Abstract
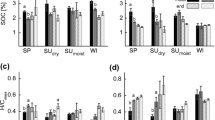
In this study, we investigated the effect of olive mill wastewater on selected soil physical and hydraulic properties. Olive mill wastewater was added to each column every week at different loading rates (0, 50, 100, and 200 m3 ha−1). Physicochemical and hydraulic properties were determined for surface (0–8 cm) and subsurface layers (8–16 and 16–24 cm). The highest loading rate (200 m3 ha−1) showed an increase in aggregate stability from 18% (control) to 31 and to 38%, penetration resistance from 1.8 kg cm−2 (control) to 3.5 and to 4.5 kg cm−2, hydraulic conductivity from 43 cm day−1 (control) to 15.3 and 3.3 cm day−1, and water repellency from < 5 s (control) to 120 and 261 s in the first and second months for the surface layer, respectively. The opposite was observed for the infiltration rate, where it decreased from 39.01 mm h−1 (control) to 1.26 and 0.42 mm h−1 for the first and second months, respectively. This study showed that application of olive mill wastewater deteriorated the physical and hydraulic properties of soil proportional to loading rates and more specifically at the surface layer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedi-Koupai, J., Mostafazadeh-Fard, B., Afyuni, M., & Bagheri, M. (2006). Effect of treated wastewater on soil chemical and physical properties in an arid region. Plant, Soil and Environment, 52, 335–344.
Abichou, M., Labiadh, M., & Cornelis, W. (2009). The olive mills waste water (OMW) as an organic amendment for controlling wind erosion in southern Tunisia by improving the soil surface structure. Journal of Arid Land Studies, 19-1, 242–246.
Abu-Zreig, M., & Al-Widyan, M. (2002). Influence of olive mills solid waste on soil hydraulic properties. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 33, 505–517.
Albalasmeh, A. A., & Ghezzehei, T. A. (2014). Interplay between soil drying and root exudation in rhizosheath development. Plant and Soil, 374, 739–751.
Attom, M., Abed, F., Elemam, M., Nazal, M., & ElMessalami, N. (2016). The effect of treated waste-water on compaction and compression of fine soil. International Journal of Civil, Environmental, Structural, Construction and Architectural Engineering, 10, 1111–1115.
Ayoub, S., Al-Absi, K., Al-Shdiefat, S., Al-Majali, D., & Hijazean, D. (2014). Effect of olive mill wastewater land-spreading on soil properties, olive tree performance and oil quality. Scientia Horticulturae, 175, 160–166.
Azam, F., Mu ̈ller, C., Weiske, A., Benckiser, G., & Ottow, J. (2002). Nitrification and denitrification as sources of atmospheric nitrous oxide – Role of oxidizable carbon and applied nitrogen. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 35(1), 54–61.
Azouzi, R., Charef, A., zaghdoudi, S., Khadhar, S., Shabou, N., Boughanmi, H., Hjiri, B., & Hajjaj, S. (2015). Effect of long-term irrigation with treated wastewater of three soil types on their bulk densities, chemical properties and pahs content in semi-arid climate. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9, 3.
Barbera, A. C., Maucieri, C., Cavallaro, V., Ioppolo, A., & Spagna, G. (2013). Effects of spreading olive mill wastewater on soil properties and crops, a review. Agricultural Water Management, 119, 43–53.
Bene, C. D., Pellegrino, E., Debolini, M., Silvestri, N., & Bonari, E. (2013). Short- and long- term effects of olive mill wastewater land spreading on soil chemical and biological properties. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 56(0), 21–30.
Bisdom, E., Dekker, L. W., & Schoute, J. F. (1993). Water repellency of sieve fractions from sandy soils and relationships with organic material and soil structure. Geoderma, 56(1), 105–118.
Chaari, L., Elloumi, N., Gargouri, K., Bourouina, B., Michichi, T., & Kallel, M. (2014). Evolution of several soil properties following amendment with olive mill wastewater. Desalination and Water Treatment, 52, 2180–2186.
Chenu, C., Le Bissonnais, Y., & Arrouays, D. (2000). Organic matter influence on clay wettability and soil aggregate stability. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 64, 1479–1486.
Cox, L., Becker, A., Celis, R., López, R., Hermosin, M., & Cornejo, J. (1996). Movement of clopyralid in a soil amended with olive oil mill wastewater as related to soil porosity. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 5, 167–171.
