Abstract
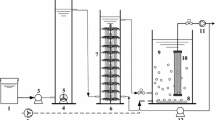
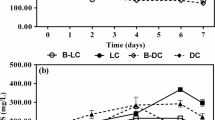
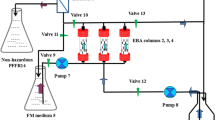
An erythromycin-degrading bacterium was isolated from the activated sludge of a sewage treatment plant (STP). Based on the morphological and physiological characteristics, the isolated strain was identified and named as Pseudomonas sp. ERY-E. In an inorganic salt medium inoculated at 1 % (v/v) of ERY-E strain containing 50 mg/L of erythromycin (ERY), the removal efficiency of ERY as high as 83.7 % was obtained under the optimum conditions with temperature of 30 °C, pH of 7.0, and 10 mg/L of yeast as the external carbon source. Subsequently, the ERY-E strain was used for bioaugmenting a biological aerated filter (BAF) to treat surface water containing low-concentration ERY. The influence of hydraulic retention time (HRT) and air-liquid ratio (A/L) on the performance of BAF was investigated. The average removal efficiencies of ERY and permanganate index (CODMn) were about 60.6 and 26.1 % in bioaugmented system (BAF2) and 26.9 and 26.0 % in unbioaugmented system (BAF1), respectively, under the optimum conditions with HRT of 4.0 h and A/L of 4:1 at steady state. Due to the stable removal of CODMn in BAF2 as compared with BAF1, it can be concluded that the introduction of ERY-E strain could collaborate with the indigenous microorganisms to attain a better ERY removal efficiency. As a result, the bioaugmented BAF method can be considered as an alternative technology for the treatment of surface water containing low-concentration emerging pollutants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, Y. H., Sun, Q. H., Sun, R. H., Wen, D. H., & Tang, X. Y. (2011). Bioaugmentation and adsorption treatment of coking wastewater containing pyridine and quinoline using zeolite-biological aerated filters. Environmental Science and Technology, 45(5), 1940–1948.
Barthélémy, P., Autisser, D., Gerbaud, G., & Courvalin, P. (1984). Enzymatic hydrolysis of erythromycin by Escherichia coli. A new mechanism of resistance. Journal of Antibiotics, 37(12), 1692–1696.
Bouchez, T., Patureau, D., Dabert, P., Juretschko, S., Doré, J., Delgenès, P., Moletta, R., & Wagner, M. (2000). Ecological study of a bioaugmentation failure. Environmental Microbiology, 2(2), 179–190.
Bouchez, T., Patureau, D., Delgenès, J. P., & Moletta, R. (2009). Successful bacterial incorporation into activated sludge flocs using alginate. Bioresource Technology, 100(2), 1031–1032.
Dong, X. Z., & Cai, M. Y. (2001). Handbook of Common Bacteria Identification System. Beijing: Science Press.
Fatta-Kassinos, D., Meric, S., & Nikolaou, A. (2011). Pharmaceutical residues in environmental waters and wastewater: current state of knowledge and future research. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 399(1), 251–275.
Feng, Y., Yu, Y. Z., Qiu, L. P., Zhang, J. W., & Gao, L. L. (2012). The characteristics and application of grain-slag media in a biological aerated filter (BAF). Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 18(3), 1051–1057.
Fischer, K., & Majewsky, M. (2014). Cometabolic degradation of organic wastewater micropollutants by activated sludge and sludge-inherent microorganisms. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98(15), 6583–6597.
Focazio, M. J., Kolpin, D. W., Barnes, K. K., Furlong, E. T., Meyer, M. T., Zaugg, S. D., Barber, L. B., & Thurman, M. E. (2008). A national reconnaissance for pharmaceuticals and other organic wastewater contaminants in the United States - II) Untreated drinking water sources. Science of the Total Environment, 402(2-3), 201–216.
Gao, P., Munir, M., & Xagoraraki, I. (2012a). Correlation of tetracycline and sulfonamide antibiotics with corresponding resistance genes and resistant bacteria in a conventional municipal wastewater treatment plant. Science of the Total Environment, 421–422, 173–183.
Gao, P., Ding, Y. J., Li, H., & Xagoraraki, I. (2012b). Occurrence of pharmaceuticals in a municipal wastewater treatment plant: Mass balance and removal processes. Chemosphere, 88(1), 17–24.
Gao, P., He, S., Huang, S. L., Li, K. Z., Liu, Z. H., Xue, G., & Sun, W. M. (2015). Impacts of coexisting antibiotics, antibacterial residues, and heavy metals on the occurrence of erythromycin resistance genes in urban wastewater. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99, 3971–3980.
Göbel, A., Thomsen, A., McArdell, C. S., Joss, A., & Giger, W. (2005). Occurrence and sorption behavior of sulfonamide, macrolides, and trimethoprim in activated sludge treatment. Environmental Science and Technology, 39(11), 3981–3989.
González-Pleiter, M., Gonzalo, S., Rodea-Palomares, I., Leganés, F., Rosal, R., Boltes, K., Marco, E., & Fernández-Piñas, F. (2013). Toxicity of five antibiotics and their mixtures towards photosynthetic aquatic organisms: Implications for environmental risk assessment. Water Research, 47(6), 2050–2064.
Kim, Y. H., Cha, C. J., & Cerniglia, C. E. (2002). Purification and characterization of an erythromycin esterase from an erythromycin-resistant Pseudomonas sp. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 210(2), 239–244.
Kim, Y. H., Pak, K., Pothuluri, J. V., & Cerniglia, C. E. (2004). Mineralization of erythromycin A in aquaculture sediments. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 234(1), 169–175.
