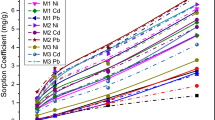
Abstract
Residues from mining, as metabasalt powder from amethyst exploration, can be used to improve soil properties. Although there is a high-load content of clay minerals in metabasalt, the effects of this residue on cooper (Cu2+) and zinc (Zn2+) sorption and desorption have not been studied. The aim of this work was to evaluate Cu2+ and Zn2+ sorption capacity of metabasalt powder and to discuss the mineralogical behavior facing this phenomenon. This residue sorption capacity was compared to reference clay minerals under two Cu2+ and Zn2+ concentrations (8 and 16 cmolc/kg) in a competitive system (Cu2+ + Zn2+). The sorption capacity was estimated by sequential desorption using cation exchange resin. A survey of mineralogical and Cu2+ and Zn2+ concentrations was performed on metabasalt before and after sorption, and after desorption tests. All materials sorbed higher amounts of Cu2+ than Zn2+. The sorption magnitude decreased in the following order: metabasalt > montmorillonite > illite > kaolinite. Cu2+ and Zn2+ desorption from metabasalt is lower than the standard clay minerals, since the metabasalt sorption sites are expandable interlayers of clay minerals. The relevance and application of our findings are critical in providing information for the management of metabasalt residue, suggesting potential use as a remediation agent in contaminated water, especially those with high Cu2+ and Zn2+ loading. It also suggests that the Cu2+ and Zn2+ enrichment of this residue could potentially be used for converting the metabasalt into a useful source of slow nutrient supply for agricultural soils.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel, S., Nybom, I., Mäenpäa, K., Hale, S. E., Cornelissen, G., & Akkanen, J. (2017). Mixing and capping techniques for activated carbon based sediment remediation—efficiency and adverse effects for Lumbriculus variegatus. Water Research, 114, 104–112.
Abreu, A. T., Korchagin, J., Bergmann, M., & Bortoluzzi, E. D. (2014). Nutrient desorption from basaltic rock. In V. M. Benites et al. (Eds.), Technological innovation for a sustainable tropical agriculture (pp. 183–185). Rio de Janeiro: Proceedings.
Al-Rashdi, T. T., & Sulaimanan, H. (2013). Bioconcentration of heavy metals in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) from farm soils around Sohar Industrial Area in Oman. Procedia, 5, 271–278.
Baghernejad, M., Javaheri, F., & Moosavi, A. A. (2015). Adsorption isotherms of copper and zinc in clay minerals of calcareous soils and their effects on X-ray diffraction. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 61(8), 1061–1077.
Boock, M. V., & Machado Neto, J. G. (2005). Estudos sobre a toxicidade aguda do oxicloreto de cobre para o peixe poecilia reticulata. Boletim do Instituto de Pesca, 31(1), 29–35.
Bortoluzzi, E. C., & Poleto, C. (2013). Methodologies for sediment study: emphasis on the proportion and mineralogical nature of the particles. In C. Poleto & G. H. Merten (Eds.), Sediment quality (pp. 35–90). Porto Alegre: URGS.
Bortoluzzi, E. C., Korchagin J., Moterle, D. F., dos Santos, D. R., & Caner L. (2019). Accumulation and precipitation of Cu and Zn in a Centenarian Vineyard. Soil Science Society of America Journal. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2018.09.0328.
Bourliva, A., Christophoridis, C., Papadopoulou, L., Giouri, K., Papadopoulos, A., Mitsika, E., & Fytianos, K. (2016). Caracterização, teor de metais pesados e avaliação dos riscos para a saúde das mulheres urbanas do centro histórico da cidade de Salónica, Grécia. Geoquímica Ambiental e Saúde, 38, 1–24.
Brindley, G. W., & Brown, G. (1980). Crystal structures of clays minerals and their X-ray identification. London: Mineralogical Society.
Brunetto, G., de Melo, G. W. B., Terzano, R., Del Buono, D., Astolfi, S., Tomasi, N., Pii, Y., Mimmo, T., & Cesco, S. (2016). Copper accumulation in vineyard soils: rhizosphere processes and agronomic practices to limit its toxicity. Chemosphere, 162, 293–307.
Caridi, F., Messina, M., & D’Agostino, M. (2017). An investigation about natural radioactivity, hydrochemistry, and metal pollution in groundwater from Calabrian selected areas, southern Italy. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 76, 668–679.
Carrado, K. A., & Wasserman, S. R. (1996). Stability of Cu(II)− and Fe(III)−porphyrins on montmorillonite clay: an X-ray absorption study. Chemistry of Materials, 8, 219–225.
Carter, D. L., Heiman, R., & Gonzales, C. L. (1965). Ethylene glycol monoethyl ether for determining surface area of silicate minerals. Soil Science, 100, 356–360.
Cheng, H., Zhang, S., Liu, Q., Li, X., & Frost, L. R. (2015). The molecular structure of kaolinite–potassium acetate intercalation complexes: a combined experimental and molecular dynamic simulation study. Applied Clay Science, 116-117, 273–280.
