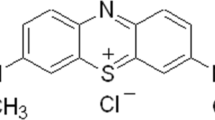
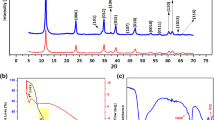
Abstract
Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) are promising adsorbents for the removal of various contaminants from water. However, a comprehensive understanding of how ternary LDHs differ from the divalent ones in terms of dye adsorption capacity and the underlying mechanisms still remain unknown. Remazol brilliant blue reactive (RBBR) adsorption on pristine and calcined (C) ZnAl, MgAl, and ZnMgAl LDHs were comprehensively investigated for the first time in this study. The characteristics of the pristine and calcined samples were established with X-ray diffractometer, Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometer, zeta potential analyzer, and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller method. A considerably larger adsorption capacity was obtained with pristine MgAl (220 mg/g) and ZnAl (191 mg/g) compared to that of ZnMgAl (164 mg/g) at all studied initial dye concentrations (10–250 mg/L) and solution pH (3–12). However, when the LDH samples were calcined, the largest RBBR mass adsorbed was achieved with ZnMgAl-C (263 mg/g) followed by MgAl-C (247 mg/g) and ZnAl-C (236 mg/g). In comparison to the pristine samples, the faster adsorption rate and higher adsorption capacity of the calcined samples were attributed to the large specific surface area and enhanced electrostatic interactions due to the higher positive charge obtained after calcination. ZnMgAl-C had the largest surface area and the charge, explaining its superior adsorption capacity over the divalent LDHs. Pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, and Elovich models described the kinetics data well while Freundlich and Redlich–Peterson isotherms suitably fit to the equilibrium data for the pristine and calcined LDHs. Surface adsorption via electrostatic interactions was found to be the effective mechanism for RBBR adsorption on all pristine and calcined LDHs while intercalation was not.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkader, N. B., Bentouami, A., Derriche, Z., Bettahar, N., & Ménorval, L. D. (2011). Synthesis and characterization of Mg – Fe layer double hydroxides and its application on adsorption of Orange G from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 169(1–3), 231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.03.019.
Abdellaoui, K., Pavlovic, I., Bouhent, M., Benhamou, A., & Barriga, C. (2017). A comparative study of the amaranth azo dye adsorption/desorption from aqueous solutions by layered double hydroxides. Applied Clay Science, 143, 142–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.03.019.
Aissat, M., Hamouda, S., Benhadria, N., Chellali, R., & Bettahar, N. (2018). Alizarin red S dye removal from contaminated water on calcined [Mg/Al, Zn/Al and MgZn/Al]-LDH. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1968(May). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5039164.
Banat, I. M., Nigam, P., Singh, D., & Marchant, R. (1996). Microbial decolorization of textile-dye-containing effluents: A review. Bioresource Technology, 58(3), 217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(96)00113-7.
Barrett, E. P., Joyner, L. G., & Halenda, P. P. (1951). The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from Nitrogen Isotherms. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 73(1), 373–380. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01145a126.
Bediako, J. K., Lin, S., Sarkar, A. K., Zhao, Y., Choi, J. W., Song, M. H., Cho, C. W., & Yun, Y. S. (2019). Evaluation of orange peel-derived activated carbons for treatment of dye-contaminated wastewater tailings. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07031-8.
Berraho, M., Legrouri, A., Bentaleb, K. A., El Khattabi, E., Lakraimi, M., Benaziz, L., Sabbar, E., Berraho, M., & Legrouri, A. (2016). Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by anionic clays. J. Mater. Environ. Sci, 7(8), 2886–2896 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306168055.
Boubakri, S., Djebbi, M. A., Bouaziz, Z., Namour, P., Jaffrezic-Renault, N., Amara, A. B. H., Trabelsi-Ayadi, M., Ghorbel-Abid, I., & Kalfat, R. (2018). Removal of two anionic reactive textile dyes by adsorption into MgAl-layered double hydroxide in aqueous solutions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(24), 23817–23832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2391-6.
Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H., & Teller, E. (1938). Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 60(2), 309–319. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01269a023.
Casenave, S., Martinez, H., Guimon, C., Auroux, A., Hulea, V., Cordoneanu, A., & Dumitriu, E. (2001). Acid-base properties of Mg-Ni-Al mixed oxides using LDH as precursors. Thermochimica Acta, 379(1–2), 85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(01)00606-2.
