Abstract
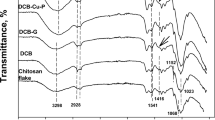
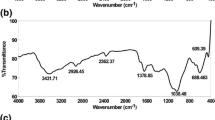
To remove phosphate from solution, a new class of sorbent based on chitosan bead (CB) was prepared using copper ion (Cu(II)) with/without a traditional crosslinking agent (glutaraldehyde [GLA]); these materials are referred to as CB-G-Cu and CB-Cu, respectively. Copper ions play a key role in the CB synthesis; these species crosslink each polymer chain, and during phosphate removal, they are the active functional group. Overall, 2.5 % (w/w) of chitosan is necessary to maintain the physical properties of the bead. In the FTIR spectra, adding GLA decreased the intensity of the amino group in chitosan, lowering the amount of copper in the CB. The maximum phosphate uptake (Q) for CB-Cu was 53.6 mg g−1 when calculated with the Langmuir isotherm, and the phosphate equilibrium was achieved in 12 h. Although the solution pH was not strongly affected, values below 7 are optimal for phosphate removal. The CB-Cu can be feasibly applied during a fixed column test, revealing that the phosphate breakthrough was 1.5 times higher than with CB-G-Cu.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agboh, O. C., & Qin, Y. (1997). Chitin and chitosan fibers. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 8, 355–365.
An, B., & Zhao, D. Y. (2012). Immobilization of As(III) in soil and groundwater using a new class of polysaccharide stabilized Fe–Mn oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 211, 332–341.
An, B., Nam, J., Choi, J. W., Hong, S. W., & Lee, S. H. (2013a). Enhanced phosphate selectivity from wastewater using copper-loaded chelating resin functionalized with polyethylenimine. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 409, 129–134.
An, B., Son, H., Chung, J., Choi, J. W., Lee, S. H., & Hong, S. W. (2013b). Calcium and hydrogen effects during sorption of copper onto an alginate-based ion exchanger: batch and fixed-bed column studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 232, 51–58.
Bajpai, S. K., & Sharma, S. (2004). Investigation of swelling/degradation behaviour of alginate beads crosslinked with Ca2+ and Ba2+ ions. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 59, 129–140.
Barreiro-Iglesias, R., Coronilla, R., Concheiro, A., & Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. (2005). Preparation of chitosan beads by simultaneous cross-linking/insolubilisation in basic pH rheological optimisation and drug loading/release behavior. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 24, 77–84.
Berger, J., Reist, M., Mayer, J. M., Felt, O., Peppas, N. A., & Gurny, R. (2004). Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 57, 19–34.
Celi, L., Barberis, E., & Marsan, F. A. (2000). Sorption of phosphate on goethite at high concentrations. Soil Science, 165, 657–664.
Chen, C. C., & Chung, Y. C. (2006). Arsenic removal using a biopolymer chitosan sorbent. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 41, 645–658.
Conley, D. J., Paerl, H. W., Howarth, R. W., Boesch, D. F., Seitzinger, S. P., Havens, K. E., Lancelot, C., & Likens, G. E. (2009). Ecology controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science, 323, 1014–1015.
Dai, J., Yang, H., Yan, H., Shangguan, Y. G., Zheng, Q. A., & Cheng, R. S. (2011). Phosphate adsorption from aqueous solutions by disused adsorbents: chitosan hydrogel beads after the removal of copper(II). Chemical Engineering Journal, 166, 970–977.
Dambies, L., Vincent, T., Domard, A., & Guibal, E. (2001). Preparation of chitosan gel beads by ionotropic molybdate gelation. Biomacromolecules, 2, 1198–1205.
Domard, A. (1987). Determination of N-acetyl content in chitosan samples by Cd measurements. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 9, 333–336.
Dorfner, K. (1972). Ion exchangers; properties and applications. Ann Arbor Science.
Elwakeel, K. Z. (2010). Environmental application of chitosan resins for the treatment of water and wastewater: a review. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 31, 273–288.
Fernandes, A. L. P., Morais, W. A., Santos, A. I. B., de Araujo, A. M. L., dos Santos, D. E. S., dos Santos, D. S., Pavinatto, F. J., Oliveira, O. N., Dantas, T. N. C., Pereira, M. R., & Fonseca, J. L. C. (2005). The influence of oxidative degradation on the preparation of chitosan nanoparticles. Colloid and Polymer Science, 284, 1–9.
Guibal, E., Milot, C., Eterradossi, O., Gauffier, C., & Domard, A. (1999). Study of molybdate ion sorption on chitosan gel beads by different spectrometric analyses. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 24, 49–59.
Hsien, T. Y., & Rorrer, G. L. (1995). Effects of acylation and cross-linking on the material properties and cadmium ion adsorption capacity of porous chitosan beads. Separation Science and Technology, 30, 2455–2475.