Choy, J. H., Yoon, J. B., & Jung, H. (2002). Polarization-dependent X-ray absorption spectroscopic study of [Cu(cyclam)]2+-intercalated saponite. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 106, 11120–11126.
Dawson, C. R., & Tarplay, W. B. (1951). The copper oxidases. In J. B. Sumner & K. Myrback (Eds.), The enzymes (pp. 454–489). New York: Elsevier.
Dias, N. S., & Blanco, F. F. (2010). Effects of salts on soil and plant. Salinity management in agriculture: basic and applied studies. Fortaleza: INCTSal.
Ely, A., Baudua, M., Baslya, J. P., & Kankoub, M. O. S. A. O. (2009). Copper and nitrophenol pollutants removal by Na-montmorillonite/alginate microcapsules. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171, 405–409.
Falchuk, K. H., Ulpino, L., Mazus, B., & Vallee, B. L. (1977). E. gracilis RNA polymerase I: a zinc metalloenzyme. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 74, 1206–1212.
Gee, G. W., & Bauder, J. W. (1986). Particle-size analysis. In A. Klute (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis, part 1: physical and mineralogical methods, agronomy monograph (No. 9, 2nd edn.). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Gomes, P. C., Fontes, M. P., da Silva, A. G., de Mendoca, S., & Netto, E. (2001). Selectivity sequence and competitive adsorption of heavy metals by Brazilian soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 1115–1121.
Gongadze, E., & Iglic, A. (2015). Asymmetric size of ions and orientational ordering of water dipoles in electric double layer model—an analytical mean-field approach. Electrochimica Acta, 178, 541–545.
Grattan, J. P., Adams, R. B., Friedman, H., Gilbertson, D. D., Haylock, K. I., Hunt, C. O., & Kent, M. (2016). The first polluted river? Repeated copper contamination of fluvial sediments associated with Late Neolithic human activity in southern Jordan. Science of the Total Environment, 573, 247–257.
Hartmann, L. A. (2010). Geodos com ametistas formados por água quente no tempo dos dinossauros. Porto Alegre: UFRGS.
Hartmann, L., & Silva, J. T. (2010). Tecnologias no Setor de Gemas, Joias e Mineração: IGEO. Porto Alegre: UFRGS.
He, H. P., Guo, J. G., Xie, X. D., & Peng, J. L. (2001). Location and migration of cations in Cu2+adsorbed montmorillonite. Environment International, 26, 347–352.
Hoog, D. S., McLaren, R. G., & Swift, R. S. (1993). Desorption of copper from some New Zealand soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 57(2), 361–366.
Hsu, P. H. (1989). Aluminum hydroxides and oxyhydroxides. In J. B. Dixon & B. Weed (Eds.), Minerals in soil environments (pp. 331–378). Madison: Soil Science Society of America.
Kang, F., Ge, Y., Hu, X., Goikavi, C., Waigi, M. G., Gao, Y., & Ling, W. (2016). Understanding the sorption mechanisms of aflatoxin B1 to kaolinite, illite, and smectite clays via a comparative computational study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 320, 80–87.
Korchagin, J., Caner, L., & Bortoluzzi, E. (2019). Variability of amethyst mining waste: a mineralogical and geochemical approach to evaluate the potential use in agriculture. Journal of Cleaner Production, 210, 749–758.
Kukkadapu, R. K., & Kevan, L. (1988). Synthesis and electron spin resonance studies of copper-doped alumina-pillared montmorillonite clay. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 92, 6073–6078.
Li, Z., Schulz, L., Ackley, C., & Fenske, N. (2010). Adsorption of tetracycline on kaolinite with pH-dependent surface charges. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 351(1), 254–260.
Malandrino, M., Abollino, O., Giacomino, A., Aceto, M., & Mentasti, E. (2006). Adsorption of heavy metals on vermiculite: influence of pH and organic ligands. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 299, 537–546.
McKean, S. J., & Warren, G. P. (1996). Determination of phosphate desorption characteristics in soils using successive resin extractions. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 27, 2397–2417.
Meunier, A., Formoso, M. L. L., Patrier, P., & Chies, J. O. (1988). Altération Hydrothermale de roches Volcaniques Liée à la Genése des Améthystes - Bassin du Paraná - Sud du Brésil. Geochimica Brasiliensis, 2, 127–142.
Minkina, T. M., Pinskii, D. L., Bauer, T. V., Nevidomskaya, D. G., Mandzhieva, S. S., & Sushkova, S. N. (2017). Sorption of Cu2+ by chernozems in southern Russia. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 174, 107–112.
Morgan, R. K., & Taylor, E. (2004). Copper accumulation in vineyard soils in New Zealand. Environmental Science & Technology, 1, 139–167.
Morton, J. D., Semrau, J. D., & Hayes, K. F. (2001). An X-ray absorption spectroscopy study of the structure and reversibility of copper adsorbed to montmorillonite clay. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65, 2709–2722.
