Abstract
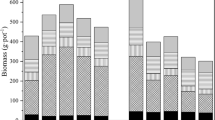
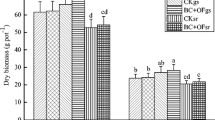
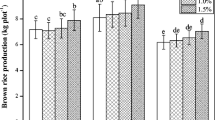
At present, the remediation of heavy-metal-polluted cropland soil is a considerable problem. In this study, in situ immobilization field experiment was conducted by planting rice (Oryza sativa L.) in low Cd-contaminated paddy soil to determine the optimal soil amendment that would reduce the accumulation of Cd in brown rice. GL (main component is alkaline residue), FG (main components are Si and Ca), and SH (main component is lime) were utilized as amendments. The remediation effects of the amendments on the soil and rice were investigated, and the potential mechanisms of reducing Cd availability to rice were analyzed. Amendment application significantly increased the soil pH value, reduced the DTPA-extractable Cd concentrations, and shifted Cd species from the exchangeable Cd fractions to the carbonate-bound, Fe-Mn oxides and residual fractions in paddy soil. For the plant, amendment application apparently increased the concentrations of Ca in rice plants, which could compete with Cd in root uptake. Besides, amendment application also effectively restricted the translocation of Cd from roots to shoots and consequently led to a notable decrease of Cd concentration in brown rice. These results demonstrated that the FG ameliorant could be effective in reducing Cd bioavailability and accumulation in rice grown on low Cd-contaminated paddy soils.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DTPA:
-
Diethylene triamine pentacetic acid
- CEC:
-
Cation exchange capacity
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
References
Bolan, N. S., Makino, T., Kunhikrishnan, A., Kim, P. J., Ishikawa, S., Murakami, M., et al. (2013). Chapter Four—Cadmium Contamination and Its Risk Management in Rice Ecosystems. Advances in Agronomy, 119(47), 183–273.
Broadley, M., Brown, P., Buerkert, A., Cakmak, I., Cooper, J., Eichert, T., et al. (2012). Copyright——Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants (Third Edition). Marschners Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 68(4), iv.
Cho, S. C., Chao, Y. Y., & Kao, C. H. (2012). Calcium deficiency increases Cd toxicity and Ca is required for heat-shock induced Cd tolerance in rice seedlings. Journal of Plant Physiology, 169(9), 892–898.
Grasshoff, K., Kremling, K., & Ehrhardt, M. (2007). Chapter 13. Determination of natural radioactive tracers: Wiley − VCH Verlag GmbH.
Gu, H. H., Qiu, H., Tian, T., Zhan, S. S., Deng, T. H. B., Chaney, R. L., et al. (2011). Mitigation effects of silicon rich amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on multi-metal contaminated acidic soil. Chemosphere, 83(9), 1234–1240.
Huang, J. H., Hsu, S. H., & Wang, S. L. (2011). Effects of rice straw ash amendment on Cu solubility and distribution in flooded rice paddy soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186(2-3), 1801–1807.
Janoš, P., Vávrová, J., Herzogová, L., & Pilařová, V. (2010). Effects of inorganic and organic amendments on the mobility (leachability) of heavy metals in contaminated soil: a sequential extraction study. Geoderma, 159(3–4), 335–341.
JF, M., K, T., N, Y., N, M., S, K., M, K., et al. (2006). A silicon transporter in rice. Nature, 440(7084), 688-691.
Komárek, M., Vaněk, A., & Ettler, V. (2013). Chemical stabilization of metals and arsenic in contaminated soils using oxides—a review. Environmental Pollution, 172(172C), 9–22.
Liang, X., Han, J., Xu, Y., Sun, Y., Wang, L., & Tan, X. (2014). In situ field-scale remediation of Cd polluted paddy soil using sepiolite and palygorskite. Geoderma, 235–236(4), 9–18.
Lindsay, W. L., & Norvell, W. A. (1966). Development of a DTPA Soil Test for Zinc, Iron, Manganese, and Copper. Voprosy Virusologii, 11(5), 421–428.
Makino, T., Sugahara, K., Sakurai, Y., Takano, H., Kamiya, T., Sasaki, K., et al. (2006). Remediation of cadmium contamination in paddy soils by washing with chemicals: selection of washing chemicals. Environmental Pollution, 144(1), 2–10.
