Abstract
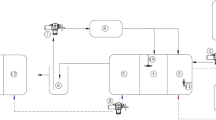
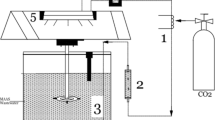
The wastewater with a high concentration of organics and salt is a major contaminant in the production of sauerkraut. In this study, a multistage active biological process (MSABP) system was constructed to treat sauerkraut wastewater. The key process parameters of the MSABP system were analyzed and optimized by response surface methodology. The optimization results indicated that the most optimal removal efficiencies and removal loading rates of chemical oxygen demand (COD) and NH4+-N were 87.9%, 95.5%, 2.11 kg·m−3·d−1 and 0.12 kg·m−3·d−1, respectively, with hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 2.5 d and pH of 7.3. Meanwhile, this system could also be improved for the further treatment of COD and total nitrogen by effluent recycle and ozone oxidation. The COD and total nitrogen removal efficiencies of the modified MSABP system were 99.9% and 60.2%, respectively. In addition, the modified system could also reduce the potential harm from high concentrations of NO2−-N.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the authors.
References
Fuchs W, Binder H, Mavrias G, Braun R (2003) Anaerobic treatment of wastewater with high organic content using a stirred tank reactor coupled with a membrane filtration unit. Water Res 37:902–908
Ahmad NNR, Ang WL, Leo CP et al (2021) Current advances in membrane technologies for saline wastewater treatment: a comprehensive review. Desalination. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2021.115170
Zhao L, She Z, Jin C et al (2016) Characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances from sludge and biofilm in a simultaneous nitrification and denitrification system under high salinity stress. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 39:1375–1389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1613-x
Luo G, Wang Z, Li Y et al (2019) Salinity stresses make a difference in the start-up of membrane bioreactor: performance, microbial community and membrane fouling. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42:445–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-018-2048-3
Tan X, Acquah I, Liu H et al (2019) A critical review on saline wastewater treatment by membrane bioreactor (MBR) from a microbial perspective. Chemosphere 220:1150–1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.027
Li J, Qi P, Qiang Z et al (2018) Is anammox a promising treatment process for nitrogen removal from nitrogen-rich saline wastewater? Bioresour Technol 270:722–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.08.115
Wang J, Liu Q, Wu B et al (2020) Effect of salinity on mature wastewater treatment biofilm microbial community assembly and metabolite characteristics. Sci Total Environ 711:134437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134437
Wang R, Xu Q, Chen C et al (2021) Microbial nitrogen removal in synthetic aquaculture wastewater by fixed-bed baffled reactors packed with different biofilm carrier materials. Bioresour Technol 331:125045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125045
Zhang K, Chen S, Chang M et al (2019) Treatment of polyacrylamide production wastewater by multistage contact reactor with activated and anammox sludge. Biochem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.107287
Chang M, Wang Y, Zhong R et al (2020) Performance of HABR + MSABP system for the treatment of dairy wastewater and analyses of microbial community structure and low excess sludge production. Bioresour Technol 311:123576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123576
Lau PL, Trzcinski AP (2022) A review of modified and hybrid anaerobic baffled reactors for industrial wastewater treatment. Water Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2022.06.004
Mendez R, Juan M et al (1995) Treatment of seafood-processing wastewaters in mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic filters. Water Environ Res 67:33–45
Shi L, Ma B, Li X et al (2019) Advanced nitrogen removal without addition of external carbon source in an anaerobic/aerobic/anoxic sequencing batch reactor. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42:1507–1515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02148-z
APHA AWWAA, Water environment federation (AEF). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (Washington, DC, USA). In: 2005.
