Abstract
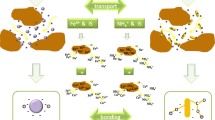
Arsenate is a common groundwater contaminant that poses serious threat to human health. Although arsenate is mainly transported in dissolved form in groundwater under certain conditions, some studies found a large fraction of arsenate is associated with mineral and organic colloids in natural water, indicating co-transport of arsenate, and particulate matters may significantly alter arsenate migration. Silicate minerals are known to adsorb arsenate, and silicate–mineral colloids are the most abundant form of mineral colloids in many soil water and groundwater. However, the role of silicate–mineral colloids in mediating arsenate transport is not clear, especially when silicate–mineral colloids co-exist with natural organic matters. The objective of this study is to determine and compare the roles of silicate–mineral colloid and natural organic matters in arsenate transport and examine how natural organic matters influence mineral–colloid-facilitated arsenate transport. Arsenate-spiked solution with or without illite colloids and/or humic acid was injected into water-saturated sand columns, and effluent arsenate concentrations were measured. Our results showed that the roles of illite colloids and humic acid in arsenate transport were very different. While illite colloids did not influence arsenate transport due to their low affinity for arsenate under typical groundwater conditions, humic acid substantially increased arsenate transport via competition against arsenate for adsorptive sites on the transport medium and potential formation of non-adsorbing aqueous phase arsenate–humic acid complexes. Although illite colloids were highly mobile in the presence of humic acid, arsenate adsorption to illite colloids was low and transport of illite-associated arsenate was insignificant. Since the affinity of illite for arsenate is intermediate among different clay minerals, our results imply that clay–mineral colloids in general may not have a large potential to increase As transport, and that natural organic matters are the most important type of natural colloids that may influence arsenate transport in groundwater.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbour, R. A., Douch, J., Hamdani, M., & Schmitz, P. (2002). Transport of kaolinite colloids through quartz sand: influence of humic acid, Ca2+, and trace metals. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 253, 1–8.
Alam, M. S., & Cheng, T. (2014). Uranium release from sediment to groundwater: influence of water chemistry and insights into release mechanisms. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 164, 72–87.
Alam, M. S., Wu, Y., & Cheng, T. (2014). Silicate minerals as a source of arsenic contamination in groundwater. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 225, 2201.
Antelo, J., Avena, M., Fiol, S., Lopez, R., & Arce, F. (2005). Effects of pH and ionic strength on the adsorption of phosphate and arsenate at the goethite-water interface. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 285, 476–486.
Arnarson, T. S., & Keil, R. G. (2000). Mechanisms of pore water organic matter adsorption to montmorillonite. Marine Chemistry, 71, 309–320.
Baumann, T., Fruhstorfer, P., Klein, T., & Niessner, R. (2006). Colloid and heavy metal transport at landfill sites in direct contact with groundwater. Water Research, 40, 2776–2786.
Borggaard, O. K., Raben-Lange, B., Gimsing, A. L., & Strobel, B. W. (2005). Influence of humic substances on phosphate adsorption by aluminium and iron oxides. Geoderma, 127, 270–279.
Bouby, M., Geckeis, H., Lutzenkirchen, J., Mihai, S., & Schafer, T. (2011). Interaction of bentonite colloids with Cs, Eu, Th and U in presence of humic acid: a flow field-flow fractionation study. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75, 3866–3880.
Boyle, D. R., Turner, R. J. W., & Hall, G. E. M. (1998). Anomalous arsenic concentrations in groundwaters of an island community, Bowen Island, British Columbia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 20, 199–212.
Buschmann, J., Kappeler, A., Lindauer, U., Kistler, D., Berg, M., & Sigg, L. (2006). Arsenite and arsenate binding to dissolved humic acids: influence of pH, type of humic acid, and aluminum. Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 6015–6020.
Chakraborty, S., Wolthers, M., Chatterjee, D., & Charlet, L. (2007). Adsorption of arsenite and arsenate onto muscovite and biotite mica. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 309, 392–401.
Charlet, L., Chakraborty, S., Varma, S., Tournassat, C., Wolthers, M., Chatterjee, D., & Ross, G. R. (2005). Adsorption and heterogeneous reduction of arsenic at the phyllosilicate-water interface. In P. A. Oday, D. Vlassopoulos, Z. Meng, & L. G. Benning (Eds.), Advances in arsenic research: integration of experimental and observational studies and implications for mitigation (pp. 41–59). Washington: American Chemical Society.
