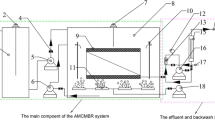
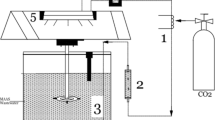
Abstract
The implementation of the latest International Maritime Organization (IMO) emission standard has raised stringent requirements for marine domestic sewage discharge. In this study, a novel aerobic-anaerobic micro-sludge membrane bioreactor (O-AMSMBR) was used to analyze the effect of pH variation on the effluent chemical oxygen demand (COD) and total nitrogen (TN) for marine domestic sewage. Results showed that the novel MBR achieved better COD and TN removal efficiency (Ravg(COD) = 87.77% and Ravg(TN) = 91.01%). In acid environment (pH = 5), anaerobic micro-sludge MBR technology can enhance the pollutants removal efficiency under pH shock. These two findings indicated that anaerobic micro-sludge membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology has great potential in acidity or alkalinity wastewater treatment. The activity of six different enzymes was analyzed in this study. The results showed that nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase can serve as special indicating factors for anaerobic micro-sludge MBR technology on domestic ship sewage. Moreover, wavelet neural network (WNN) and back-propagation neural network (BPNN) were used to simulate the effect of pH on reactor performance. The order of relative importance inculcated that pH is the key factor to consider for biodegradation of organic matter in O-AMSMBR system. The outcomes of this study suggest that post-anaerobic integrated with micro-sludge methods can play a vital role in keeping good pollutant degradation in ship wastewater treatment under pH shift.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alejandro, R. S., Barbara, M. P., Miguel, H. M., Maria, A. R., Jose, M. P., & Jesus, G. L. (2018). Maximum influent salinity affects the diversity of mineral-precipitation-mediating bacterial communities in membrane biofilm of hybrid moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 229, 342.
Alex, M. A., Rafael, B. M., Carvalho, A. K. F., Castro, H. F., & Andrade, G. S. S. (2019). Penicillium citrinum whole-cells catalyst for the treatment of lipid-rich wastewater. Biomass and Bioenergy, 120, 433–438.
APHA. (2012). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Bella, G. D., Prima, N. D., Trapani, D. D., Freni, G., Giustra, M. G., Torregrossa, M., & Viviani, G. (2015). Performance of membrane bioreactor (MBR) systems for the treatment of shipboard slops: assessment of hydrocarbon biodegradation and biomass activity under salinity variation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 300, 765–778.
Cai, H., & Shen, R. (2005). Determination of soil protease activity with modified ninhydrin colorimetry. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 42, 306–313 (in Chinese).
Cai, Y. H., Beng, T., Asad, A. Z., Shi, Y., & Zhang, K. (2019a). Nitrogen removal augmentation of ship sewage by an innovative aerobicanaerobic micro-sludge MBR technology. Process Biochemistry, 82, 123–134.
Cai, Y. H., Li, X., Asad, A. Z., Shi, Y., Zhang, K., Sun, P. Q., & Lu, Z. (2019b). Processing efficiency, simulation and enzyme activities analysis of an air-lift multilevel circulation membrane bioreactor (AMCMBR) on marine domestic sewage treatment. Periodica Polytechnica Chemical Engineering, 63(3), 448–458.
Capodaglio, A. G., & Callegari, A. (2015). Onsite management of tanker ships’ rinse water by means of a compact bioreactor. Water Practice & Technology, 10(4), 681–687.
Cecconet, D., Callegari, A., Hlavínek, P., & Capodaglio, A. G. (2019). Membrane bioreactors for sustainable, fit-for-purpose greywater treatment: a critical review. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 21, 745–762.
Chae, S. R., & Shin, H. S. (2007). Characteristics of simultaneous organic and nutrient removal in a pilot-scale vertical submerged membrane bioreactor (VSMBR) treating municipal wastewater at various temperatures. Process Biochemistry, 42, 193–198.
Chen, Z. B., He, Z. W., Hu, D. X., Cun, Y. B., Ran, C. Q., Ge, H., Zhang, S. L., Shi, Y., Yang, M. J., Wang, A. J., Chen, Z. Q., & Ren, N. Q. (2015). Effect of temperature on treating chemical synthesis-based pharmaceutical wastewater containing 7-ACA by a novel multi-stage loop membrane bioreactor. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 90, 1002–1012.