Zhu W, Li J, Wang B, Chen G (2020) Enhancement of pollutants removal from saline wastewater through simultaneous anammox and denitrification (SAD) process with glycine betaine addition. Bioresour Technol 315:123784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123784
Guo G, Tian F, Zhang L et al (2020) Effect of salinity on removal performance in hydrolysis acidification reactors treating textile wastewater. Bioresour Technol 313:123652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123652
Ganesan S, Limphattharachai S, Chawengkijwanich C et al (2022) Influence of salinity on biofilm formation and COD removal efficiency in anaerobic moving bed biofilm reactors. Chemosphere 304:135229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135229
Ji B, Zhang H, Zhou L et al (2021) Effect of the rapid increase of salinity on anoxic-oxic biofilm reactor for treatment of high-salt and high-ammonia-nitrogen wastewater. Bioresour Technol 337:125363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125363
Corsino SF, Capodici M, Di Pippo F et al (2019) Comparison between kinetics of autochthonous marine bacteria in activated sludge and granular sludge systems at different salinity and SRTs. Water Res 148:425–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.10.086
Xu A, Yu D, Qiu Y et al (2022) A novel process of salt tolerance partial denitrification and anammox (ST-PDA) for treating saline wastewater. Bioresour Technol 345:126472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126472
Ravichandran P, Balaji K (2020) Effect of HRT on performance of hybrid upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (HUASB) reactor using bio balls in treatment of pulp and paper mill bagasse wash water. Mater Today: Proc 22:627–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.09.011
Ji J, Chen Y, Hu Y et al (2021) One-year operation of a 20-L submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor for real domestic wastewater treatment at room temperature: pursuing the optimal HRT and sustainable flux. Sci Total Environ 775:1457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145799
Kim W, Shin SG, Lim J, Hwang S (2013) Effect of temperature and hydraulic retention time on volatile fatty acid production based on bacterial community structure in anaerobic acidogenesis using swine wastewater. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36:791–798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-0905-7
Wang Y, Zhu T, Chang M, Jin D (2021) Performance of a hybrid membrane aerated biofilm reactor (H-MBfR) for shortcut nitrification. Biochem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2021.108089
Popat A, Nidheesh PV, Anantha Singh TS, Suresh Kumar M (2019) Mixed industrial wastewater treatment by combined electrochemical advanced oxidation and biological processes. Chemosphere 237:124419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124419
Zhang Z, Ni BJ, Zhang L et al (2022) Medium-chain fatty acids production from carbohydrates-rich wastewater through two-stage yeast biofilm processes without external electron donor addition: biofilm development and pH impact. Sci Total Environ 828:154428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154428
Hao TB, Balamurugan S, Zhang ZH et al (2022) Effective bioremediation of tobacco wastewater by microalgae at acidic pH for synergistic biomass and lipid accumulation. J Hazard Mater 426:1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127820
Lan M, Yang P, Xie L et al (2022) Start-up and synergistic nitrogen removal of partial nitrification and anoxic/aerobic denitrification in membrane aerated biofilm reactor. Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113901
Amalraj Appavoo I, Hu J, Huang Y et al (2014) Response surface modeling of Carbamazepine (CBZ) removal by Graphene-P25 nanocomposites/UVA process using central composite design. Water Res 57:270–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.03.007
Almomani F, Bohsale RR (2020) Optimizing nutrient removal of moving bed biofilm reactor process using response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 305:123059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123059
Kieu TQ, Nguyen TY, Dang TY et al (2015) Optimization of sulfide production by an indigenous consortium of sulfate-reducing bacteria for the treatment of lead-contaminated wastewater. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38:2003–2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1441-4
Choi D, Cho K, Jung J (2019) Optimization of nitrogen removal performance in a single-stage SBR based on partial nitritation and ANAMMOX. Water Res 162:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.06.044
Zhang M, Wang X, Zhang D et al (2022) Food waste hydrolysate as a carbon source to improve nitrogen removal performance of high ammonium and high salt wastewater in a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour Technol 349:126855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.126855
