Abstract
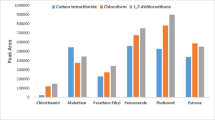
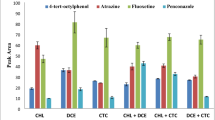
In this work the dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction technique (DLLME) is presented as an important alternative to the classical extraction methods and was used to extract and concentrate estrogens’ before its quantification by HPLC in environmental water samples. For the evaluation of the analytical methodology, the following conditions were used: sample volume 8 mL, extraction solvent 200 μL of chlorobenzene, and dispersive solvent 2000 μL of acetone. The enrichment factor (EF) was 140 for estrone, 202 for 17β-estradiol (E2), and 199 for 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2). Limit of detection was 20 ng L−1 for E1, 3.1 ng L−1 for E2, and 2.7 ng L−1 for EE2. Repeatability and intermediate reproducibility presented values of relative standard deviation lower than 10%. Finally, recovery tests were performed to evaluate the water matrices’ effects on the extraction performance, resulting in recoveries between 76 and 110% in surface water and between 84 and 109% in wastewater.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves, A., Vanermen, G., Covaci, A., & Voorspoels, S. (2016). Ultrasound assisted extraction combined with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction ( US-DLLME )—a fast new approach to measure phthalate metabolites in nails. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9727-1.
Becker, D., Rodriguez-Mozaz, S., Insa, S., Schoevaart, R., Barceló, D., De Cazes, M., et al. (2017). Removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals in wastewater by enzymatic treatment with fungal laccases. Organic Process Research and Development, 21(4), 480–491. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.6b00361.
Berenger, J. N., Moraes, J. C., Oliveira, M., Raimundo, J. M., & Molisani, M. M. (2017). Effects of diesel oil and environmental quality on the enzymatic activities of a tropical estuarine catfish and implications for contamination assessment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Contamination, 12(1), 103–111. https://doi.org/10.5132/eec.2017.01.13.
Česen, M., & Heath, E. (2017). Disk-based solid phase extraction for the determination of diclofenac and steroidal estrogens E1, E2 and EE2 listed in the WFD watch list by GC–MS. Science of the Total Environment, 590–591, 832–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.222.
da Silva, G. S., Lima, D. L. D., & Esteves, V. I. (2017). Salicylic acid determination in estuarine and riverine waters using hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction and capillary zone electrophoresis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9183-2.
de Jesus Gaffney, V., Almeida, C. M. M., Rodrigues, A., Ferreira, E., Benoliel, M. J., & Cardoso, V. V. (2015). Occurrence of pharmaceuticals in a water supply system and related human health risk assessment. Water Research, 72, 199–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.027.
Dévier, M. H., Le Menach, K., Viglino, L., Di Gioia, L., Lachassagne, P., & Budzinski, H. (2013). Ultra-trace analysis of hormones, pharmaceutical substances, alkylphenols and phthalates in two French natural mineral waters. Science of the Total Environment, 443, 621–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.10.015.
Di Donato, M., Cernera, G., Giovannelli, P., Galasso, G., Bilancio, A., Migliaccio, A., & Castoria, G. (2017). Recent advances on bisphenol-A and endocrine disruptor effects on human prostate cancer. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 457, 35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2017.02.045.
do Nascimento, M. T. L., Santos, A. D. d. O., Felix, L. C., Gomes, G., de Oliveira, e. S. M., da Cunha, D. L., et al. (2018). Determination of water quality, toxicity and estrogenic activity in a nearshore marine environment in Rio de Janeiro, southeastern Brazil. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 149(2017), 197–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.045.
Dodgen, L. K., Kelly, W. R., Panno, S. V., Taylor, S. J., Armstrong, D. L., Wiles, K. N., et al. (2017). Characterizing pharmaceutical, personal care product, and hormone contamination in a karst aquifer of southwestern Illinois, USA, using water quality and stream flow parameters. Science of the Total Environment, 578, 281–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.103.
Ekpeghere, K. I., Sim, W.-J., Lee, H.-J., & Oh, J.-E. (2018). Occurrence and distribution of carbamazepine, nicotine, estrogenic compounds, and their transformation products in wastewater from various treatment plants and the aquatic environment. Science of the Total Environment, 640–641, 1015–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2018.05.218.