Chen, Z. B., Li, X., Hu, D. X., Cui, Y. B., Gu, F. G., Jia, F. Q., Xiao, T. T., Su, H. Y., Xu, J., Wang, H. X., Wu, P., Zhang, Y., & Jiang, N. (2018). Performance and methane fermentation characteristics of a pilot scale anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) for treating pharmaceutical wastewater containing m-cresol (MC) and iso-propyl alcohol (IPA). Chemosphere, 206, 750–758.
Cortés, L., Díaz, M. R., Lopez, C. L., Peinado, M. S., Rodelas, B., & López, J. G. (2012). Effect of salinity on enzymatic activities in a submerged fixed bed biofilm reactor for municipal sewage treatment. Bioresource Technology, 121, 312–319.
Corzo, A., & Niell, F. X. (1991). Determination of reductase activity in Ulva rigida C.a gardh by the in situ method. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 146, 181–191.
Fang, J., Ju, O. Y., Qiu, J., & Chen, K. (2010). Regularity for change of urease and catalase in wastewater treatment with activated sludge process. In: 2010 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Chengdu, China, 2010, pp. 1–5.
Forstner, U. (1998). Water pollution: wastewater. Integrated Pollution Co Ntrol, 197–238.
Gao, F., Nan, J., Li, S. N., & Wang, Y. R. (2018). Modeling and simulation of a biological process for treating different COD:N ratio wastewater using an extended ASM1 model. Chemical Engineering Journal, 332, 671–681.
Goel, R., Mino, T., Satoh, H., & Matsuo, T. (1992). Enzyme activities under anaerobic and aerobic conditions in activated sludge sequencing batch reactor. Water Research, 32(7), 2081–2088.
Guo, Q. J., Qi, X. N., Zheng, W., Yin, Q., Sun, P., Guo, P. J., & Liu, J. C. (2019). Modeling and characteristic analysis of fouling in a wet cooling tower based on wavelet neural networks. Applied Thermal Engineering, 152, 907–916.
Han, H., Zhang, Y. Y., Cui, C. C., & Zheng, S. K. (2010). Effect of COD level and HRT on microbial community in a yeast-predominant activated sludge system. Bioresource Technology, 101, 3463–3465.
Hu, D. X., Li, X., Chen, Z. B., Cui, Y. B., Gu, F. G., Jia, F. Q., Xiao, T. T., Su, H. Y., Xu, J., Wang, H. X., Wu, P., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Performance and extracellular polymers substance analysis of a pilot scale anaerobic membrane bioreactor for treating tetrahydrofuran pharmaceutical wastewater at different HRTs. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 342, 383–391.
Huang, Z., Ong, S. L., & Ng, H. Y. (2011). Submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor for low-strength wastewater treatment: effect of HRT and SRT on treatment performance and membrane fouling. Water Research, 45, 705–713.
Huang, B., Wang, H. C., Cui, D., Zhang, B., Chen, Z. B., & Wang, A. J. (2018). Effect of operational modes on nitrogen removal and nitrous oxide emission in the process of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification. Chemical Engineering Journal, 341, 238–247.
IMO-MEPC (2006). Revised guidelines on implementation of effluent standards and performance tests for sewage treatment plants. In: Committee MEP, editor. 159(55). MEPC 55/23 Annex 26.
IMO-MEPC (2010). Revised guidelines on implementation of effluent standards and performance tests for sewage treatment plants. In: Committee MEP, editor. 227(64). MEPC 64/23 Annex 22.
Jessica, U. C., Santos, M. M., Romera, E. R., & Crespo, J. L. L. (2019). Implications of denitrification in the ecological status of an urban river using enzymatic activities in sediments as an indicator. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 75, 255–268.
Kinh, C. T., Suenag, T., Hori, T., Riya, S., Hosomi, M., Smets, B. F., & Terad, A. (2017). Counter-diffusion biofilms have lower N2O emissions than codiffusion biofilms during simultaneous nitrification and denitrification: insights from depth-profile analysis. Water Research, 124, 363–371.
