Abstract
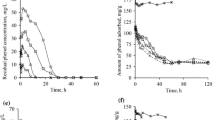
Two types of tailored activated carbons (BC-41-OG and BC-41-MnN) with favorable physicochemical characteristics were employed as adsorbents to study effects of synthetic small organic molecular (phenolics) on fulvic acid (FA) removal. The adsorption of FA on activated carbon was greatly declined due to competitive adsorption as a result of oxidation coupling of phenolics. However, the physicochemical characteristics of novel activated carbons (surface metal oxides and mesoporosity) can play an important role in alleviating this effect. The adsorption of FA onto F400 fluctuated a lot due to a relatively lower mesoporosity and surface basicity. Kinetic study was also conducted to determine the effects of oxidative coupling on adsorption kinetics of FA. The results demonstrated that presence of phenolics caused more significant effect on FA adsorption kinetics as compared to humic acid (HA).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolto, B., Dixon, D., Eldridge, R., & King, S. (2002). Removal of THM precursors by coagulation or ion exchange. Water Research, 36, 5066–5073.
Chu, C., & Lu, C. (2004). Effects of oxalic acid on the regrowth of heterotrophic bacteria in the distributed drinking water. Chemosphere, 57, 531–539.
Dastgheib, S. A., Karanfil, T., & Cheng, W. (2004). Tailoring activated carbons for enhanced removal of natural organic matter from natural waters. Carbon, 42, 547–557.
Gu, B., Schmitt, J., Chen, Z., Liang, L., & McCarthy, J. F. (1994). Adsorption and desorption of natural organic matter on iron oxide: mechanisms and models. Environmental Science & Technology, 28, 38–46.
Kilduff, J. E., & Karanfil, T. (2002). Trichloroethylene adsorption by activated carbon preloaded with humic substances: effects of solution chemistry. Water Research, 36, 1685–1698.
Kilduff, J. E., Karanfil, T., Chin, Y.-P., & Weber, W. J. (1996). Adsorption of natural organic polyelectrolytes by activated carbon: a size-exclusion chromatography study. Environmental Science & Technology, 30, 1336–1343.
Krasner, S. W., Westerhoff, P., Chen, B., Rittmann, B. E., & Amy, G. (2009). Occurrence of disinfection byproducts in United States wastewater treatment plant effluents. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 8320–8325.
Li, Q., Snoeyink, V. L., Mariaas, B. J., & Campos, C. (2003). Elucidating competitive adsorption mechanisms of atrazine and NOM using model compounds. Water Research, 37, 773–784.
Lu, C., & Chu, C. (2005). Effects of acetic acid on the regrowth of heterotrophic bacteria in the drinking water distribution system. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 21, 989–998.
Musikavong, C., Wattanachira, S., Marhaba, T. F., & Pavasant, P. (2005). Reduction of organic matter and trihalomethane formation potential in reclaimed water from treated industrial estate wastewater by coagulation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 127, 48–57.
Pelekani, C., & Snoeyink, V. L. (1999). Competitive adsorption in natural water: role of activated carbon pore size. Water Research, 33, 1209–1219.
Uranowski, L. J., Tessmer, C. H., & Vidic, R. D. (1998). The effect of surface metal oxides on activated carbon adsorption of phenolics. Water Research, 32, 1841–1851.
Yan, L., Deeter, V., Lalley, J., Medellin, O., Kupferle, M. J., & Sorial, G. A. (2014). Effects of oligomerization phenomenon on dissolved organic matter removal kinetics on novel activated carbons. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 278, 514–519.
Yan, L., Fitzgerald, M., Khov, C., Schafermeyer, A., Kupferle, M. J., & Sorial, G. A. (2013). Elucidating the role of phenolic compounds in the effectiveness of DOM adsorption on novel tailored activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 262, 100–105.
Yan, M., Wang, D., Qu, J., Ni, J., & Chow, C. W. (2008). Enhanced coagulation for high alkalinity and micro-polluted water: the third way through coagulant optimization. Water Research, 42, 2278–2286.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the financial support from Science Technology Department of Zhejiang province (Project 2014C03002), National Science Foundation (award #51309242), Powerchina Huadong Engineering Corporation (Project KY2014-02-26), and Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Environmental Change and Ecological Construction project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 262 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, L., Jiang, L., Tang, Y. et al. Investigating the Effects of Small Synthetic Organic Matters on Dissolved Organic Matter Adsorption. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 377 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2643-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2643-8