Chagas, L. H., De Carvalho, G. S. G., Do Carmo, W. R., San Gil, R. A. S., Chiaro, S. S. X., Leitão, A. A., Diniz, R., De Sena, L. A., & Achete, C. A. (2015). MgCoAl and NiCoAl LDHs synthesized by the hydrothermal urea hydrolysis method: Structural characterization and thermal decomposition. Materials Research Bulletin, 64, 207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2014.12.062.
Choy, J. H., Kim, Y. K., Son, Y. H., Choy, Y. B., Oh, J. M., Jung, H., & Hwang, S. J. (2008). Nanohybrids of edible dyes intercalated in ZnAl layered double hydroxides. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 69(5–6), 1547–1551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2007.11.009.
Darmograi, G., Prelot, B., Layrac, G., Tichit, D., Martin-Gassin, G., Salles, F., & Zajac, J. (2015). Study of adsorption and intercalation of orange-type dyes into Mg-Al layered double hydroxide. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 119(41), 23388–23397. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b05510.
De Sá, F. P., Cunha, B. N., & Nunes, L. M. (2013). Effect of pH on the adsorption of Sunset Yellow FCF food dye into a layered. Chemical Engineering Journal, 215–216, 122–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.024.
dos Santos, R. M. M., Gonçalves, R. G. L., Constantino, V. R. L., Santilli, C. V., Borges, P. D., Tronto, J., & Pinto, F. G. (2017). Adsorption of Acid Yellow 42 dye on calcined layered double hydroxide: Effect of time, concentration, pH and temperature. Applied Clay Science, 140, 132–139.
Dudek, B., Kuśtrowski, P., Bialas, A., Natkanśki, P., Piwowarska, Z., Chmielarz, L., Kozak, M., & Michalik, M. (2012). Influence of textural and structural properties of Mg Al and Mg Zn Al containing hydrotalcite derived oxides on Cr(VI) adsorption capacity. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 132(2–3), 929–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.12.037.
El Hassani, K., Beakou, B. H., Kalnina, D., Oukani, E., & Anouar, A. (2017). Effect of morphological properties of layered double hydroxides on adsorption of azo dye Methyl Orange: A comparative study. Applied Clay Science, 140, 124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.02.010.
Elkhattabi, E. H., Lakraimi, M., Badreddine, M., Legrouri, A., Cherkaoui, O., & Berraho, M. (2013). Removal of Remazol blue 19 from wastewater by zinc–aluminium–chloride-layered double hydroxides. Applied Water Science, 3(2), 431–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0092-3.
Extremera, R., Pavlovic, I., Pérez, M. R., & Barriga, C. (2012). Removal of acid orange 10 by calcined mg/Al layered double hydroxides from water and recovery of the adsorbed dye. Chemical Engineering Journal, 213, 392–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.10.042.
Ferreira, G. M. D., Ferreira, G. M. D., Hespanhol, M. C., de Paula Rezende, J., dos Santos Pires, A. C., Gurgel, L. V. A., & da Silva, L. H. M. (2017). Adsorption of red azo dyes on multi-walled carbon nanotubes and activated carbon: A thermodynamic study. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 529, 531–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.06.021.
Flores, J., Lima, E., Maubert, M., Aduna, E., & Rivera, J. L. (2011). Clean-up of wastes from the textile industry using anionic clays. Clays and Clay Minerals, 59(3), 240–249. https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2011.0590303.
Forgacs, E., Cserháti, T., & Oros, G. (2004). Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: A review. Environment International, 30(7), 953–971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.02.001.
Geethakarthi, A., & Phanikumar, B. R. (2011). Industrial sludge based adsorbents / industrial byproducts in the removal of reactive dyes – A review. International Journal of Water Resources and Environmental Engineering, 3(January), 1–9.
Goh, K. H., Lim, T. T., & Dong, Z. (2008). Application of layered double hydroxides for removal of oxyanions: A review. Water Research, 42(6–7), 1343–1368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.10.043.
Guo, Y., Zhu, Z., Qiu, Y., & Zhao, J. (2013). Enhanced adsorption of acid brown 14 dye on calcined Mg/Fe layered double hydroxide with memory effect. Chemical Engineering Journal, 219, 69–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.12.084.
Ifebajo, A. O., Oladipo, A. A., & Gazi, M. (2019). Efficient removal of tetracycline by CoO/CuFe2O4 derived from layered double hydroxides. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 17(1), 487–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0781-0.
