf gas exchange, and photosynthetic pigments of maize plants under combined cadmium and arsenic stress. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 228, 13.
Anjum, S. A., Tanveer, M., Hussain, S., Bao, M., Wang, L. C., Khan, I., Ullah, E., Tung, S. A., Samad, R. A., & Shahzad, B. (2015). Cadmium toxicity in maize (Zea mays L.): consequences on antioxidative systems, reactive oxygen species and cadmium accumulation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 17022–17030.
Bhattacharya, P., Chakraborty, N., & Pal, R. (2015). Bioremediation of toxic metals using algae. In D. Das (Ed.), Algal biorefinery: an integrated approach (pp. 439–462). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Brisbin, J. A., B’Hymer, C., & Caruso, J. A. (2002). A gradient anion exchange chromatographic method for the speciation of arsenic in lobster tissue extracts. Talanta, 58, 133–145.
Carbonell-Barrachina, A. A., Aarabi, M. A., Delaune, R. D., Gambrell, R. P., & Patrick, W. H. (1998). Arsenic in wetland vegetation: availability, phytotoxicity, uptake and effects on plant growth and nutrition. Science of the Total Environment, 217, 189–199.
Challenger, F. (1945). Biological methylation. Chemical Reviews, 36, 315–361.
Chatterjee, D., Halder, D., Majumder, S., Biswas, A., Nath, B., Bhattacharya, P., Bhowmick, S., Mukherjee-Goswami, A., Saha, D., Hazra, R., Maity, P. B., Chatterjee, D., Mukherjee, A., & Bundschuh, J. (2010). Assessment of arsenic exposure from groundwater and rice in Bengal Delta region, West Bengal India. Water Research, 44, 5803–5812.
Chen, X., O’Halloran, J., & Jansen, M. A. K. (2018). Time matters: the toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to Lemna minor L. increases with exposure time. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 229, 99.
Choi, H., Park, S. K., Kim, D. S., & Kim, M. (2011). Determination of 6 arsenic species present in seaweed by solvent extraction, clean–up, and LC–ICP/MS. Food Science and Biotechnology, 20, 39–44.
Clemens, S., & Ma, J. F. (2016). Toxic heavy metal and metalloid accumulation in crop plants and foods. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 67, 89–512.
Cullen, W. R., Harrison, L. G., Li, H., & Hewitt, G. (1994a). Bioaccumulation and excretion of arsenic compounds by a marine unicellular alga, Polyphysa peniculus. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 8, 313–324.
Cullen, W. R., Li, H., Pergantis, S. A., Eigendorf, G. K., & Harrison, L. G. (1994b). The methylation of arsenate by a marine alga Polyphysa peniculus in the presence of L–methionine–methyl–d3. Chemosphere, 28, 1009–1019.
DeNardis, N. I., Ilić, J. P., Ružić, I., Novosel, N., Radić, T. M., Weber, A., Kasum, D., Pavlinska, Z., Balogh, R. K., Hajdu, B., Chorvátová, M. A., Gyurcsik, B. (2019). Algal cell response to laboratory–induced cadmium stress: a multimethod approach. European Biophysics Journal, 1–18.
Duncan, E. G., Maher, W. A., & Foster, S. D. (2015). The contribution of arsenic species in unicellular algae to the cycling of arsenic in marine ecosystems. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(1), 33–50.
García-Salgado, S., Raber, G., Raml, R., Magnes, C., & Francesconi, K. A. (2012). Arsenosugar phospholipids and arsenic hydrocarbons in two species of brown macroalgae. Environmental Chemistry, 9(1), 63–66.
Geiszinger, A., Goessler, W., Pedersen, S. N., & Francesconi, K. A. (2001). Arsenic biotransformation by the brown macroalga Fucus serratus. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20, 2255–2262.
Goyer, R. A. (2001). Toxic effects of metals. In: Klaassen, CD., editor. Cassarett and Doull’s toxicology: the basic science of poisons (pp. 811–867). New York: McGraw–Hill Publisher.
