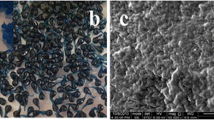
Abstract
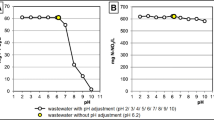
Four types of chitosan bead (CB) were tested to find the removal efficiency for cation and anion from solution. Hydrogel chitosan bead (HCB) was first prepared and then modified by chemical and physical treatment. Both the Cu(II) and phosphate removal were investigated based on the batch removal efficiency, a pH test, kinetics, and an isotherm test. For Cu(II) application, the highest Cu(II) uptake (approximately 83%) was obtained for the HCB; the modification by crosslinking by glutaraldehyde (GA) and air drying decreased this to approximately 60%, while phosphate removal was not affected by crosslinking and drying. Below pH 4.0, the removal efficiency of Cu(II) was decreased by approximately 20% for all type of CB, while phosphate uptake was determined by the type of CB, regardless of the initial pH. The maximum Cu(II) and phosphate uptake (Q) were 129 and 232 mg/g for the HCB and dried chitosan bead (DCB), respectively. The phosphate sorption rate was faster than Cu(II) at the beginning of the reaction for the hydrogel bead, while the dried bead reached the equilibrium in 72 h.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, R., & Gupta, M. N. (1995). Evaluation of glutaraldehyde-modified chitosan as a matrix for hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Analytica Chimica Acta, 313, 253–257.
An, B., Jung, K. Y., Lee, S. H., Lee, S., & Choi, J. W. (2014a). Effective phosphate removal from synthesized wastewater using copper-chitosan bead: batch and fixed-bed column studies. Water Air Soil Pollution, 225, 2050.
An, B., Jung, K. Y., Zhao, D., Lee, S. H., & Choi, J. W. (2014b). Preparation and characterization of polymeric ligand exchanger based on chitosan hydrogel for selective removal of phosphate. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 85, 45–53.
Cegłowski, M., Gierczyk, B., Frankowski, M., & Popenda, L. (2018). A new low-cost polymeric adsorbents with polyamine chelating groups for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from water solutions. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 131, 64–74.
Chang, X., Chen, D., & Jiao, X. (2008). Chitosan-based aerogels with high adsorption performance. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 112(26), 7721–7725.
Chen, F., Wu, Q., Lü, Q., Xu, Y., & Yu, Y. (2015). Synthesis and characterization of bifunctional mesoporous silica adsorbent for simultaneous removal of lead and nitrate ions. Separation and Purification Technology, 151, 225–231.
Chiou, M. S., & Li, H. Y. (2002). Equilibrium and kinetic modeling of adsorption of reactive dye on cross-linked chitosan bead. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 93, 233–248.
Conley, D. J., Paerl, H. W., Howarth, R. W., Boesch, D. F., Seitzinger, S. P., Havens, K. E., Lancelot, C., & Likens, G. E. (2009). Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science, 323, 1014–1015.
Denizli, A., Say, R., Patır, S., & Arıca, M. Y. (2000). Adsorption of heavy metal ions onto ethylene diamine-derived and cibacron blue F3GA-incorporated microporous poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) membranes. Reactive functional Polymers, 43, 17–24.
Domard, A. (1987). Determination of N-acetyl content in chitosan samples by c.d. measurements. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 9, 333–336.
Gerente, C., Andres, Y., McKay, G., & Le Cloirec, P. (2010). Removal of arsenic(V) onto chitosan: From sorption mechanism explanation to dynamic water treatment process. Chemical Engineering Journal, 158, 593–598.
Guibal, E. (2004). Interactions of metal ions with chitosan-based sorbents: A review. Separation and Purification Technology, 38, 43–74.
Guibal, E., Milot, C., & Tobin, J. M. (1998). Metal-anion sorption by chitosan beads: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 37, 1454–1463.
He, Y., Lin, H., Dong, Y., Liu, Q., & Wang, L. (2016). Simultaneous removal of ammonium and phosphate by alkaline-activated and lanthanum-impregnated zeolite. Chemosphere., 164, 387–395.
