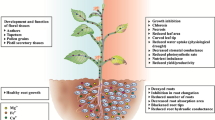
Abstract
Earthworms are important soil macroinvertebrates and are often used in assessing soil pollution. The present study was conducted in order to investigate the effect of two compounds, triple superphosphate (TSP; fertilizer), sekator (herbicide), and their mixture at two agricultural doses on a Lumbricus terrestris population. Neurotoxicity (acetylcholinesterase (AChE)), metabolization (glutathione-S-transferase (GST)), glutathione (GSH), and protein content were evaluated as biomarkers. Treated earthworms with sekator showed a non-significant increase of protein content (p > 0.05). In contrast, protein content increased significantly (p < 0.0001) up to (104.75 ± 4.75 and 109.09 ± 5.4 μg/worm) after 72 h of exposure with TSP and the mixture, respectively. As compared with TSP exposure, sekator in mixture substantially decreased AChE activity. In control series, the GST activities and GSH concentrations remain stable after 72 h while sekator and TSP induced the biomarker responses, which was proportional to exposure time and administered dose. Non-significant correlations were recorded between AChE and GSH, GST and the protein contents in most interactions. The obtained results indicate that application of sekator in mixture with triple superphosphate could have harmful effects on earthworms since it caused significant changes in measured biomarkers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aly, M. A., & Schröder, P. (2008). Effect of herbicides on glutathione S-transferases in the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 15, 143–149.
Badamassi, D. (2006). Les phosphates naturels de Tahoua (éd.), RECA, Niger.
Barlett, M. D., Briones, M. J. I., Neilson, R., Schmidt, O., Spurgeon, D., & Creamer, R. E. (2010). A critical review of current methods in earthworm ecology: from individuals to populations. European Journal of Soil Biology, 46, 67–73.
Bélanger, D. (2009). Utilisation de la faune marcobenthique comme bioindicateur de la qualité de l’environnement marin cotier, Sherbrooke (ed.), Québec, Canada.
Booth, L. H., Happelthwaite, V. J., & Ohallaron, K. (2000). Growth, development and fecundity of the earthworm Aporrectodea calignosa after exposure to two organosphosphates. New Zealand Plant Protection, 53, 221–225.
Bradford, M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Calisi, A., Lionetto, M. G., & Schettino, T. (2011). Biomarker response in the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris exposed to chemical pollutants. Science of the Total Environment, 409, 4456–4464.
Calisi, A., Zaccarelli, N., Lionetto, M. G., & Schettino, T. (2013). Integrated biomarker analysis in the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris: application to the monitoring of soil heavy metal pollution. Chemosphere, 90, 2637–2644.
Capowiez, Y., Rault, M., Mazzia, C., & Belzunces, L. (2003). Earthworm behaviour as a biomarker—a case study using imidacloprid. Pedobiologia, 47, 542–547.
Pelosi, C., Barot, S., Capowiez, Y., Hedde, M., & Vandenbulcke, F. (2013). Pesticides and earthworms. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 34, 199–228.
Denoyelle, R., Rault, M., Mazzia, C., Mascle, O., & Capowiez, Y. (2007). Cholinesterase activity as a biomarker of pesticide exposure in Allolobophora chlorotica earthworms living in apple orchards under different management strategies. Environmental Toxicology Chemistry, 26, 2644–2649.
Ellman, G. L., Courtney, K. D., Andres, V., & Featherstone, R. M. (1961). A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochemical Pharmacology, 7, 88–90.
Fonte, S. J., Winsome, T., & Six, J. (2009). Earthworm populations in relation to soil organic matter dynamics and management in California tomato cropping systems. Applied Soil Ecology, 41, 206–214.
Gambi, N., Pasteris, A., & Fabbri, E. (2007). Acetylcholinesterase activity in the earthworm Eisenia andrei at different conditions of carbaryl exposure. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. C, 145, 678–685.
Gastaldi, L., Hankard, P., Peres, G., Canesi, L., Viarengo, A., & Pons, G. (2007). Application of a biomarker battery for the evaluation of the sublethal effects of pollutants in the earthworm Eisenia andrei. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. C, 146, 398–405.
Gudbrandsen, M., Line, L. E., Aamodt, S., & Stenersen, J. (2007). Short-term pre-exposure increases earthworm tolerance to mercury. European Journal of Soil Biology, 43, 261–267.
Habig, W. H., Pabst, M. J., & Jakoby, W. B. (1974). Glutathion S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 249, 7130–7137.
Hans, R. K., Khan, M. A., Farooq, M., & Beg, M. U. (1993). Glutathione-S-transferase activity in an earthworm (Pheretima posthuma) exposed to three insecticides. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 25, 509–511.
Hayes, J. D., Flanagan, J. U., & Jowsey, I. R. (2005). Glutathione transferases. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 45, 51–88.
Jemec, A., Drobne, D., Tišler, T., Trebše, P., Roš, M., & Sepčić, K. (2007). The applicability of acetylcholinesterase and glutathione S-transferase in Daphnia magnatoxicity test. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. C, 144, 303–309.
Ketterer, B., Coles, B., & Meyer, D. J. (1983). The role of glutathione in detoxication. Environmental Health Perspectives, 49, 59–69.
Khati, W., Ouali, K., Bensouilah, M., Gnassia-barelli, M., & Romeo, M. (2007). Effet du cadmium sur certains bio-marqueurs de stress chez la moule Perna perna du golfe d’Annaba (Algérie) Laboratoire d’Ecobiologie des Milieux Marins et Littoraux- Université d’Annaba. Algérie.