Granchinho, S. C. R., Polishchuk, E., Cullen, W. R., & Reimer, K. J. (2001). Biomethylation and bioaccumulation of arsenic(V) by marine alga Fucus gardneri. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 15, 553–560.
Gu, J. G., Zhou, Q. X., & Wang, X. (2003). Reused path of heavy metal pollution in soils and its research advance. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 11(2), 143–151.
Guillard, R. R. L. (1975). Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of marine invertebrate animals (pp. 29–60). New York: Plenum Publishing Corporation.
Gupta, D. K., Huang, H. G., Nicoloso, F. T., Schetinger, M. R., Farias, J. G., Li, T. Q., Razafindrabe, B. H. N., Aryal, N., & Inouhe, M. (2013). Effect of Hg, As and Pb on biomass production, photosynthetic rate, nutrients uptake and phytochelatin induction in Pfaffia glomerata. Ecotoxicology, 9, 1403–1412.
Hellweger, F. L., & Lall, U. (2004). Modeling the effect of algal dynamics on arsenic speciation in Lake Biwa. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 6716–6723.
Hopenhayn, C. (2006). Arsenic in drinking water: impact on human health. Elements, 2, 103–107.
Hughes, M. F. (2002). Arsenic toxicity and potential mechanisms of action. Toxicology Letters, 133, 1–16.
Karadjova, I. B., Slaveykova, V. I., & Tsalev, D. (2008). The biouptake and toxicity of arsenic species on the green microalga Chlorella salina in seawater. Aquatic Toxicology, 87, 264–271.
Karimi, N., Siyahat Shayesteh, L., Ghasmpour, H., & Alavi, M. (2013). Effects of arsenic on growth, photosynthetic activity, and accumulation in two new hyperaccumulating populations of Isatis cappadocica Desv. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 32, 823–830.
Lee, M. C., Libatique, M. J. H., & Yeh, S. Y. (2019). The effect of environmental factors on total arsenic accumulation in Sarcodia suiae, Rhodophyta. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 102(3), 385–390.
Libatique, M. J. H., Lee, M. C., Yeh, H. Y. (2019). Effect of light intensity on the mechanism of inorganic arsenic accumulation and patterns in the red macroalga, Sarcodia suiae. Biological Trace Element Research, 1–10.
Liu, W. J., Zhu, Y. G., Smith, F. A., & Smith, S. E. (2004). Do iron plaque and genotypes affect arsenate uptake and translocation by rice? Journal of Experimental Botany, 55, 1707–1713.
Liu, J., Mooney, H., Hull, V., Davis, S. J., Gakell, J., Hertel, T., Lubchenco, J., Seto, K. C., Gleick, P., Kremen, C., & Li, S. (2015). Systems integration for global sustainability. Science, 347(6225), 963.
Ma, Z., Lin, L., Wu, M., Yu, H., Shang, T., Zhang, T., & Zhao, M. (2018). Total and inorganic arsenic contents in seaweeds: absorption, accumulation, transformation and toxicity. Aquaculture, 497, 49–55.
Marques, D. M., Júnior, V. V., da Silva, A. B., Mantovani, J. R., Magalhães, P. C., de Souza, T. C. (2018). Copper toxicity on photosynthetic responses and root morphology of Hymenaea courbaril L. (Caesalpinioideae). Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 229, 138.
McLusky, D. S., & Elliott, M. (2004). The estuarine ecosystem: ecology, threats and management. Oxford University Press on Demand.
Millward, G. E., Kitts, H. J., Comber, S. D. W., Ebdon, L., & Howard, A. G. (1996). Methylated arsenic in the Southern North Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 43, 1–18.
Millward, G. E., Ebdon, L., & Walton, A. P. (1993). Seasonality in estuarine sources of methylated arsenic. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 7, 499–511.
Mitra, A., Chatterjee, S., & Gupta, D. K. (2017). Uptake, transport, and remediation of arsenic by algae and higher plants. In D. K. Gupta & S. Chatterjee (Eds.), Arsenic contamination in the environment: the issues and solutions (pp. 145–169). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Neff, J. M. (1997). Ecotoxicology of arsenic in the marine environment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 16(5), 917–927.