Hu, Y. N., & Cheng, H. F. (2013). Water pollution during China’s industrial transition. Environmental Development, 8, 57–73.
Ishii, T., Sorita, A., Sawamura, M., Kusunose, H., & Ukeda, H. (1997). Determination of the reaction-product of glutaraldehyde and amine based on the binding ability of Coomassie brilliant blue. Analytical Sciences, 13, 5–9.
Jabli, M., Baouab, M. H. V., Sintes-Zydowicz, N., & Hassine, B. B. (2011). Dye molecules/copper(II)/macroporous glutaraldehyde-chitosan microspheres complex: Surface characterization, kinetic, and thermodynamic investigations. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 123, 3412–3424.
Jo, H. J., Choi, J. W., Lee, S. H., & Hong, S. W. (2012). Acute toxicity of Ag and CuO nanoparticle suspensions against Daphnia magna: The importance of their dissolved fraction varying with preparation methods. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 227–228, 301–308.
Kannamba, B., Reddy, K. L., & AppaRao, B. V. (2010). Removal of cu(II) from aqueous solutions using chemically modified chitosan. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 175, 939–948.
Kildeeva, N. R., Perminov, P. A., Vladimirov, L. V., Novikov, V. V., & Mikhailov, S. N. (2009). About mechanism of chitosan cross-linking with glutaraldehyde. Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry, 35(3), 397–407.
Kim, H., Choi, J. W., Kim, T. H., Park, J. S., & An, B. (2018). Effect of TSS removal from stormwater by mixed media column on T-N, T-P, and organic material removal. Water, 10(8), 1069.
Li, B., Shan, C. L., Zhou, Q., Fang, Y., Wang, Y. L., Xu, F., Han, L. R., Ibrahim, M., Guo, L. B., Xie, G. L., & Sun, G. C. (2013). Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of cross-linked chitosan-glutaraldehyde. Marine Drugs, 11, 1534–1552.
Liu, X., & Zhang, L. (2015). Removal of phosphate anions using the modified chitosan beads: Adsorption kinetic, isotherm and mechanism studies. Powder Technolog, 277, 112–119.
Liu, Y., Yan, C., Zhao, J., Zhang, Z., Wang, H., Zhou, S., & Wu, L. (2018). Synthesis of zeolite P1 from fly ash under solven-free conditions for ammonium removal from water. Journal of Cleaner Production., 202, 11–22.
Malwal, D., & Gopinath, P. (2017). Silica stabilized magnetic-chitosan beads for removal of arsenic from water. Colloid and Interface Science Communications., 19, 14–19.
Modrezejewska, Z. (2013). Sorption mechanism of copper in chitosan hydrogel. Reactive Functional Polymers, 73, 719–726.
Monteiro Jr., O. A. C., & Airoldi, C. (1999). Some studies of crosslinking chitosan–glutaraldehyde interaction in a homogeneous system. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 26, 119–128.
Noel, S. P., Courtney, H. S., Bumgardner, J. D., & Haggard, W. O. (2010). Chitosan sponges to locally deliver amikacin and vancomycin: A pilot in vitro evaluation. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 468(8), 2074–2080.
Osman, Z., & Arof, A. K. (2003). FTIR studies of chitosan acetate based polymer electrolytes. Electrochimica Acta, 48, 993–999.
Papageorgiou, S. K., Katsaros, F. K., Kouvelos, E. P., Nolan, J. W., Le Deit, H., & Kanellopoulos, N. K. (2006). Heavy metal sorption by calcium alginate beads from Laminaria digitata. Journal of Hazard Materials., 137(3), 1765–1772.
Pillai, C. K. S., Paul, W., & Sharma, C. P. (2009). Chitin and chitosan polymers: Chemistry, solubility and fiber formation. Progress in Polymer Science, 34(7), 641–678.