Klose, S., & Tabatabai, M. (2000). Urease activity of microbial biomass in soils as affected by cropping systems. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 31(3–4), 191–199.
Li, L. P., Tian, Y., Zhang, J., Zuo, W., Li, H., Li, A. R., Huang, D. P., Liu, J., Liu, Y. H., Sun, Z. M., & Liu, Y. S. (2017). Insight into the roles of worm reactor on wastewater treatment and sludge reduction in anaerobic-anoxic-oxic membrane bioreactor (A2O-MBR): performance and mechanism. Chemical Engineering Journal, 330, 718–726.
Li, M., Liang, Z. L., Callier, M. D., D'orbcaste, E. R., Sun, G. X., Ma, X. N., Li, X., Wang, S. K., Liu, Y., & Song, X. F. (2018). Nutrients removal and substrate enzyme activities in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands for mariculture wastewater treatment: effects of ammonia nitrogen loading rates and salinity levels. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 131, 142–150.
Li, B., Qiu, Y., Li, J., Peng, L., & Huang, X. (2019). Removal of antibiotic resistance genes in four full-scale membrane bioreactors. Science of the Total Environment, 653, 112–119.
Ma, W. W., Han, Y. X., Ma, W. C., Han, H. J., Zhu, H., Xu, C. Y., Li, K., & Wang, D. X. (2017). Enhanced nitrogen removal from coal gasification wastewater by simultaneous nitrification and denitrification (SND) in an oxygen-limited aeration sequencing batch biofilm reactor. Bioresource Technology, 244, 84–91.
Mannina, G., Cosenza, A., Trapani, D. D., Capodici, M., & Viviani, G. (2016). Membrane bioreactors for treatment of saline wastewater contaminated by hydrocarbons (diesel fuel): an experimental pilot plant case study. Chemical Engineering Journal, 291, 269–278.
OMI-MEPC. (2006). Revised guidelines on implementation of effluent standards and performance tests for sewage treatment plants. In: Committee MEP, editor. 159(55). MEPC 55/23 Annex 26.
OMI-MEPC. (2010). Revised guidelines on implementation of effluent standards and performance tests for sewage treatment plants. In: Committee MEP, editor. 227(64). MEPC 64/23 Annex 22.
Rao, L. V. M., DATTA, N., SOPORY, S. K., & GUHA-MUKHERJEE, S. (1980). Phytochrome mediated induction of nitrate reductase activity in etiolated maize leaves. Physiologia Plantarum, 2, 208–212.
Ridvan, K., & Bayrakl, B. (2005). Effects of N-enriched sewage sludge on soil enzyme activities. Applied Soil Ecology., 30, 192–202.
Serra, W. C., Houot, S., & Barriuso, E. (1995). Soil enzymatic response to addition of municipal solid-waste compost. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 20, 226–236.
Shi, Y., Zhao, X. T., Zhang, Y. M., & Ren, N. Q. (2009). Back propagation neural network (BPNN) prediction model and control strategies of methanogen phase reactor treating traditional Chinese medicine wastewater (TCMW). Journal of Biotechnology, 144, 70–74.
Song, H. T., Zhou, L. C., Zhang, L. J., Gao, B., Wei, D. Z., Shen, Y. L., Wang, R., Catherine, M., & Jiang, Z. B. (2011). Construction of a whole-cell catalyst displaying a fungal lipase for effective treatment of oily wastewaters. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 71, 166–170.
Su, X. M., Wang, Y. Y., Xue, B. B., Hashmi, M. Z., Lin, H. J., Chen, J. R., Wang, Z., Mei, R. W., & Sun, F. Q. (2019). Impact of resuscitation promoting factor (Rpf) in membrane bioreactor treating high-saline phenolic wastewater: Performance robustness and Rpf-responsive bacterial populations. Chemical Engineering Journal, 357, 715–723.
Sun, C., Leiknes, T. O., Weitzenböck, J., & Thorstensen, B. (2010). Development of an integrated shipboard wastewater treatment system using biofilm-MBR. Separation and Purification Technology, 75, 22–31.
Sun, F. Y., Wang, X. M., & Li, X. Y. (2013). An innovative membrane bioreactor (MBR) system for simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Process Biochemistry, 48, 1749–1756.
