Abstract
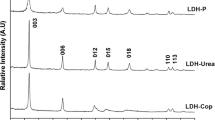
Ca-Al layered double hydroxides (LDHs) with different Ca/Al molar ratios were composited at pH ranges, using a co-precipitation method, and were experimented to remove fluoride from wastewater and studied in terms of isotherm models such as Langmuir and Freundlich reactions. The composite LDHs were characterized with X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The results showed that different synthesis conditions of Ca-Al LDHs had an influence on their morphology, layered structure, and particle size distribution, which substantially affected the uptake capacity for aqueous fluoride. LDHs with the Ca/Al molar ratio of 2 and synthesized at the pH of 12 had the highest capacity for the fluoride removal (e.g., 146.6 mg/g) and such reaction reached an equilibrium within 1 h. The Freundlich model was a better fit for this study. The high adsorption method of Ca-Al LDHs can be favorable to removing fluoride from wastewater streams.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chagas, L. H., De Carvalho, G. S. G., Do Carmo, W. R., San Gil, R. A. S., Chiaro, S. S. X., Leitão, A. A., Diniz, R., De Sena, L. A., & Achete, C. A. (2015). MgCoAl and NiCoAl LDHs synthesized by the hydrothermal urea hydrolysis method: structural characterization and thermal decomposition. Materials Research Bulletin, 64, 207–215.
Chang, Q., Zhu, L., Luo, Z., Lei, M., Zhang, S., & Tang, H. (2011). Sono-assisted preparation of magnetic magnesium-aluminum layered double hydroxides and their application for removing fluoride. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 18, 553–561.
Goh, K. H., Lim, T. T., & Dong, Z. (2008). Application of layered double hydroxides for removal of oxyanions: a review. Water Research, 42, 1343–1368. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.10.043.
Kang, D., Yu, X., Tong, S., Ge, M., Zuo, J., Cao, C., & Song, W. (2013). Performance and mechanism of Mg/Fe layered double hydroxides for fluoride and arsenate removal from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 228, 731–740. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.041.
Koilraj, P., & Kannan, S. (2013). Aqueous fluoride removal using ZnCr layered double hydroxides and their polymeric composites: batch and column studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 234, 406–415. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2013.08.101.
Kovanda, F., et al. (2009). Effect of hydrothermal treatment on properties of Ni–Al layered double hydroxides and related mixed oxides. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 182, 27–36. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2008.09.014.
Li, X., Wu, P., Han, Z., & Shi, J. (2016). Sources, distributions of fluoride in waters and its influencing factors from an endemic fluorosis region in central Guizhou, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75:981. doi:10.1007/s12665-016-5779-y.
Ma, W., Lv, T., Song, X., Cheng, Z., Duan, S., Xin, G., Liu, F., & Pan, D. (2014). Characteristics of selective fluoride adsorption by biocarbon-Mg/Al layered double hydroxides composites from protein solutions: kinetics and equilibrium isotherms study. Journal of Hazardous materials, 268, 166–176. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.013.
Mandal, S., & Mayadevi, S. (2008a). Adsorption of fluoride ions by Zn–Al layered double hydroxides. Applied Clay Science, 40, 54–62. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2007.07.004.
Mandal, S., & Mayadevi, S. (2008b). Cellulose supported layered double hydroxides for the adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution. Chemosphere, 72, 995–998. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.03.053.
Mandal, S., Tripathy, S., Padhi, T., Sahu, M. K., & Patel, R. K. (2013). Removal efficiency of fluoride by novel Mg-Cr-Cl layered double hydroxide by batch process from water. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25, 993–1000. doi:10.1016/s1001-0742(12)60146-6.
Miller, L., & Witt, J. (1929). Solubility of calcium hydroxide. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 33, 285–289.
Rao, P., Sun, Z., Zhang, W., Yao, W., Wang, L., & Ding, G. (2015). Preparation and application of amorphous Fe–Ti bimetal oxides for arsenic removal. RSC Advances, 5, 89545–89551.
Riahi, F., Bagherzadeh, M., & Hadizadeh, Z. (2015). Modification of Fe3O4 superparamagnetic nanoparticles with zirconium oxide; preparation, characterization and its application toward fluoride removal. RSC Advances, 5, 72058–72068.
Sajil Kumar, P. J., Jegathambal, P., & James, E. J. (2014). Factors influencing the high fluoride concentration in groundwater of Vellore District, South India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72, 2437–2446.
Theiss, F. L., Ayoko, G. A., & Frost, R. L. (2016). Synthesis of layered double hydroxides containing Mg2+, Zn2+, Ca2+ and Al3+ layer cations by co-precipitation methods—a review. Applied Surface Science, 383, 200–213.
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking-water quality: recommendations[M]. World Health Organization vol 1.
Xu, S., Zhang, B., Chen, Z., Yu, J., Evans, D. G., & Zhang, F. (2011). A general and scalable formulation of pure CaAl-Layered double hydroxide via an organic/water solution route. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 50, 6567–6572. doi:10.1021/ie102135k.
Yan, L., Yang, K., Shan, R., Yan, T., Wei, J., Yu, S., Yu, H., & Du, B. (2015). Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic investigations of phosphate adsorption onto core-shell Fe3O4@LDHs composites with easy magnetic separation assistance. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 448, 508–516. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2015.02.048.
Zhang, T., Li, Q., Xiao, H., Lu, H., & Zhou, Y. (2012). Synthesis of Li–Al layered double hydroxides (LDHs) for efficient fluoride removal. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 51, 11490–11498.
Zhang, T., Li, Q., Xiao, H., Mei, Z., Lu, H., & Zhou, Y. (2013). Enhanced fluoride removal from water by non-thermal plasma modified CeO2/Mg–Fe layered double hydroxides. Applied Clay Science, 72, 117–123. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2012.12.003.
Zhang, J., Chen, N., Tang, Z., Yu, Y., Hu, Q., & Feng, C. (2015). A study of the mechanism of fluoride adsorption from aqueous solutions onto Fe-impregnated chitosan. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 17, 12041–12050.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Park, JS., Kim, D. et al. Synthesis and Adsorption Properties of Ca-Al Layered Double Hydroxides for the Removal of Aqueous Fluoride. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 23 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3160-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3160-0