Nordberg, G. F., Jin, T., Hong, F., Zhang, A., Buchet, J. P., & Bernard, A. (2005). Biomarkers of cadmium and arsenic interactions. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 206, 191–197.
Rahman, M. A., Hasegawa, H., Ueda, K., Maki, T., & Rahman, M. M. (2008). Influence of phosphate and iron ions in selective uptake of arsenic species by water fern (Salvinia natans L.). Chemical Engineering Journal, 145, 179–184.
Sanders, J. G., & Windom, H. L. (1980). The uptake and reduction of arsenic species by marine algae. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science, 10, 555–567.
Schindler, D. E., & Hilborn, R. (2015). Prediction, precaution, and policy under global change. Science, 347, 953–954.
Singh, R., Singh, S., Parihar, P., Singh, V. P., & Prasad, S. M. (2015). Arsenic contamination, consequences and remediation techniques: a review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 112, 247–270.
Takahashi, A., Kawakami, H., Bada, A., Okonogi, Y., & Matsuto, S. (2004). Effects of phosphate on arsenate inhibition in a marine cyanobacterium, Phormidium sp. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 4, 269–279.
Thiel, T. (1988). Phosphate transport and arsenate resistance in the cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis. Journal of Bacteriology, 170, 1143–1147.
Vetrimurugan, E., Shruti, V. C., Jonathan, M. P., Roy, P. D., Kunene, N. W., & Villegas, L. E. C. (2017). Metal concentration in the tourist beaches of South Durban: an industrial hub of South Africa. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 117(1), 538–546.
Wang, Z., & Rossman, T. G. (1996). The toxicology of metals. Cheng, L.W., Editor. Vol. 1. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 221–243.
Wang, Z., Luo, Z., & Yan, C. (2013). Accumulation, transformation, and release of inorganic arsenic by the freshwater cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 7286–7295.
Xu, X., Li, X., Chen, M., Li, X., Duan, X., Zhu, G., Feng, Z., & Ma, Z. (2016). Land–ocean–human interactions in intensively developing coastal zone: demonstration of case studies. Ocean & Coastal Management, 133, 28–36.
Xue, P. Y., Yan, C. Z., Sun, G. X., & Luo, Z. X. (2012). Arsenic accumulation and speciation in the submerged macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 19, 3969–3976.
Yamaoka, Y., Takamura, O., Fuse, H., & Murakami, K. (1999). Effect of glutathione on arsenic accumulation by Dunaliella salina. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 13, 89–94.
Ybarra, G. R., & Webb, R. (1998). Differential responses of groel and metallothionein genes to divalent metal cations and the oxyanions of arsenic in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC7942. Proceedings of the 1998 Conference on Hazardous Waste Research, 76–86.
Zhang, S. Y., Sun, G. X., Yin, X. X., Rensing, C., & Zhu, Y. G. (2013). Biomethylation and volatilization of arsenic by the marine microalgae Ostreococcus tauri. Chemosphere, 93(1), 47–53.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the full support system given by the research team of Algal Cultivation and Biotechnology Laboratory (613) of the Aquaculture Department, National Taiwan Ocean University (NTOU). Likewise, we are thankful to the Traceability Certification and Inspection Center of the Department of Aquaculture, NTOU headed by Dr. Nan, Fan-Hua (Director), for accommodating our samples and providing the laboratory facilities. Their assistance made this study possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MJHL performed the experiments and wrote the draft of the manuscript. FJJ and HYY designed the experimental design and helped in the experiment. MCL provided the experiment resources, supervised the work, and reviewed the manuscript. All authors contributed to the interpretation of data, read, edit, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 20 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Libatique, M.J.H., Lee, MC., Yeh, HY. et al. The Response of Sarcodia suiae to Long-term Exposure of Arsenic (Arsenate): Growth, Morphology, and Arsenic Alterations. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 212 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04603-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04603-0