Chen, G. X., Liu, X. Y., & Su, C. M. (2012). Distinct effects of humic acid on transport and retention of TiO2 Rutile nanoparticles in saturated sand columns. Environmental Science & Technology, 46, 7142–7150.
Chen, Z. R., Cai, Y., Liu, G. L., Solo-Gabriele, H., Snyder, G. H., & Cisar, J. L. (2008). Role of soil-derived dissolved substances in arsenic transport and transformation in laboratory experiments. Science of the Total Environment, 406, 180–189.
Cheng, H. F., Hu, Y. N., Luo, J., Xu, B., & Zhao, J. F. (2009). Geochemical processes controlling fate and transport of arsenic in acid mine drainage (AMD) and natural systems. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165, 13–26.
Cheng, T., & Saiers, J. E. (2009). Mobilization and transport of in situ colloids during drainage and imbibition of partially saturated sediments. Water Resources Research, 45, W08414.
Cheng, T., & Saiers, J. E. (2010). Colloid-facilitated transport of cesium in vadose-zone sediments: the importance of flow transients. Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 7443–7449.
Darland, J. E., & Inskeep, W. P. (1997). Effects of pH and phosphate competition on the transport of arsenate. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26, 1133–1139.
Fein, J. B., Boily, J.-F., Güçlü, K., & Kaulbach, E. (1999). Experimental study of humic acid adsorption onto bacteria and Al-oxide mineral surfaces. Chemical Geology, 162, 33–45.
Filip, Z., & Alberts, J. J. (1994). Adsorption and transformation of salt marsh related humic acids by quartz and clay minerals. Science of the Total Environment, 153, 141–150.
Gao, X. B., Wang, Y. X., Hu, Q. H., & Su, C. L. (2011). Effects of anion competitive adsorption on arsenic enrichment in groundwater. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part a-Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 46, 471–479.
Ghosh, A., Mukiibi, M., Sáez, A. E., & Ela, W. P. (2006). Leaching of arsenic from granular ferric hydroxide residuals under mature landfill conditions. Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 6070–6075.
Goldberg, S. (2002). Competitive adsorption of arsenate and arsenite on oxides and clay minerals. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 66, 413–421.
Gradusov, B. P. (1974). A tentative study of clay mineral distribution in soils of the world. Geoderma, 12, 49–55.
Greenland, D. J. (1971). Interactions between humic and fulvic acids and clays. Soil Science, 111, 34–41.
Grolimund, D., Borkovec, M., Barmettler, K., & Sticher, H. (1996). Colloid-facilitated transport of strongly sorbing contaminants in natural porous media: a laboratory column study. Environmental Science & Technology, 30, 3118–3123.
Gu, B. H., Schmitt, J., Chen, Z. H., Liang, L. Y., & McCarthy, J. F. (1994). Adsorption and desorption of natural organic matter on iron-oxide: mechanisms and models. Environmental Science & Technology, 28, 38–46.
Gu, X., & Evans, L. J. (2007). Modelling the adsorption of Cd(II), Cu(II), Ni(II), Pb(II), and Zn(II) onto Fithian illite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 307, 317–325.
Guo, H. M., Zhang, B., Yang, S. Z., Li, Y., Stuben, D., Norra, S., & Wang, J. J. (2009). Role of colloidal particles for hydrogeochemistry in As-affected aquifers of the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. Geochemical Journal, 43, 227–234.
Guo, H. M., Zhang, B., & Zhang, Y. (2011). Control of organic and iron colloids on arsenic partition and transport in high arsenic groundwaters in the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia. Applied Geochemistry, 26, 360–370.
Halter, W. E., & Pfeifer, H.-R. (2001). Arsenic(V) adsorption onto α-Al2O3 between 25 and 70 °C. Applied Geochemistry, 16, 793–802.
Haque, S., & Johannesson, K. H. (2006). Arsenic concentrations and speciation along a groundwater flow path: the Carrizo Sand aquifer, Texas, USA. Chemical Geology, 228, 57–71.
Hossain, M. S., & Islam, M. R. (2008). Experimental and numerical modeling of arsenic transport in limestone. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 30, 1189–1201.
Hu, L. G., Diez-Rivas, C., Hasan, A. R., Solo-Gabriele, H., Fieber, L., & Cai, Y. (2010). Transport and interaction of arsenic, chromium, and copper associated with CCA-treated wood in columns of sand and sand amended with peat. Chemosphere, 78, 989–995.