Yao J, Li W, Ou D et al (2021) Performance and granular characteristics of salt-tolerant aerobic granular reactors response to multiple hypersaline wastewater. Chemosphere 265:129170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129170
Srivastava A, Parida VK, Majumder A et al (2021) Treatment of saline wastewater using physicochemical, biological, and hybrid processes: Insights into inhibition mechanisms, treatment efficiencies and performance enhancement. J Environ Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105775
Qu J, Chen X, Zhou J et al (2019) Treatment of real sodium saccharin wastewater using multistage contact oxidation reactor and microbial community analysis. Bioresour Technol 289:121714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121714
Kim JH, Kang YJ, Kim KI et al (2019) Toxic effects of nitrogenous compounds (ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate) on acute toxicity and antioxidant responses of juvenile olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 67:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.02.001
Valencia-Castaneda G, Frias-Espericueta MG, Vanegas-Perez RC et al (2019) Toxicity of ammonia, nitrite and nitrate to Litopenaeus vannamei juveniles in low-salinity water in single and ternary exposure experiments and their environmental implications. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 70:1031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.05.002
Khuntia S, Kumar Sinha M, Saini B (2018) An approach to minimize the ozone loss in a series reactor: a case of peroxone process. J Enviro Chem Eng 6:6916–6922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.10.069
Ng KK, Shi X, Ong SL et al (2016) An innovative of aerobic bio-entrapped salt marsh sediment membrane reactor for the treatment of high-saline pharmaceutical wastewater. Chem Eng J 295:317–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.046
Zhou G, Wang Z, Li W et al (2015) Graphene-oxide modified polyvinyl-alcohol as microbial carrier to improve high salt wastewater treatment. Mater Lett 156:205–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.05.110
Aloui F, Khoufi S, Loukil S, Sayadi S (2009) Performances of an activated sludge process for the treatment of fish processing saline wastewater. Desalination 246:389–396
Wang H, Guo L, Ren X et al (2022) Enhanced aerobic granular sludge by static magnetic field to treat saline wastewater via simultaneous partial nitrification and denitrification (SPND) process. Bioresour Technol 350:126891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.126891
Zhao Y, Park HD, Park JH et al (2016) Effect of different salinity adaptation on the performance and microbial community in a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour Technol 216:808–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.032
Xu M, Zhou W, Chen X et al (2021) Analysis of the biodegradation performance and biofouling in a halophilic MBBR-MBR to improve the treatment of disinfected saline wastewater. Chemosphere 269:128716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128716
Jamal MT, Pugazhendi A (2021) Treatment of fish market wastewater and energy production using halophiles in air cathode microbial fuel cell. J Environ Manage 292:112752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112752
Zhang M, Han F, Li Y et al (2021) Nitrogen recovery by a halophilic ammonium-assimilating microbiome: a new strategy for saline wastewater treatment. Water Res 207:117832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117832
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Young and middle-aged scientific and technological innovation talents program of Shenyang in 2020 (RC200538), National Key R&D Program of China (2020YFC1806402), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21677030) and Major key and core technology research project (direction of water pollution control industry chain), Science and Technology Plan of Shenyang in 2020 (20-202-4-37). Mingdong Chang was financially supported by the scholarship (202106080057) from China Scholarship Council (CSC). Special thanks also go to Dr. FUMITAKE NISHIMURA (Kyoto University), who has commented on numerous earlier drafts of this paper.
Funding
Young and middle-aged scientific and technological innovation talents program of Shenyang in 2020, RC200538, Major key and core technology research project (direction of water pollution control industry chain), Science and Technology Plan of Shenyang in 2020,20-202-4-37, National Key R&D Program of China, 2020YFC1806402, National Natural Science Foundation of China, 21677030, China Scholarship Council, 202106080057.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhu, T., Wong, Y.J. et al. Treatment performance of multistage active biological process (MSABP) reactor for saline sauerkraut wastewater: acclimatization, optimization and improvement. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 46, 981–993 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02877-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02877-2