Ifebajo, A. O., Oladipo, A. A., & Gazi, M. (2020). Sun-light driven enhanced azo dye decontamination from aqueous solution by CoO − CuFe2O4 derived from layered double hydroxide. Desalination and Water Treatment, 1, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25247.
Iftekhar, S., Küçük, M. E., Srivastava, V., Repo, E., & Sillanpää, M. (2018). Application of zinc-aluminium layered double hydroxides for adsorptive removal of phosphate and sulfate: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic. Chemosphere, 209, 470–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.115.
Kowalik, P., Konkol, M., Kondracka, M., Próchniak, W., Bicki, R., & Wiercioch, P. (2013). Memory effect of the CuZnAl-LDH derived catalyst precursor - In situ XRD studies. Applied Catalysis A: General, 464–465, 339–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2013.05.048.
Lei, X., Jin, M., & Williams, G. R. (2014). Layered double hydroxides in the remediation and prevention of water pollution. Energy and Environment Focus, 3, 4–22. https://doi.org/10.1166/eef.2014.1086.
Lei, C., Zhu, X., Zhu, B., Jiang, C., Le, Y., & Yu, J. (2017). Superb adsorption capacity of hierarchical calcined Ni/mg/Al layered double hydroxides for Congo red and Cr(VI) ions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 321, 801–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.070.
Li, B., Zhang, Y., Zhou, X., Liu, Z., Liu, Q., & Li, X. (2016). Different dye removal mechanisms between monodispersed and uniform hexagonal thin plate-like MgAl-CO32--LDH and its calcined product in efficient removal of Congo red from water. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 673, 265–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.02.248.
Ling, F., Fang, L., Lu, Y., Gao, J., Wu, F., Zhou, M., & Hu, B. (2016). A novel CoFe layered double hydroxides adsorbent: High adsorption amount for methyl orange dye and fast removal of Cr(VI). Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 234, 230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.07.015.
Liu, Y., Shi, J., Peng, Q., & Li, Y. (2012). Self-assembly of ZnO nanocrystals into nanoporous pyramids: High selective adsorption and photocatalytic activity. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 22(14), 6539–6541. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm16729h.
Liu, Y., Wang, G., Yang, W., Yang, J., & Li, J. (2019). Biotemplated synthesis of hierarchically porous ZnAl-CLDH/FeWO4 for effective removal of dyes from water. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 230(4). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4134-9.
Mahjoubi, F. Z., Khalidi, A., Abdennouri, M., & Barka, N. (2017). Zn–Al layered double hydroxides intercalated with carbonate, nitrate, chloride and sulphate ions: Synthesis, characterisation and dye removal properties. Journal of Taibah University for Science, 11(1), 90–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtusci.2015.10.007.
Malik, A., & Grohmann, E. (2012). Environmental protection strategies for sustainable development. In Environmental Protection Strategies for Sustainable Development. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-1591-2.
Meng, Z., Li, X., Lv, F., Zhang, Q., Chu, P. K., & Zhang, Y. (2015). Structure, molecular simulation, and release of a spirin from intercalated Zn-Al-layered double hydroxides. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 135, 339–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.07.069.
Ni, Z. M., Xia, S. J., Wang, L. G., Xing, F. F., & Pan, G. X. (2007). Treatment of methyl orange by calcined layered double hydroxides in aqueous solution: Adsorption property and kinetic studies. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 316(2), 284–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.07.045.
Oladipo, A. A., Ifebajo, A. O., & Gazi, M. (2019). Magnetic LDH-based CoO–NiFe2O4 catalyst with enhanced performance and recyclability for efficient decolorization of azo dye via Fenton-like reactions. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 243, 243–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.10.050.
Paneysar, J. S., Sawant, S., Ip, M. H., Bhullar, S. K., Barton, S., Ambre, P., & Coutinho, E. (2019). Nanofibers for textile waste water management. Water Practice and Technology, 14(2), 297–310. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2019.014.
Pourfaraj, R., Fatemi, S. J., Kazemi, S. Y., & Biparva, P. (2017). Synthesis of hexagonal mesoporous MgAl LDH nanoplatelets adsorbent for the effective adsorption of Brilliant Yellow. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 508, 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.07.101.
Praveen, S., GR, C., & Thomas, E. (2009). Mutagenicity testing of some commonly used azo dyes. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 42(4), 641–648.