Laszczyca, P., Augustyniak, M., Babczynska, A., Bednarska, K., Kafel, A., Migula, P., Wilczek, G., & Witas, I. (2004). Profiles of enzymatic activity in earthworms from zinc, lead and cadmium polluted areas near Olkusz (Poland). Environment International, 30, 901–910.
Li, X., Luo, Y., Yun, M., Wang, J., & Wang, J. (2010). Effects of 1-methyl-3-octylimidazolium bromide on the anti-oxidant system of earthworm. Chemosphere, 78, 853–85.
Luo, Y., Zang, Y., Zhong, Y., & Kong, Z. (1999). Toxicological study of two novel pesticides on earthworm Eisenia foetida. Chemosphere, 39, 2347–2356.
Maity, S., Roy, S., Chaudhury, S., & Bhattacharya, S. (2008). Antioxidant responses of the earthworm Lampito mauritii exposed to Pb and Zn contaminated soil. Environmental Pollution, 151, 1–7.
Mosleh, Y. Y., Paris-Palacios, S., Couderchet, M., & Vernet, G. (2003). Effects of the herbicide isoproturon on survival, growth rate, and protein content of mature earthworms (Lumbricus terrestris L.) and its fate in the soil. Applied Soil Ecology, 23, 69–77.
Mosleh, Y. Y., Paris-Palacios, S., & Biagianti-Risbourg, S. (2006). Metallothioneins induction and antioxidative response in aquatic worms Tubifex tubifex (Oligochaeta, Tubificidae) exposed to copper. Chemosphere, 64, 121–128.
OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development) (1984). Test 207: Earthworm, acute toxicity tests. In: Organization for economic co-operation and development, OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals.
Pandey, S., & Singh, D. K. (2004). Total bacterial and fungal population after chlorpyrifos and quinalphos treatments in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) soil. Chemosphere, 55, 197–205.
Paoletti, M. G., Sommaggio, D., Favretto, M. R., Petruzzelli, G., Pezzarossa, M., & Barbaferi, M. (1998). Earthworms as useful bioindicators of agroecosystem sustainability in orchards and vineyards with different inputs. Applied Soil Ecology, 10, 137–150.
Paris-Palacios, S., Biagianti-Risbourg, S., & Vernet, G. (2000). Biochemical and (ultra) structural hepatic perturbations of Brachydanio rerio (Teleostei, Cyprinidae) exposed to two sublethal concentrations of copper sulphate. Aquatic Toxicology, 50, 109–124.
Rao, J. V., Shilpanjali, D., & Kavitha, P. (2003). Toxic effects of profenofos on tissue acetylcholinesterase and gill morphology in a euryhaline fish, Oreochromis mossambicus. Archives of Toxicology, 77, 227–232.
Reddy, N. C., & Rao, J. V. (2008). Biological response of earthworm, Eisenia foetida (Savigny) to an organophosphorous pesticide, profenofos. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 71, 574–582.
Reinecke, S. A., & Reinecke, A. J. (2007). The impact of organophosphate pesticides in orchards on earthworms in the Western Cape, South Africa. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 66, 244–251.
Rombke, J. J., Rombke, S., & Didden, W. (2005). The use of earthworms in ecological soil classification and assessment concepts. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 62, 249–265.
Saint-Denis, M., Narbonne, J. F., Arnaud, C., & Ribera, D. (2001). Biochemical responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei exposed to contaminated artificial soil: effect of lead acetate. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33, 395–404.
Sanchez-Hernandez, J. C., Mazzia, C., Capowiez, Y., & Rault, M. (2009). Carboxylesterase activity in earthworm gut contents: potential ecotoxicological implications. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. C, 150, 503–511.
Schreck, E., Geret, F., Gontier, L., & Treilhou, M. (2008). Neurotoxic effect and metabolic responses induced by a mixture of six pesticides on the earthworm Aporrectodea Caliginosa nocturna. Chemosphere, 71, 1832–1893.
Schreck, E., Geret, F., Gontier, L., & Treilhou, M. (2009). ChE, GST and CAT: evaluation of the efficiency of a combined buffer for protein extraction. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72, 1609–1613.
Sizmur, T., & Hodson, M. E. (2009). Do earthworms impact metal mobility and availability in soil? A review. Environmental Pollution, 157, 1981–1989.
Stegeman, J. J., Brouwer, M., Di Giulio, R. T., Forlin, L., Fowler, B. A., Sanders, B. M., & Van Veld, P. A. (1992). Enzyme and protein synthesis as indicators of contaminant exposure and effect. In R. J. Huggett, R. A. Kimerie, P. M. Mehrle, & H. L. Bergman (Eds.), Biomarkers -biochemical, physiological, and histological markers of anthropogenic stress. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers.
Velki, M., & Hackenberger, B. K. (2013). Biomarker responses in earthworm Eisenia andrei exposed to pirimiphos-methyl and deltamethrin using different toxicity tests. Chemosphere, 90, 1216–1226.
Weckberker, G., & Cory, J. G. (1988). Ribonucleotide reductase activity and growth of glutathione-depleted mouse leukemia L1210 cells in vitro. Cancer Letters, 40, 257–264.
Xue, Y. G., Gu, X. Y., Wang, X. R., Sun, C., Xu, X. H., Sun, J., & Zhang, B. G. (2009). The hydroxyl radical generation and oxidative stress for the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to tetrabromobisphenol A. Ecotoxicology, 18, 693–699.
Yan, T., Teo, L. H., & Sin, Y. M. (1997). Effect of Mercury and lead on tissue Glutathion of the Green Mussel, Perna viridis L. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 58, 845–850.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mekahlia, M.N., Tine, S., Menasria, T. et al. In Vitro Biomarker Responses of Earthworm Lumbricus terrestris Exposed to Herbicide Sekator and Phosphate Fertilizer. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 15 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2712-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2712-z