Fredj, S. B., Nobbs, J., Tizaoui, C., & Monser, L. (2015). Removal of estrone (E1), 17b-estradiol (E2), and 17a-ethinylestradiol (EE2) from wastewater by liquid–liquid extraction. Chemical Engineering Journal, 262, 417–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.10.007.
Gałuszka, A., Migaszewski, Z., & Namieśnik, J. (2013). The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TrAC, Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 50, 78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2013.04.010.
Hadjmohammadi, M. R., & Ghoreishi, S. S. (2011). Determination of estrogens in water samples using dispersive liquid liquid microextraction and high performance liquid chromatography. Acta Chimica Slovenica, 58(4), 765–771.
Kleywegt, S., Pileggi, V., Yang, P., Hao, C., Zhao, X., Rocks, C., et al. (2011). Pharmaceuticals, hormones and bisphenol A in untreated source and finished drinking water in Ontario, Canada-occurrence and treatment efficiency. Science of the Total Environment, 409(8), 1481–1488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.01.010.
Koçoğlu, E. S., Sözüdoğru, O., Komesli, O. T., Yılmaz, A. E., & Bakırdere, S. (2019). Simultaneous determination of drug active compound, hormones, pesticides, and endocrine disruptor compounds in wastewater samples by GC-MS with direct calibration and matrix matching strategies after preconcentration with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(11), 653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7676-9.
Kocúrová, L., Balogh, I. S., Šandrejová, J., & Andruch, V. (2012). Recent advances in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction using organic solvents lighter than water. A review. Microchemical Journal, 102, 11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2011.12.002.
Kumar, R., Gaurav, H., Malik, A. K., Kabir, A., & Furton, K. G. (2014). Efficient analysis of selected estrogens using fabric phase sorptive extraction and high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. Journal of Chromatography A, 1359, 16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.07.013.
Kuster, M., Azevedo, D. A., López de Alda, M. J., Aquino Neto, F. R., & Barceló, D. (2009). Analysis of phytoestrogens, progestogens and estrogens in environmental waters from Rio de Janeiro (Brazil). Environment International, 35(7), 997–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2009.04.006.
Liao, K., Mei, M., Li, H., Huang, X., & Wu, C. (2016). Multiple monolithic fiber solid-phase microextraction based on a polymeric ionic liquid with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of steroid sex hormones in water and urine. Journal of Separation Science, 39(3), 566–575. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201501156.
Lima, D. L. D., Silva, C. P., Otero, M., & Esteves, V. I. (2013). Low cost methodology for estrogens monitoring in water samples using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and HPLC with fluorescence detection. Talanta, 115, 980–985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.07.007.
Lima, D. L. D., Silva, C. P., & Otero, M. (2018). Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the quantification of venlafaxine in environmental waters. Journal of Environmental Management, 217, 71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.060.
Melo, S. M., & Brito, N. M. (2014). Analysis and occurrence of endocrine disruptors in Brazilian water by HPLC-fluorescence detection. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 225(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1783-y.
Peñalver, A., Pocurull, E., Borrull, F., & Marcé, R. M. (2002). Method based on solid-phase microextraction-high-performance liquid chromatography with UV and electrochemical detection to determine estrogenic compounds in water samples. Journal of Chromatography A, 964(1–2), 153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(02)00694-5.
Pessoa, G. P., de Souza, N. C., Vidal, C. B., Alves, J. A. C., Firmino, P. I. M., Nascimento, R. F., & dos S, A. B. (2009). Simultaneous determination of ten estrogens and their metabolites in waters by improved two-step SPE followed by LC-MS. Chromatographia, 69(7–8), 621–628. https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-0957-7.
Peters, F. T., Drummer, O. H., & Musshoff, F. (2007). Validation of new methods. Forensic Science International, 165(2–3), 216–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2006.05.021.
Razmkhah, K., & Sereshti, H. (2018). Extraction and determination of three steroid molecules in milk using functionalized magnetic carbon nanotube-based solid phase extraction coupled with HPLC, 3179–3189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1298-7.
Rezaee, M., Assadi, Y., Milani Hosseini, M.-R., Aghaee, E., Ahmadi, F., & Berijani, S. (2006). Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Journal of Chromatography A, 1116(1–2), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.03.007.
Rocha, M. J., Cruzeiro, C., Reis, M., Rocha, E., & Pardal, M. (2013a). Determination of seventeen endocrine disruptor compounds and their spatial and seasonal distribution in Ria Formosa lagoon (Portugal). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(10), 8215–8226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3168-5.