Piron, E., & Domarda, A. (1998). Interaction between chitosan and uranyl ions. Part 2. Mechanism of interaction. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 22(1), 33–40.
Poon, L., Wilson, L. D., & Headley, J. V. (2014). Chitosan-glutaraldehyde copolymers and their sorption properties. Carbohydrate Polymers, 109, 92–101.
Queiroz, M. F., Melo, K. R. T., Sabry, D. A., Sassaki, G. L., & Rocha, H. A. O. (2015). Does the use of chitosan contribute to oxalate kidney stone formation? Marine Drugs, 13, 141–158.
Rajeswari, A., Amalraj, A., & Pius, A. (2015). Removal of phosphate using chitosan-polymer composites. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3, 2331–2341.
Sampaio, R. M. M., Timmers, R. A., Xu, Y., Keesman, K. J., & Lens, P. N. L. (2009). Selective precipitation of cu from Zn in a Ps controlled continuously stirred tank reactor. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165, 256–265.
Schindler, D. W. (1974). Eutrophication and recovery in experimental lakes: Implications for lake management. Science, 184, 897–899.
Shah, B., & Chudasama, U. (2014). Synthesis and characterization of a novel hybrid material as amphoteric ion exchanger for simultaneous removal of cations and anions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 276, 138–148.
Sorvari, J., & Sillanpää, M. (1996). Influence of metal complex formation on heavy metal and free EDTA and DTPA acute toxicity determined by Daphnia magna. Chemosphere, 33(6), 1119–1127.
Stoll, A., & Duncan, J. R. (1996). Enhanced heavy metal removal from waste water by viable, glucose pretreated Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Biotechnology Letters, 18(10), 1209–1212.
Thakur, V. K., & Voicu, S. I. (2016). Recent advances in cellulose and chitosan based membranes for water purification: A concise review. Carbohydrate Polyhmers, 146, 148–165.
USEPA, EPA440/5–86-001, Washington, DC, 1986.
Verbych, S., Bryk, M., Chornokur, G., & Fuhr, B. (2005). Removal of copper (II) from aqueous solutions by chitosan adsorption. Separation Science and Technology, 40, 1749–1759.
Wan Ngah, W. S., Endud, C. S., & Mayanar, R. (2002). Removal of copper(II) ions from aqueous solution onto chitosan and cross-linked chitosan beads. Reactive and Functional Polymer, 50(2), 181–190.
Wang, Q. Z., Chen, X. G., Liu, N., Wang, S. X., Liu, C. S., Meng, X. H., & Liu, C. G. (2006). Protonation constants of chitosan with different molecular weight and degree of deacetylation. Carbohydrate Polymers, 65, 194–201.
Wang, J. J., Zeng, Z. W., Xiao, R. Z., Xie, T., Zhou, G. L., Zhan, X. R., & Wang, S. L. (2011). Recent advances of chitosan nanoparticles as drug carriers. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 6, 765–774.
Wu, Q., Chen, F., Xu, Y., & Yu, Y. (2015). Simultaneous removal of cations and anions from waste water by bifunctional mesoporous silica. Applied Surface Science, 351, 155–163.
Xie, Y. L., Wang, M. J., & Yao, S. J. (2009). Preparation and characterization of biocompatible microcapsules of sodium cellulose sulfate/chitosan by means of layer-by-layer self-assembly. Langmuir., 25(16), 8999–9005.
Zhao, F., Yu, B., Yue, Z., Wang, T., Wen, X., Liu, Z., & Zhao, C. (2007). Preparation of porous chitosan gel beads for copper(II) ion adsorption. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147, 67–73.
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2016R1D1A1B03930265) and the Korea Ministry of Environment as a “Global Top Project” (Project No.: 2016002190003). This work was also supported by the Technology Innovation Program (10082572, Development of Low Energy Desalination Water Treatment Engineering Package System for Industrial Recycle Water Production) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, B., Choi, JW. An Experimental Application of Four Types of Chitosan Bead for Removal of Cationic and Anionic Pollutants. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 314 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4365-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4365-9