Rezaee, A., Ghaneian, M. T., Khavanin, A., Hashemian, S. J., Moussavi, G. H., Ghanizadeh, G. H., & Hajizadeh, E. (2008). Photochemical oxidation of reactive blue 19 dye (RB19) in textile wastewater by UV/K2S2O8 process. Iranian Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 5(2), 95–100.
Sajid, M., & Basheer, C. (2016). Layered double hydroxides: Emerging sorbent materials for analytical extractions. TrAC - Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 75, 174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.06.010.
Shan, R. R., Yan, L. G., Yang, Y. M., Yang, K., Yu, S. J., Yu, H. Q., Zhu, B. C., & Du, B. (2015). Highly efficient removal of three red dyes by adsorption onto Mg-Al-layered double hydroxide. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 21, 561–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.03.019.
Sheng, T., Zhang, Z., Hu, Y., Tao, Y., Zhang, J., Shen, Z., Feng, J., & Zhang, A. (2019). Adsorption of phosphorus by using magnetic Mg–Al-, Zn–Al- and Mg–Fe-layered double hydroxides: Comparison studies and adsorption mechanism. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(7), 7102–7114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04191-5.
Tezuka, S., Chitrakar, R., Sakane, K., Sonoda, A., Ooi, K., & Tomida, T. (2004). The synthesis and phosphate adsorptive properties of Mg(II)-Mn(III) layered double hydroxides and their heat-treated materials. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 77(11), 2101–2107. https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.77.2101.
Theiss, F. L., Ayoko, G. A., & Frost, R. L. (2016). Synthesis of layered double hydroxides containing Mg2+ , Zn2+ , Ca2+ and Al3+ layer cations by co-precipitation methods - A review. Applied Surface Science, 383, 200–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.04.150.
Tran, H. N., You, S. J., Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A., & Chao, H. P. (2017). Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Research, 120, 88–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014.
Ulibarri, M. A., Pavlovic, I., Barriga, C., Hermosín, M. C., & Cornejo, J. (2001). Adsorption of anionic species on hydrotalcite-like compounds: Effect of interlayer anion and crystallinity. Applied Clay Science, 18(1–2), 17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1317(00)00026-0.
Wang, C., Chen, Y., Shang, X., Hou, X., Li, H., & Guo, Z. (2016). Facile synthesis of Ca/Mg/Al/Fe layered double hydroxides using steelmaking slag as raw material. Materials Letters, 173, 115–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.03.022.
Wong, Y., & Yu, J. (1999). Laccase-catalyzed decolorization of synthetic dyes. Water Research, 33(16), 3512–3520. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00066-4.
Yagub, M. T., Sen, T. K., Afroze, S., & Ang, H. M. (2014). Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 209, 172–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.04.002.
Yang, L., Shahrivari, Z., Liu, P. K. T., Sahimi, M., & Tsotsis, T. T. (2005). Removal of trace levels of arsenic and selenium from aqueous solutions by calcined and uncalcined layered double hydroxides (LDH). Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 44(17), 6804–6815. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie049060u.
Zaghouane-Boudiaf, H., Boutahala, M., & Arab, L. (2012). Removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution by uncalcined and calcined MgNiAl layered double hydroxides (LDHs). Chemical Engineering Journal, 187, 142–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.112.
Zheng, Y. M., Li, N., & Zhang, W. D. (2012). Preparation of nanostructured microspheres of Zn-Mg-Al layered double hydroxides with high adsorption property. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 415, 195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2012.10.014.
Zhou, H., Jiang, Z., Wei, S., & Liang, J. (2018). Adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by a novel layered double hydroxide FeMnMg-LDH. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 229(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3597-9.
Zhu, J., Zhu, Z., Zhang, H., Lu, H., & Qiu, Y. (2019). Calcined CoAl-layered double hydroxide as a heterogeneous catalyst for the degradation of acetaminophen and rhodamine B: Activity, stability, and mechanism. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06390-6.
Zubair, M., Daud, M., McKay, G., Shehzad, F., & Al-Harthi, M. A. (2017). Recent progress in layered double hydroxides (LDH)-containing hybrids as adsorbents for water remediation. Applied Clay Science, 143(March), 279–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.04.002.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Eastern Mediterranean University for the technical support during zeta potential analysis of the LDH samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3334 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gidado, S.M., Akanyeti, İ. Comparison of Remazol Brilliant Blue Reactive Adsorption on Pristine and Calcined ZnAl, MgAl, ZnMgAl Layered Double Hydroxides. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 146 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04522-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04522-0