Decagon. (2014). Minidisk Infiltrometer User’s Manual (09th ed.). Pullman: Decagon Devices, Inc.
Dekker, L. W., & Jungerius, P. D. (1990). Water repellency in the dunes with special reference to the Netherlands. Catena, 18, 173–183.
Diamantis, V., Pagorogon, L., Gazani, E., Doerr, S. H., Pliakas, F., & Ritsema, C. J. (2013). Use of olive mill wastewater (OMW) to decrease hydrophobicity in sandy soil. Ecological Engineering, 58(0), 393–398.
Gharaibeh, M. A., Eltaif, N. I., & Al-Abdullah, B. (2007). Impact of field application of treated wastewater on hydraulic properties of vertisols. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 184, 347–353.
Gharaibeh, M. A., Eltaif, N. I., & Albalasmeh, A. A. (2011). Reclamation of highly calcareous saline sodic soil using Atriplex halimus and by-product gypsum. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 13(9), 873–883.
Gonza ́lez-Vila, F., Verdejo, T., Rio, J. D., & Martin, F. (1995). Accumulation of hydrophobic compounds in the soil lipidic and humic fractions as result of a long term land treatment with olive oil mill effluents (alpechin). Chemosphere, 31, 3681–3686.
Hanifi, S., & El-Hadrami, I. (2008). Olive mill wastewaters fractioned soil-application for safe agronomic reuse in date palm (phoenix dactylifera l.) fertilization. Journal of Agronomy, 7, 63–69.
Kapellakis, I., Tzanakakis, V., & Angelakis, A. (2015). Land application-based olive mill wastewater management. Water, 7, 362–376.
Kavdir, Y., & Killi, D. (2008). Influence of olive oil solid waste applications on soil pH, electrical conductivity, soil nitrogen transformations, carbon content and aggregate stability. Bioresource Technology, 99, 2326–2332.
Kemper, W., Rosenau, R., 1986. Aggregate stability and size distribution. In: Methods of soil analysis, part 1. Physical and mineralogical methods. Agronomy monograph. No. 9. Society of Agronomy/Soil Science Society of America, pp. 425–442.
Kurtz, M. P., Peikert, B., Bru ̈hl, C., Dag, A., Zipori, I., Shoqeir, J. H., & Schaumann, G. E. (2015). Effects of olive mill wastewater on soil microarthropods and soil chemistry in two different cultivation scenarios in Israel and Palestinian territories. Agriculture, 5, 857–878.
Levy, G. J., Dag, A., Raviv, M., Zipori, I., Medina, S., Saadi, I., Krasnovski, A., Eizenberg, H., & Laor, Y. (2017). Annual spreading of olive mill wastewater over consecutive years: Effects on cultivated soils’ physical properties. Land Degradation & Development, 29, 176–187.
Mahmoud, M., Janssen, M., Haboub, N., Nassour, A., & Lennartz, B. (2010). The impact of olive mill wastewater application on flow and transport properties in soils. Soil and Tillage Research, 107, 36–41.
Mahmoud, M., Janssen, M., Peth, S., Horn, R., & Lennartz, B. (2012). Long-term impact of irrigation with olive mill wastewater on aggregate properties in the top soil. Soil and Tillage Research, 124, 24–31.
Mekki, A., Dhouib, A., & Sayadi, S. (2006). Changes in microbial and soil properties following amendment with treated and untreated olive mill wastewater. Microbiological Research, 161(2), 93–101.
Mekki, A., Dhouib, A., & Sayadi, S. (2007). Polyphenols dynamics and phytotoxicity in a soil amended by olive mill wastewaters. Journal of Environmental Management, 84(2), 134–140.
Mekki, A., Dhouib, A., & Sayadi, S. (2009). Evolution of several soil properties following amendment with olive mill wastewater. Progress in Natural Science, 19, 1515–1521.
Mekki, A., Dhouib, A., & Sayadi, S. (2013). Effects of olive mill wastewater application on soil properties and plants growth. International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture, 2, 1), 1–1), 7.
Mohawesh, O., Mahmoud, M., Janssen, M., & Lennartz, B. (2014). Effect of irrigation with olive mill wastewater on soil hydraulic and solute transport properties. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 11, 927–934.