Rocha, M. J., Cruzeiro, C., Reis, M., Rocha, E., & Pardal, M. A. (2013b). Determination of 17 endocrine disruptor compounds and their spatial and seasonal distribution in the Sado River estuary (Portugal). Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 95(2), 237–253. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2012.758730.
Rodenas, M. C., Cabas, I., Gómez-González, N. E., Arizcun, M., Meseguer, J., Mulero, V., & García-Ayala, A. (2017). Estrogens promote the production of natural neutralizing antibodies in fish through G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1. Frontiers in Immunology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00736.
Seebunrueng, K., Santaladchaiyakit, Y., & Srijaranai, S. (2014). Vortex–assisted low density solvent liquid– Liquid microextraction and salt–induced de-mulsification coupled to high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of five organophosphorus pesticide residues in fruits Ketsarin. Talanta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.10.020.
Sifakis, S., Androutsopoulos, V. P., Tsatsakis, A. M., & Spandidos, D. A. (2017). Human exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals: effects on the male and female reproductive systems. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 51, 56–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.02.024.
Sodré, F. F., Locatelli, M. A. F., & Jardim, W. F. (2010a). Occurrence of emerging contaminants in Brazilian drinking waters: a sewage-to-tap issue. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 206(1–4), 57–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0086-9.
Sodré, F. F., Pescara, I. C., Montagner, C. C., & Jardim, W. F. (2010b). Assessing selected estrogens and xenoestrogens in Brazilian surface waters by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Microchemical Journal, 96(1), 92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2010.02.012.
Spietelun, A., Marcinkowski, Ł., De La Guardia, M., & Namieśnik, J. (2014). Green aspects, developments and perspectives of liquid phase microextraction techniques. Talanta, 119(2017), 34–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.10.050.
Thrupp, T. J., Runnalls, T. J., Scholze, M., Kugathas, S., Kortenkamp, A., & Sumpter, J. P. (2018). The consequences of exposure to mixtures of chemicals: something from ‘nothing’ and ‘a lot from a little’ when fish are exposed to steroid hormones. Science of the Total Environment, 619–620, 1482–1492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.081.
Torres, N. H., Aguiar, M. M., Ferreira, L. F. R., Américo, J. H. P., Machado, Â. M., Cavalcanti, E. B., & Tornisielo, V. L. (2015). Detection of hormones in surface and drinking water in Brazil by LC-ESI-MS/MS and ecotoxicological assessment with Daphnia magna. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4626-z.
Tuzen, M., Uluozlu, O. D., Mendil, D., Soylak, M., Machado, L. O. R., Santos, W. N. L., & Ferreira, S. L. C. (2017). A simple, rapid and green ultrasound assisted and ionic liquid dispersive microextraction procedure for the determination of tin in foods employing ETAAS. Food Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.115.
Wang, L., Cai, Y. Q., He, B., Yuan, C. G., Shen, D. Z., Shao, J., Jiang, & Bin, G. (2006). Determination of estrogens in water by HPLC-UV using cloud point extraction. Talanta, 70(1 SPEC. ISS), 47–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2006.01.013.
Wang, S., Huang, W., Fang, G., He, J., & Zhang, Y. (2008). On-line coupling of solid-phase extraction to high-performance liquid chromatography for determination of estrogens in environment. Analytica Chimica Acta, 606(2), 194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.11.030.
Wu, C.-Q., Chen, D.-Y., Feng, Y.-S., Deng, H.-M., Liu, Y.-H., & Zhou, A.-J. (2012). Determination of estrogens in water samples by ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography. Analytical Letters, 45(14), 1995–2005. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2012.680086.
Funding
The authors Erika Sousa, Reyla Dias, Lanna Silva, and Gilmar Silva would like to acknowledge Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa (Fapema) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for the funding obtained in this work. Diana Lima was funded by national funds (OE), through FCT Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P., in the scope of the framework contract foreseen in the numbers 4, 5, and 6 of the article 23, of the Decree-Law 57/2016, of August 29, changed by Law 57/2017, of July 19. Also, thanks are due for the financial support to CESAM (UIDB/50017/2020+UIDP/50017/2020) and to FCT/MCTES through national funds and funding by FEDER through CENTRO 2020 and by national funds through within the research project PTDC/ASP-PES/29021/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sousa, É.M.L., Dias, R.A.S., Sousa, E.R. et al. Determination of Three Estrogens in Environmental Water Samples Using Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Fluorescence Detector. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 172 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04552-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04552-8