Abstract
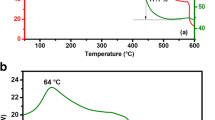
A rutin-Cr(III) loaded alginate microspheres, which can act as reduction-adsorption microreactor, was designed to reduce Cr(VI) to Cr(III) and recover it. Different from the rutin-Cr(III) complex in alginate-chitosan microcapsule we previously reported, which can sustained release rutin-Cr(III) and reduce Cr(VI) to Cr(III), this microreactor can not only reduce Cr(VI) but also adsorb/recover Cr(III) in aqueous solution. This microreactor was prepared by loading metal complex of rutin into alginate microsphere. It was found that Cr(VI) was initially reduced to Cr(III) by rutin-Cr(III), and then the product Cr(III) was absorbed in the microspheres. Both Cr(VI) reduction rate and Cr(III) adsorption rate were pH-dependent. Cr(VI) can be completely reduced to Cr(III) at pH 1–4 with a reduction capability of 1.27 (±0.078) mmol/g (pH 1, 4 h). The highest blank alginate microsphere adsorption capacity was 1.82 (±0.042) mmol/g at pH 4. It was assumed that reduction-adsorption was the mechanism of total Cr removal by the reduction-absorption microreactor. Recovery experiment showed that 93% and 98% of Cr(III) can be recovered by EDTA and sodium citrate, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertoni, F. A., Bellu, S. E., Gonzalez, J. C., & Sala, L. F. (2014). Reduction of hypervalent chromium in acidic media by alginic acid. Carbohydrate Polymers, 114, 1–11.
Chauhan, D., Jaiswal, M., & Sankararamakrishnan, N. (2012). Removal of cadmium and hexavalent chromium from electroplating waste water using thiocarbamoyl chitosan. Carbohydrate Polymers, 88, 670–675.
Chen, W., Sun, S., Cao, W., Liang, Y., & Song, J. (2009). Antioxidant property of quercetin-Cr(III) complex: the role of Cr(III) ion. Journal of Molecular Structure, 918, 194–197.
Chen, J. H., Xing, H. T., Guo, H. X., Li, G. P., Weng, W., & Hu, S. R. (2013). Preparation, characterization and adsorption properties of a novel 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane functionalized sodium alginate porous membrane adsorbent for Cr(III) ions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 248, 285–294.
Chueh, B.-H., Zheng, Y., Torisawa, Y.-S., Hsiao, A. Y., Ge, C., Hsiong, S., Huebsch, N., Franceschi, R., Mooney, D. J., & Takayama, S. (2010). Patterning alginate hydrogels using light-directed release of caged calcium in a microfluidic device. Biomedical Microdevices, 12, 145–151.
Fruchter, J. S., Cole, C. R., Williams, M. D., Vermeul, V. R., Amonette, J. E., Szecsody, J. E., Istok, J. D., & Humphrey, M. D. (2000). Creation of a subsurface permeable treatment zone for aqueous chromate contamination using in situ redox manipulation. Ground Water Monitoring and Remediation, 20, 66–77.
Gaserod, O., Sannes, A., & Skjak-Braek, G. (1999). Microcapsules of alginate-chitosan. II. A study of capsule stability and permeability. Biomaterials, 20, 773–783.
Gupta, S., & Babu, B. V. (2009). Removal of toxic metal Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using sawdust as adsorbent: equilibrium, kinetics and regeneration studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 150, 352–365.
Ibanez, J. P., & Umetsu, Y. (2002). Potential of protonated alginate beads for heavy metals uptake. Hydrometallurgy, 64, 89–99.
Ibanez, J. P., & Umetsu, Y. (2004). Uptake of trivalent chromium from aqueous solutions using protonated dry alginate beads. Hydrometallurgy, 72, 327–334.
Jin, F., Xiang, Q., Chen, X., Peng, X., & Xing, X. (2016). An environmentally benign dual action antimicrobial: quaternized chitosan/sodium alga acid multilayer films and silver nanoparticles decorated onto magnetic nanoparticles. Journal of Biomaterials Science Polymer Edition, 27, 1447–1461.
Kaygusuz, H., Çoşkunırmak, M. H., Kahya, N., & Erim, F. B. (2014). Aluminum alginate–montmorillonite composite beads for defluoridation of water. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 226, 1–9.
Kumar, A. S. K., Jiang, S.-J., & Tseng, W.-L. (2015). Effective adsorption of chromium(VI)/Cr(III) from aqueous solution using ionic liquid functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a super sorbent. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 3, 7044–7057.
Li, Y., Liu, F., Xia, B., Du, Q., Zhang, P., Wang, D., Wang, Z., & Xia, Y. (2010). Removal of copper from aqueous solution by carbon nanotube/calcium alginate composites. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177, 876–880.
Li, H., Li, J., Wang, W., Yang, Z., Xu, Q., & Hu, X. (2013). A subnanomole level photoelectrochemical sensing platform for hexavalent chromium based on its selective inhibition of quercetin oxidation. Analyst, 138, 1167–1173.
Lu, M., Cheng, Y., Pan, S.-l., Yang, T.-l., & Zhang, Z.-Z. (2015). Preparation of TiO2/Silicalite-2@CoFe2O4 magnetic composites and evaluation of their photocatalytic activity in Cr(VI) removal. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 226, 1–10.