Ishak, C. F., Seaman, J. C., Miller, W. P., & Sumner, M. (2002). Contaminant mobility in soils amended with fly ash and flue-gas gypsum: intact soil cores and repacked columns. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 134, 287–305.
Jada, A., Ait Akbour, R., & Douch, J. (2006). Surface charge and adsorption from water onto quartz sand of humic acid. Chemosphere, 64, 1287–1295.
Johnson, P. R., Sun, N., & Elimelech, M. (1996). Colloid transport in geochemically heterogeneous porous media: modeling and measurements. Environmental Science & Technology, 30, 3284–3293.
Ko, I., Kim, J.-Y., & Kim, K.-W. (2004). Arsenic speciation and sorption kinetics in the As–hematite–humic acid system. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 234, 43–50.
Kosmulski, M. (2011). The pH-dependent surface charging and points of zero charge: V. Update. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 353, 1–15.
Kraemer, S. M., Xu, J. D., Raymond, K. N., & Sposito, G. (2002). Adsorption of Pb(II) and Eu(III) by oxide minerals in the presence of natural and synthetic hydroxamate siderophores. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 1287–1291.
Kretzschmar, R., Borkovec, M., Grolimund, D., & Elimelech, M. (1999). Mobile subsurface colloids and their role in contaminant transport. Advances in Agronomy, 66(66), 121–193.
Kubicki, J. D., Schroeter, L. M., Itoh, M. J., Nguyen, B. N., & Apitz, S. E. (1999). Attenuated total reflectance Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy of carboxylic acids adsorbed onto mineral surfaces. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63, 2709–2725.
Laegdsmand, M., de Jonge, L. W., & Moldrup, P. (2005). Leaching of colloids and dissolved organic matter from columns packed with natural soil aggregates. Soil Science, 170, 13–27.
Lin, Z., & Puls, R. W. (2000). Adsorption, desorption and oxidation of arsenic affected by clay minerals and aging process. Environmental Geology, 39, 753–759.
Lippold, H., & Lippmann-Pipke, J. (2009). Effect of humic matter on metal adsorption onto clay materials: testing the linear additive model. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 109, 40–48.
Liu, A. G., & Gonzalez, R. D. (1999). Adsorption/desorption in a system consisting of humic acid, heavy metals, and clay minerals. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 218, 225–232.
Mamindy-Pajany, Y., Hurel, C., Marmier, N., & Roméo, M. (2011). Arsenic (V) adsorption from aqueous solution onto goethite, hematite, magnetite and zero-valent iron: Effects of pH, concentration and reversibility. Desalination, 281, 93–99.
Manning, B. A., & Goldberg, S. (1997). Adsorption and stability of arsenic(III) at the clay mineral-water interface. Environmental Science & Technology, 31, 2005–2011.
McCarthy, J. F., & McKay, L. D. (2004). Colloid mobilization and transport in groundwater. Vadose Zone Journal, 3, 326–337.
Paktunc, D., Foster, A., & Laflamme, G. (2003). Speciation and characterization of arsenic in Ketza River mine tailings using x-ray absorption spectroscopy. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 2067–2074.
Plaschke, M., Romer, J., Klenze, R., & Kim, J. I. (1999). In situ AFM study of sorbed humic acid colloids at different pH. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 160, 269–279.
Pokrovsky, O. S., & Schott, J. (2002). Iron colloids/organic matter associated transport of major and trace elements in small boreal rivers and their estuaries (NW Russia). Chemical Geology, 190, 141–179.
Polubesova, T., & Nir, S. (1999). Modeling of organic and inorganic cation sorption by illite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 47, 366–374.
Puls, R. W., & Powell, R. M. (1992). Transport of inorganic colloids through natural aquifer material: implications for contaminant transport. Environmental Science & Technology, 26, 614–621.
Ransom, B., & Helgeson, H. C. (1993). Compositional end members and thermodynamic components of illite and dioctahedral aluminous smectite solid-solutions. Clays and Clay Minerals, 41, 537–550.
Raven, K. P., Jain, A., & Loeppert, R. H. (1998). Arsenite and arsenate adsorption on ferrihydrite: kinetics, equilibrium, and adsorption envelopes. Environmental Science & Technology, 32, 344–349.
Redman, A. D., Macalady, D. L., & Ahmann, D. (2002). Natural organic matter affects arsenic speciation and sorption onto hematite. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 2889–2896.
Saiers, J. E., & Hornberger, G. M. (1999). The influence of ionic strength on the facilitated transport of cesium by kaolinite colloids. Water Resources Research, 35, 1713–1727.