Ouzounidou, G., & Asfi, M. (2012). Determination of olive mill wastewater toxic effects on three mint species grown in hydroponic culture. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 35(5), 726–738.
Peikert, B., Schaumann, G., Keren, Y., Bukhanovsky, N., Borisover, M., Garfha, M., Shoqeric, J., & Dag, A. (2015). Characterization of topsoils subjected to poorly controlled olive oil mill wastewater pollution in West Bank and Israel. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 199, 176–189.
Piotrowska, A., Iamarino, G., Rao, M. A., & Gianfreda, L. (2006). Short-term effects of olive mill waste water (OMW) on chemical and biochemical properties of a semiarid Mediterranean soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38(3), 600–610.
Piotrowska, A., Rao, M. A., Scotti, R., & Gianfreda, L. (2011). Changes in soil chemical and biochemical properties following amendment with crude and dephenolized olive mill waste water (OMW). Geoderma, 161(1–2), 8–17.
Rusan, M. J. M., & Malkawi, H. I. (2016). Dilution of olive mill wastewater (OMW) eliminates its phytotoxicity and enhances plant growth and soil fertility. Desalination and Water Treatment, 7, 1–9.
Rusan, M. J. M., Albalasmeh, A. A., Zuraiqi, S., & Bashabsheh, M. (2015). Evaluation of phytotoxicity effect of olive mill wastewater treated by different technologies on seed germination of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(12), 9127–9135.
Rusan, M., Albalasmeh, A. A., & Malkawi, H. I. (2016). Treated olive mill wastewater effects on soil properties and plant growth. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 227(5), 1–10.
Saadi, I., Raviv, M., Berkovich, S., Hanan, A., Aviani, I., & Laor, Y. (2013). Fate of soil-applied olive mill wastewater and potential phytotoxicity assessed by two bioassay methods. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42(6), 1791–1801.
Sahraoui, H., Kanzari, S., Hachicha, M., & Mellouli, H. J. (2015). Olive mill wastewater spreading effects on hydraulic soil properties. The experiment, 30(4), 2002–2011.
Sayadi, S., Allouche, N., Jaoua, M., & Aloui, F. (2000). Detrimental effects of high molecular- mass polyphenols on olive mill wastewater biotreatment. Process Biochemistry, 35(7), 725–735.
Steinmetz, Z., Kurtz, M. P., Dag, A., Zipori, I., & Schaumann, G. E. (2015). The seasonal influence of olive mill wastewater applications on an orchard soil under semi-arid conditions. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 178, 641–648.
Tamimi, N. (2016). Effects of seasonal olive mill wastewater application on soil: Field experiment in Bait Reema village. Palestine.
Tarchitzky, J., Lerner, O., Shani, U., Arye, G., Lowengart-Aycicegi, A., Brener, A., & Chen, Y. (2007). Water distribution pattern in treated wastewater irrigated soils: Hydrophobicity effect. European Journal of Soil Science, 58, 573–588.
Tisdall, J. M., & Oades, J. M. (1982). Organic matter and water-stable aggregates in soils. European Journal of Soil Science, 33, 141–163.
Travis, M. J., Weisbrod, N., & Gross, A. (2008). Accumulation of oil and grease in soils irrigated with greywater and their potential role in soil water repellency. Science of the Total Environment, 394, 68–74.
Urena, C., Azanon, J., Corpas, F., Nieto, F., Leon, C., & Perez, L. (2013). Magnesium hydroxide, seawater and olive mill wastewater to reduce swelling potential and plasticity of bentonite soil. Construction and Building Materials, 45, 289–297.
Woudt, B. D. v. (1959). Particle coatings affecting the wettability of soils. Journal of Geo- physical Research, 64, 263–267.
Zenjari, B., & Nejmeddine, A. (2001). Impact of spreading olive mill wastewater on soil characteristics: Laboratory experiments. Agronomie, 21(8), 749–755.
Zhang, R. (1997). Determination of soil sorptivity and hydraulic conductivity from the disk infiltrometer. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 61, 1024–1030.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Ahmad M. Alqudah for his help in the statistical analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the Deanship of Research at the Jordan University of Science and Technology under grant number 189/2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albalasmeh, A.A., Alajlouni, M.A., Ghariabeh, M.A. et al. Short-Term Effects of Olive Mill Wastewater Land Spreading on Soil Physical and Hydraulic Properties. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 208 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4243-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4243-5