Martone, N., Rahman, G. M. M., Pamuku, M., & Kingston, H. M. S. (2013). Determination of chromium species in dietary supplements using speciated isotope dilution mass spectrometry with mass balance. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61, 9966–9976.
Masuda, K., Sah, R. L., Hejna, M. J., & Thonar, E. (2003). A novel two-step method for the formation of tissue-engineered cartilage by mature bovine chondrocytes: the alginate-recovered-chondrocyte (ARC) method. Journal of Orthopaedic Research, 21, 139–148.
Ngah, W. S. W., & Fatinathan, S. (2008). Adsorption of Cu(II) ions in aqueous solution using chitosan beads, chitosan–GLA beads and chitosan–alginate beads. Chemical Engineering Journal, 143, 62–72.
Obeid, L., El Kolli, N., Dali, N., Talbot, D., Abramson, S., Welschbillig, M., Cabuil, V., & Bee, A. (2014). Adsorption of a cationic surfactant by a magsorbent based on magnetic alginate beads. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 432, 182–189.
Okello, V. A., Mwilu, S., Noah, N., Zhou, A., Chong, J., Knipfing, M. T., Doetschman, D., & Sadik, O. A. (2012). Reduction of hexavalent chromium using naturally-derived flavonoids. Environmental Science & Technology, 46, 10743–10751.
Park, D., Yun, Y. S., & Park, J. M. (2004). Reduction of hexavalent chromium with the brown seaweed Ecklonki biomass. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 4860–4864.
Park, D., Lim, S. R., Yun, Y. S., & Park, J. M. (2007a). Reliable evidences that the removal mechanism of hexavalent chromium by natural biomaterials is adsorption-coupled reduction. Chemosphere, 70, 298–305.
Park, D., Yun, Y.-S., Ahn, C. K., & Park, J. M. (2007b). Kinetics of the reduction of hexavalent chromium with the brown seaweed Ecklonia biomass. Chemosphere, 66, 939–946.
Park, D., Yun, Y.-S., Kim, J. Y., & Park, J. M. (2008a). How to study Cr(VI) biosorption: Use of fermentation waste for detoxifying Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 136, 173–179.
Park, D., Yun, Y.-S., & Park, J. M. (2008b). XAS and XPS studies on chromium-binding groups of biomaterial during Cr(VI) biosorption. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 317, 54–61.
Park, D., Yun, Y. S., Lee, H. W., & Park, J. M. (2008c). Advanced kinetic model of the Cr(VI) removal by biomaterials at various pHs and temperatures. Bioresource Technology, 99, 1141–1147.
Qi, Y., Jiang, M., Cui, Y.-L., Zhao, L., & Liu, S. (2015). Novel reduction of Cr(VI) from wastewater using a naturally derived microcapsule loaded with rutin-Cr(III) complex. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 285, 336–345.
Rajiv Gandhi, M., & Meenakshi, S. (2013). Preparation of amino terminated polyamidoamine functionalized chitosan beads and its Cr(VI) uptake studies. Carbohydrate Polymers, 91, 631–637.
Seaman, J. C., Bertsch, P. M., & Schwallie, L. (1999). In situ Cr(VI) reduction within coarse-textured, oxide-coated soil and aquifer systems using Fe(II) solutions. Environmental Science & Technology, 33, 938–944.
Shen, F., Su, J., Zhang, X., Zhang, K., & Qi, X. (2016). Chitosan-derived carbonaceous material for highly efficient adsorption of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 91, 443–449.
Sillerova, H., Chrastny, V., Cadkova, E., & Komarek, M. (2014). Isotope fractionation and spectroscopic analysis as an evidence of Cr(VI) reduction during biosorption. Chemosphere, 95, 402–407.
Tu, L., He, Y., Yang, H., Wu, Z., & Yi, L. (2015). Preparation and characterization of alginate–gelatin microencapsulated Bacillus subtilis SL-13 by emulsification/internal gelation. Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition, 26, 735–749.
Wang, W., Liu, X., Xie, Y., Zhang, H. a., Yu, W., Xiong, Y., Xie, W., & Ma, X. (2006). Microencapsulation using natural polysaccharides for drug delivery and cell implantation. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 16, 3252–3267.
Yang, J., Chen, S., & Fang, Y. (2009). Viscosity study of interactions between sodium alginate and CTAB in dilute solutions at different pH values. Carbohydrate Polymers, 75, 333–337.
Yu, K., Ho, J., McCandlish, E., Buckley, B., Patel, R., Li, Z., & Shapley, N. C. (2013). Copper ion adsorption by chitosan nanoparticles and alginate microparticles for water purification applications. Colloids and Surfaces a-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 425, 31–41.
Zhou, Q., Lin, X., Li, B., & Luo, X. (2014). Fluoride adsorption from aqueous solution by aluminum alginate particles prepared via electrostatic spinning device. Chemical Engineering Journal, 256, 306–315.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin, China, (16JCYBJC20700), Tianjin Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology (15JCZDJC40400), and Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment of China (2014ZX07203-009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, M., Qi, Y., Cui, YL. et al. Removal and Recovery of Chromium from Aqueous Solutions by Reduction-Absorption Microreactor. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 26 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3203-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3203-6