Schmitt, D., Saravia, F., Frimmel, F. H., & Schuessler, W. (2003). NOM-facilitated transport of metal ions in aquifers: importance of complex-dissociation kinetics and colloid formation. Water Research, 37, 3541–3550.
Sen, T. K., & Khilar, K. C. (2006). Review on subsurface colloids and colloid-associated contaminant transport in saturated porous media. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 119, 71–96.
Serpa, C., Batterson, M. and Guzzwell, K. (2009). The influence of bedrock and mineral occurrences on arsenic concentrations in groundwater wells in the Gander Bay Area, Newfoundland. Current Research, Newfoundland and Labrador Department of Natural Resources Geological Survey, 315-337.
Sharma, P., Rolle, M., Kocar, B., Fendorf, S., & Kappler, A. (2011). Influence of natural organic matter on as transport and retention. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 546–553.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 517–568.
Su, T. Z., Guan, X. H., Gu, G. W., & Wang, J. M. (2008). Adsorption characteristics of As(V), Se(IV), and V(V) onto activated alumina: effects of pH, surface loading, and ionic strength. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 326, 347–353.
Tatalovich, M. E., Lee, K. Y., & Chrysikopoulos, C. V. (2000). Modeling the transport of contaminants originating from the dissolution of DNAPL pools in aquifers in the presence of dissolved humic substances. Transport in Porous Media, 38, 93–115.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51, 844–851.
Tindale, K., Patel, P., & Wallschlager, D. (2011). Colloidal arsenic composition from abandoned gold mine tailing leachates in Nova Scotia, Canada. Applied Geochemistry, 26, S260–S262.
Tipping, E. (1981). The adsorption of aquatic humic substances by iron oxides. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 45, 191–199.
Wang, S., & Mulligan, C. N. (2006). Occurrence of arsenic contamination in Canada: sources, behavior and distribution. Science of the Total Environment, 366, 701–721.
Wang, S. L., & Mulligan, C. N. (2009a). Effect of natural organic matter on arsenic mobilization from mine tailings. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168, 721–726.
Wang, S. L., & Mulligan, C. N. (2009b). Enhanced mobilization of arsenic and heavy metals from mine tailings by humic acid. Chemosphere, 74, 274–279.
Williams, L. E., Barnett, M. O., Kramer, T. A., & Melville, J. G. (2003). Adsorption and transport of arsenic(V) in experimental subsurface systems. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 841–850.
Xu, H., Allard, B., & Grimvall, A. (1988). Influence of pH and organic substance on the adsorption of As(V) on geologic materials. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 40, 293–305.
Xu, H., Allard, B., & Grimvall, A. (1991). Effects of acidification and natural organic materials on the mobility of arsenic in the environment. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 57–8, 269–278.
Yang, Y., Saiers, J. E., & Barnett, M. O. (2013). Impact of Interactions between natural organic matter and metal oxides on the desorption kinetics of uranium from heterogeneous colloidal suspensions. Environmental Science & Technology, 47, 2661–2669.
Yang, Y., Saiers, J. E., Xu, N., Minasian, S. G., Tyliszczak, T., Kozimor, S. A., Shuh, D. K., & Barnett, M. O. (2012). Impact of natural organic matter on uranium transport through saturated geologic materials: from molecular to column scale. Environmental Science & Technology, 46, 5931–5938.
Zhang, H., & Selim, H. M. (2007). Colloid mobilization and arsenite transport in soil columns: effect of ionic strength. Journal of Environmental Quality, 36, 1273–1280.
Zhang, L., Yu, X., Zhang, H., Chen, E., & Dong, T. (2013). Impact of environmental conditions on the sorption behavior of 60Co(II) on illite. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 295, 1473–1485.
Zhang, W., Morales, V. L., Cakmak, M. E., Salvucci, A. E., Geohring, L. D., Hay, A. G., Parlange, J. Y., & Steenhuis, T. S. (2010). Colloid transport and retention in unsaturated porous media: effect of colloid input concentration. Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 4965–4972.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Research & Development Corporation of Newfoundland and Labrador’s Ignite R&D Program (Project # 5404.1354.101) and Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada's Discovery Grant (Application No. 402815-2012). We thank Dr. Valerie Booth and Ms. Donna Jackman for the use of Zetasizer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Cheng, T. & Wu, Y. Distinct Roles of Illite Colloid and Humic Acid in Mediating Arsenate Transport in Water-Saturated Sand Columns. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 129 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2413-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2413-7