Ming, L., Yong, Z., Khan, S., Qin, P. F., & Liao, B. H. (2010). Pollution, fractionation, and mobility of Pb, Cd, Cu, and Zn in garden and paddy soils from a Pb/Zn mining area. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 168(1-4), 215–222.
Ministry of Environmental Protection, Ministry of Land and Resources of China, 2014. National Survey of Soil Pollution Bulletin. Beijing.
Misra, U. K., Gawdi, G., Akabani, G., & Pizzo, S. V. (2002). Cadmium-induced DNA synthesis and cell proliferation in macrophages: the role of intracellular calcium and signal transduction mechanisms. Cellular Signalling, 14(4), 327–340.
Moshat, S., Datta, S., Bandyopadhyay, A., & Pal, P. K. (2010). Optimization of CNC end milling process parameters using PCA-based Taguchi method. International Journal of Engineering Science & Technology, 2(1), 92–102.
Perfus-Barbeoch, L., Leonhardt, N., Vavasseur, A., & Forestier, C. (2002). Heavy metal toxicity: cadmium permeates through calcium channels and disturbs the plant water status. Plant Journal for Cell & Molecular Biology, 32(32), 539–548.
Rizwan, M., Meunier, J. D., & Keller, C. (2012). Frontiers | Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio W.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 209–210(209-210), 326–334.
Shi, G., Cai, Q., Liu, C., & Wu, L. (2010). Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in peanut plants in relation to cadmium distribution and stimulation of antioxidative enzymes. Plant Growth Regul. Plant Growth Regulation, 61(1), 45–52.
Suthar, V., Mahmood-ul-Hassan, M., Memon, K. S., & Rafique, E. (2013). Heavy-metal phytoextraction potential of spinach and mustard grown in contaminated calcareous soils. Communications in Soil Science & Plant Analysis, 44(18), 2757–2770.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51(7), 844–851.
Tica, D., Udovic, M., & Lestan, D. (2011). Immobilization of potentially toxic metals using different soil amendments. Chemosphere, 85(4), 577–583.
Ueno, D., Koyama, E., Yamaji, N., & Ma, J. F. (2011). Physiological, genetic, and molecular characterization of a high-Cd-accumulating rice cultivar, Jarjan. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62(7), 2265–2272(2268).
Uraguchi, S., Mori, S., Kuramata, M., Kawasaki, A., Arao, T., & Ishikawa, S. (2009). Root-to-shoot Cd translocation via the xylem is the major process determining shoot and grain cadmium accumulation in rice. Journal of Experimental Botany, 60(9), 2677–2688.
Vaculík, M., Landberg, T., Greger, M., Luxová, M., Stoláriková, M., & Lux, A. (2012). Silicon modifies root anatomy, and uptake and subcellular distribution of cadmium in young maize plants. Annals of Botany, 110(2), 433–443.
Xiao, W., Ye, X., Yang, X., Li, T., Zhao, S., & Qi, Z. (2015). Effects of alternating wetting and drying versus continuous flooding on chromium fate in paddy soils. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 113c(113C), 439-445.
Zanuzzi, A., Faz, A., & Acosta, J. A. (2013). Chemical stabilization of metals in the environment: a feasible alternative for remediation of mine soils. Environmental Earth Sciences, 70(6), 2623–2632.
Zhang, J. T., Dong, Y., & Xi, Y. (2008a). A comparison of SOFM ordination with DCA and PCA in gradient analysis of plant communities in the midst of Taihang Mountains, China. Ecological Informatics, 3(6), 367–374.
Zhang, C., Wang, L., Nie, Q., Zhang, W., & Zhang, F. (2008b). Long-term effects of exogenous silicon on cadmium translocation and toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environmental & Experimental Botany, 62(3), 300–307.
Zhang, Q., Yan, C., Liu, J., Lu, H., Wang, W., Du, J., et al. (2013). Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. seedlings in relation to root anatomy and radial oxygen loss. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 76(1-2), 187–193.
Zhou, H., Zhou, X., Zeng, M., Liao, B. H., Liu, L., Yang, W. T., et al. (2014). Effects of combined amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on contaminated paddy soil. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 101(1), 226–232.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (Grant No. 2014A020216019), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (Grant No. 2015A030310221), and the Dean Fund of Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Grant No. 201524).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Lf., Ai, Sy., Wang, Yh. et al. In Situ Field-Scale Remediation of Low Cd-Contaminated Paddy Soil Using Soil Amendments. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 342 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3041-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3041-6