Nascimento, C. W. A., & Fontesr, R. L. F. (2004). Correlação entre características de latossolos e parâmetros de equações de adsorção de cobre e zinco. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 28, 965–971.
Nemeth, T., Mohai, I., & Toth, M. (2005). Adsorption of copper and zinc ions on various montmorillonites: an XRD study. Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, 46, 29–36.
Qi, S., Xue, Q., Niu, Z., Zhang, Y., & Liu, F. (2016). Chen H. Investigation of Zn2+ and Cd2+. Adsorption performance by different weathering basalts. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 227(4), 126–142.
Rezaei, A., Shayestehfar, M., Hassani, H., & Mohammadi, M. R. T. (2015). Assessment of the metals contamination and their grading by SAW method: a case study in Sarcheshmeh copper complex, Kerman, Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74, 3191–3205.
Richards, L. A. (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Washington: USSL.
Righi, D., Terribile, F., & Petit, S. (1995). Low-charge to high-charge beidellite conversion in a Vertisol from South Italy. Clays and Clay Minerals, 43, 495–502.
Rybicka, E. H., Calmano, W., & Breeger, A. (1995). Heavy metals sorption/desorption on competing clay minerals: an experimental study. Applied Clay Science, 9, 369–381.
Sdiri, A., Higashi, T., Chaabouni, R., & Jamoussi, F. (2012). Competitive removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by montmorillonitic and calcareous clays. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 223, 1191–1204.
Sheikhhosseini, A., Shirvani, M., & Shariatmadari, H. (2013). Competitive sorption of nickel, cadmium, zinc and copper on palygorskite and sepiolite silicate clay minerals. Geoderma, 192, 249–253.
Shukla, L. M. (2002). Sorption of Zn and Cd on soil clays. Agrochem, 44, 101–106.
Sipos, P. (2003). Distribution of Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in natural brown forest soil profiles from the Cserhat Mts., Ne Hungary. Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, 44, 43–50.
Sodré, F., & Lenzi, E. (2001). Use of physicochemical adsorption models in the study of copper behavior in clay soils. Química Nova, 24, 324–330.
Spark, K. M., Wells, J. D., & Johnson, B. B. (1995). Characterizing trace metal adsorption on kaolinite. European Journal of Soil Science, 46, 633–640.
Sparks, D. L. (1995). Sorption phenomena on soils. In D. L. Sparks (Ed.), Environmental soil chemistry (pp. 99–139). San Diego: Academic Press.
Sposito, G. (1989). The chemistry of soils. New York: Oxford University Press.
Stiles, W. (1961). Trace elements in plants, University Press, Cambridge. The Clay Mineral Society (2015) Source Clays. http://www.clays.org/sourceclays_available_special_clays.html. Accessed 15 January 2015.
Tiecher, T., Zafar, M., Mallmann, F. J. K., Bender, M. A., Ciotti, L. H., & dos Santos, D. R. (2014). Animal manure phosphorus characterization by sequential chemical fractionation, release kinetics and 31P-NMR analysis. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 38(5), 1506–1514.
Turan, N. G., Elevli, S., & Mesci, B. (2011). Adsorption of copper and zinc ions on illite: determination of the optimal conditions by the statistical design of experiments. Applied Clay Science, 52, 392–399.
Valladares, G. S., Azevedo, E. C. D., Camargo, O. A. D., Grego, C. R., & Rastoldo, A. M. C. S. (2009). Spatial variability and availability of copper and zinc in vineyard soils and vicinities. Bragantia, 68, 733–742.
Vega, F., Covelo, E., & Andrade, M. (2006). Competitive sorption and desorption of heavy metals in mine soils: influence of mine soil characteristics. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 298, 582–592.
Vitanović, E., Vidaček, Z., Katalinić, M., Kačić, S., & Miloš, B. (2010). Copper in surface layer of Croatian vineyard soils. Journal of Food, Agriculture and Environment, 8(1), 268–274.
Wahba, M. M., & Zaghloul, A. M. (2007). Adsorption characteristics of some heavy metals by some soil minerals. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 3, 421–426.
Welp, G., & Brümmer, G. W. (1999). Adsorption and solubility of ten metals in soil samples of different composition. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 162, 155–161.
Zhang, Q., Shu, X., Guo, X., Mo, D., Wei, S., & Yang, C. (2016). Effect of ions on sorption of tylosin on clay minerals. RSC Advances, 6, 53175–53181.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support accorded (MCTI Edital CT mineral 51/2013, 406763/2013-5).
Funding
The Coordination of Improvement of Higher-Level Personnel (Capes) by the Prosuc/Capes fellowship was accorded to L. Dalacorte. The National Research Council (CNPq) by the productivity fellowship was accorded to E.C. Bortoluzzi (306551/2015-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalacorte, L., Escosteguy, P.A.V. & Bortoluzzi, E.C. Sorption of Copper and Zinc from Aqueous Solution by Metabasalt Residue and its Mineralogical Behavior. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 90 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4141-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4141-x