Li, S. P., Cui, J. J., Zhang, Q. L., Fu, J., Lian, J. F., & Li, C. (2010). Performance of blast furnace dust clay sodium silicate ceramic particles (BCSCP) for brewery wastewater treatment in a biological aerated filter. Desalination, 258(1-3), 12–18.
Li, W. H., Shi, Y. L., Gao, L. H., Liu, J. M., & Cai, Y. Q. (2012). Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere, 89(11), 1307–1315.
Liu, F., Zhao, C. C., Zhao, D. F., & Liu, G. H. (2008). Tertiary treatment of textile wastewater with combined media biological aerated filter (CMBAF) at different hydraulic loadings and dissolved oxygen concentrations. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 160(1), 161–167.
Louvet, J. N., Heluin, Y., Attik, G., Dumas, D., Potier, O., & Pons, M. N. (2010). Assessment of erythromycin toxicity on activated sludge via batch experiments and microscopic techniques (epifluorescence and CLSM). Process Biochemistry, 45(11), 1787–1794.
Lund, M., Pasternak, B., Davidsen, R. B., Feenstra, B., Krogh, C., Diaz, L. J., Wohlfahrt, J., & Melbye, M. (2014). Use of macrolides in mother and child and risk of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: nationwide cohort study. BMJ, 348, 1908–1917.
Michael, I., Rizzo, L., McAcdell, C. S., Manaia, C. M., Merlin, C., Schwartz, T., Dagot, C., & Fatta-Kassinos, D. (2013). Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for the release of antibiotics in the environment: A review. Water Research, 47(3), 957–995.
Ministry of Environmental Protection of People’s Republic of China. (2006). Monitoring and analysis method of water and wastewater (4th ed.). Beijing: China Environmental Science Press (in Chinese).
Pala-Ozkok, I., & Orhon, D. (2013). Chronic effect of erythromycin on substrate biodegradation kinetics of activated sludge. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 81, 29–39.
Pala-Ozkok, I., Rehman, A., Ubay-Cokgor, E., Jonas, D., & Orhon, D. (2014). Pyrosequencing reveals the inhibitory impact of chronic exposure to erythromycin on activated sludge bacterial community structure. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 90, 195–205.
Payne, R. B., May, H. D., & Sowers, K. R. (2011). Enhanced reductive dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyl impacted sediment by bioaugmentation with a dehalorespiring bacterium. Environmental Science and Technology, 45(20), 8772–8779.
Shen, P., & Chen, X. D. (2007). Microbiology Experiment (4th ed.). Beijing: Higher Education Press.
Silva, B. F. D., Jelic, A., López-Serna, R., Mozeto, A. A., Petrovic, M., & Barceló, D. (2011). Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in surface water, suspended solids and sediments of the Ebro river basin, Spain. Chemosphere, 85(5), 1331–1339.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2007). MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24(8), 1596–1599.
Tao, X. Q., Lu, G. N., Dang, Z., Yang, C., & Yi, X. Y. (2007). A phenanthrene-degrading strain Sphingomonas sp. GY2B isolated from contaminated soils. Process Biochemistry, 42(3), 401–408.
Tenson, T., Lovmar, M., & Ehrenberg, M. (2003). The mechanism of action of macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramin B reveals the nascent peptide exit path in the ribosome. Journal of Molecular Biology, 330(5), 1005–1014.
USEPA (2010) Drinking Water Contaminant Candidate List 3 - CCL. http://water.epa.gov/scitech/drinkingwater/dws/ccl/ccl3.cfm
Wasi, S., Tabrez, S., & Ahmad, M. (2013). Use of Pseudomonas spp. for the bioremediation of environmental pollutants: a review. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(10), 8147–8155.
Wu, S. Q., Yue, Q. Y., Qi, Y. F., Gao, B. Y., Han, S. X., & Yue, M. (2011). Preparation of ultra-lightweight sludge ceramics (ULSC) and application for pharmaceutical advanced wastewater treatment in a biological aerobic filter (BAF). Bioresource Technology, 102(3), 2296–2300.
Xu, B. J., Gao, P., Liu, Z. H., Xue, G., Liu, Y. N., & Wu, F. (2014). Influence of cosubstrates on iopromide degradation by Pseudomonas sp. I-24. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 225(2), 1–8.
Yan, C. X., Yang, Y., Zhou, J. L., Liu, M., Nie, M. H., Shi, H., & Gu, L. J. (2013). Antibiotics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary: Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment. Environmental Pollution, 175, 22–29.
Yang, X., Flowers, R. C., Weinberg, H. S., & Singer, P. C. (2011). Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in an advanced wastewater reclamation plant. Water Research, 45(16), 5218–5228.
Yoon, J. H., Oh, H. M., Yoon, B. D., Kang, K. H., & Park, Y. H. (2003). Paenibacillus kribbensis sp. nov. and Paenibacillus terrae ap. nov., bioflocculants for efficient harvesting of algal cells. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 53(1), 295–301.
Zhang, Q. C., Lambert, G., Liao, D., Kim, H., Robin, K., Tung, C., Pourmand, N., & Austin, R. H. (2011). Acceleration of emergence of bacterial antibiotic resistance in connected microenvironments. Science, 333(6050), 1764–1767.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51208086, 51178093), the Shanghai Pujiang Program (13PJ1400100), the DHU Distinguished Young Professor Program, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, P., Wei, X., Gu, C. et al. Isolation and Characterization of an Erythromycin-Degrading Strain and Application for Bioaugmentation in a Biological Aerated Filter. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 190 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2449-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2449-8