Svojitka, J., Dvorák, L., Studer, M., Straub, J. O., Frömelt, H., & Wintgens, T. (2017). Performance of an anaerobic membrane bioreactor for pharmaceutical wastewater treatment. Bioresource Technology, 229, 180.
Tan, X., Acquah, I., Liu, H. Z., Li, W. G., & Tan, S. W. (2019). A critical review on saline wastewater treatment by membrane bioreactor (MBR) from a microbial perspective. Chemosphere, 220, 1150–1162.
Tang, J. L., Wang, X. C., Hu, Y. S., Pu, Y. H., Huang, J., Ngo, H. H., Zeng, Y. G., & Li, Y. Y. (2019). Nutrients removal performance and sludge properties using anaerobic fermentation slurry from food waste as an external carbon source for wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 271, 125–135.
Uygur, A. (2006). Specific nutrient removal rates in saline wastewater treatment using sequencing batch reactor. Process Biochemistry, 41, 61–66.
Veraart, A. J., Dimitrov, M. R., Schrier-Ujil, A. P., Smidt, H., & Klein, D. M. (2017). Abundance, activity and community structure of denitrifiers in drainage ditches in relation to sediment characteristics, vegetation and land-use. Ecosystems, 20(5), 928–943.
Wang, L., Zheng, Z., Luo, X., & Zhang, J. (2011). Performance and mechanisms of a microbial-earthworm ecofilter for removing organic matter and nitrogen from synthetic domestic wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 195, 245–253.
Wang, X. X., Wang, S. Y., Xue, T. L., Li, B. K., Dai, X., & Peng, Y. Z. (2015). Treating low carbon/nitrogen (C/N) wastewater in simultaneous nitrification-endogenous denitrification and phosphorous removal (SNDPR) systems by strengthening anaerobic intracellular carbon storage. Water Research, 77, 191–200.
Wang, C., Liu, S. T., Xu, X. C., Guo, Y. Z., Yang, F. L., & Wang, D. (2018). Role of cyclic diguanylate in affecting microbial community shifts at different pH during the operation of simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification process. Science of the Total Environment, 637-638, 155–162.
Wang, D. P., Li, T., Huang, K. L., He, X. W., & Zhang, X. X. (2019). Roles and correlations of functional bacteria and genes in the start-up of simultaneous anammox and denitrification system for enhanced nitrogen removal. Science of the Total Environment, 655, 1355–1363.
Wu, Z. S., Xu, F., Yang, C., Su, X. X., Guo, F. C., Xu, Q. Y., Peng, G. L., He, Q., & Chen, Y. (2019). Highly efficient nitrate removal in a heterotrophic denitrification system amended with redox-active biochar: a molecular and electrochemical mechanism. Bioresource Technology, 275, 297–306.
Xiao, K., Liang, S., Wang, X. M., Chen, C. S., & Huang, X. (2019). Current state and challenges of full-scale membrane bioreactor applications: a critical review. Bioresource Technology, 271(2019), 473–481.
Zhang, G. N., Chen, Z. H., Zhang, A. M., Chen, L. J., & Wu, Z. J. (2013). Nitrogen and phosphorus related hydrolytic enzyme activities influenced by N deposition under semiarid grassland soil. In Advanced Materials Research. Trans Tech Publ (pp. 3847–3854).
Zhang, F., Li, P., & Chen, M. S. (2015). Effect of operational modes on nitrogen removal and nitrous oxide emission in the process of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification. Chemical Engineering Journal, 280, 549–557.
Zhao, L. M., Zhang, C. C., Bao, M. T., & Lu, J. R. (2019). Advanced treatment for actual hydrolyzed polyacrylamide-containing wastewater in a biofilm/activated sludge membrane bioreactor system: biodegradation and interception. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 141, 120–130.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the National Key R&D Plan of China (2017YFC1404603), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51579049), the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (E2017020), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (HEUCFG201820).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Y., Ben, T., Zaidi, A.A. et al. Effect of pH on Pollutants Removal of Ship Sewage Treatment in an Innovative Aerobic-Anaerobic Micro-Sludge MBR System. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 163 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4211-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4211-0