Jeon, C., & Park, K. H. (2005). Adsorption and desorption characteristics of mercury(II) ions using aminated chitosan bead. Water Research, 39, 3938–3944.
Kildeeva, N. R., Perminov, P. A., Vladimirov, L. V., Novikov, V. V., & Mikhailov, S. N. (2009). About mechanism of chitosan cross-linking with glutaraldehyde. Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry, 35, 360–369.
Koyama, Y., & Taniguchi, A. (1986). Studies on chitin X. homogeneous cross-linking of chitosan for enhanced cupric ion adsorption. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 31, 1951–1954.
Lee, C. G., Park, J. A., & Kim, S. B. (2012). Phosphate removal from aqueous solutions using slag microspheres. Desalination and Water Treatment, 44, 229–236.
Li, N., & Bai, R. B. (2005). Copper adsorption on chitosan–cellulose hydrogel beads: behaviors and mechanisms. Separation and Purification Technology, 42, 237–247.
Li, C., & Guan, X. H. (2011). Competitive adsorption of three different phosphate species on aluminum hydroxide. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 20, 1936–1941.
Luengo, C., Brigante, M., Antelo, J., & Avena, M. (2006). Kinetics of phosphate adsorption on goethite: comparing batch adsorption and ATR-IR measurements. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 300, 511–518.
Mi, F. L., Shyu, S. S., Wu, Y. B., Lee, S. T., Shyong, Y. J., & Huang, R. N. (2001). Fabrication and characterization of a sponge-like asymmetric chitosan membrane as a wound dressing. Biomaterials, 22, 165–173.
Miretzky, P., & Cirelli, A. F. (2009). Hg(II) removal from water by chitosan and chitosan derivatives: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167, 10–23.
Modrzejewska, Z., & Kaminski, W. (1999). Separation of Cr(VI) on chitosan membranes. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 38, 4946–4950.
Muzzarelli, R. A. A. (2000). Chitosan per OS: from dietary supplement to drug carrier. Atec
Nam, J. H., Lee, S. H., Choi, J. W., Hong, S. W., & An, B. (2013). Enhanced removal of phosphate on modified ion exchanger with competing ion. Journal of Korean Society of Water and Wastewater, 27, 121–128.
Ngah, W. S. W., Endud, C. S., & Mayanar, R. (2002). Removal of copper(II) ions from aqueous solution onto chitosan and cross-linked chitosan beads. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 50, 181–190.
Pawlak, A., & Mucha, A. (2003). Thermogravimetric and FTIR studies of chitosan blends. Thermochimica Acta, 396, 153–166.
Snoeyink, V. L., & Jenkins, D. (1980). Water chemistry. Wiley
Steinwinder, B. T. R., & Zhao, D. Y. (2005). Selective removal of arsenate from drinking water using a polymeric ligand exchanger. Water Research, 39, 4993–5004.
Su, Y., Cui, H., Li, Q., Gao, S. A., & Shang, J. K. (2013). Strong adsorption of phosphate by amorphous zirconium oxide nanoparticles. Water Research, 47, 5018–5026.
Tchobanoglous, G., Burton, F. L., Metcalf, & Eddy (1991). Wastewater engineering: treatment, disposal, and reuse. McGraw-Hill
Treybal, R. E. (1998). Mass-transfer operations. McGraw-Hill.
USEPA. (2000). Nutrient criteria technical guidance manual: rivers and streams. EPA-822b-00-002. Washington, DC.
Valdes, E. T., & Trivino, G. C. (2009). Chitosan metal complexes and chitosan–Cu ESR studies. Journal of Chilean Chemical Society, 54, 1–5.
Varma, A. J., Deshpande, S. V., & Kennedy, J. F. (2004). Metal complexation by chitosan and its derivatives: a review. Carbohydrate Polymers, 55, 77–93.
Wilde, E. W., & Benemann, J. R. (1993). Bioremoval of heavy-metals by the use of microalgae. Biotechnology Advances, 11, 781–812.
Zhang, G. S., Liu, H. J., Liu, R. P., & Qu, J. H. (2009). Removal of phosphate from water by a Fe–Mn binary oxide adsorbent. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 335, 168–174.
Zhao, D. Y., & SenGupta, A. K. (1998). Ultimate removal of phosphate from wastewater using a new class of polymeric ion exchangers. Water Research, 32, 1613–1625.
Zhao, D. Y., & SenGupta, A. K. (2000). Ligand separation with a copper(II)-loaded polymeric ligand exchanger. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 39, 455–46.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the KIST Institutional Program (Project No. 2E24563) and the Korea Ministry of Environment as “Global Top Project” (GT-11-B-01-011-1). We thank Mr. Wan-Keun Park for assisting with the SEM analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, B., Jung, KY., Lee, SH. et al. Effective Phosphate Removal from Synthesized Wastewater Using Copper–Chitosan Bead: Batch and Fixed-Bed Column Studies. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 2050 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2050-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2050-6