Abstract
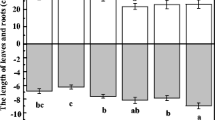
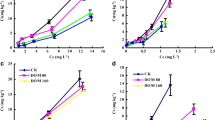
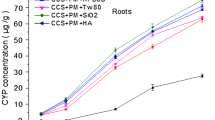
Four kinds of surfactants were used to increase accessibility of pyrene and cadmium (Cd) in simulated pyrene, Cd, and pyrene-Cd soils in this study. Tea saponin (TS) at 40 mg L−1 groups (exchangeable fraction of Cd and bioaccessible fraction of pyrene were 8.96 and 36.93 mg kg−1) showed more preferable potential application in improving solubilization capability than other surfactants. The morphology of Cd was transformed from Fe-Mn oxides (8.86 to 7.61 and 8.67 to 7.99 mg kg−1 in Cd and pyrene-Cd soil) and associated to carbonates fractions (4.46 to 4.36 and 4.28 to 4.36 mg kg−1 in Cd and pyrene-Cd soil) to exchangeable fraction with adding TS. These two morphological changes were important processes in the solubilization of Cd. The morphology of pyrene was transformed from associated fraction (72.15 to 61.95 and 71.02 to 63.48 mg kg−1 in pyrene and pyrene-Cd soil) to bioaccessible fraction (26.66 to 33.71 and 26.91 to 36.93 mg kg−1 in pyrene and pyrene-Cd soil) with adding TS. This morphological transformation was important in the improving of solubilization capacity of pyrene. In contrast, the solubilization of pyrene was promoted in the presence of Cd in pyrene-Cd soil (the bioaccessible fractions were 33.71 and 36.93 mg kg−1 in pyrene and pyrene-Cd soil), but the solubilization of Cd was hindered in the presence of pyrene (the exchangeable fractions of Cd were 8.86 and 8.67 mg kg−1 in Cd and pyrene-Cd soil). These findings will be beneficial for application of surfactants in soil remediation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alborés, A. F., Cid, B. P., Gómez, E. F., & López, E. F. (2000). Comparison between sequential extraction procedures and single extractions for metal partitioning in sewage sludge samples. The Analyst, 125(7), 1353–1357.
Almeida, C. M., Dias, A. C., Mucha, A. P., Bordalo, A. A., & Vasconcelos, M. T. (2009). Influence of surfactants on the Cu phytoremediation potential of a salt marsh plant. Chemosphere, 75(2), 135–140.
An, C. J., Huang, G. H., Wei, J., & Yu, H. (2011). Effect of short-chain organic acids on the enhanced desorption of phenanthrene by rhamnolipid biosurfactant in soil-water environment. Water Research, 45(17), 5501–5510.
Fukuda, K., Olsson, U., & Ueno, M. (2001). Microemulsion formed by alkyl polyglucoside and an alkyl glycerol ether with weakly charged films. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 20, 129–135.
Gao, Y., Zeng, Y., Shen, Q., Ling, W., & Han, J. (2009). Fractionation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon residues in soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(2-3), 897–903.
Gomez-Eyles, J. L., Collins, C. D., & Hodson, M. E. (2010). Relative proportions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons differ between accumulation bioassays and chemical methods to predict bioavailability. Environmental Pollution, 158(1), 278–284.
Haigh, S. D. (1996). A review of the interaction of surfactants with organic contaminants in soil. The Science of the Total Environment, 185, 161–170.
Iglauer, S., Wu, Y., Shuler, P., Tang, Y., & Goddard, W. A. (2009). Alkyl polyglycoside surfactant–alcohol cosolvent formulations for improved oil recovery. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 339(1-3), 48–59.
Lin, Q., Shen, K., Zhao, H., & Li, W. (2008). Growth response of Zea mays L. in pyrene-copper co-contaminated soil and the fate of pollutants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 150(3), 515–521.
Liu, F., Wang, C., Liu, X., Liang, X., & Wang, Q. (2013). Effects of alkyl polyglucoside (APG) on phytoremediation of PAH-contaminated soil by an aquatic plant in the Yangtze Estuarine Wetland. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 224(7), 1633–1643.
Luo, L., Zhang, S., & Christie, P. (2010). New insights into the influence of heavy metals on phenanthrene sorption in soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(20), 7846–7851.
Ma, B., Wang, J., Xu, M., He, Y., Wang, H., Wu, L., & Xu, J. (2012). Evaluation of dissipation gradients of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rice rhizosphere utilizing a sequential extraction procedure. Environmental Pollution, 162, 413–421.
Macleod, C. J. A., & Semple, K. T. (2003). Sequential extraction of low concentrations of pyrene and formation of non-extractable residues in sterile and non-sterile soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 35(11), 1443–1450.
Megharaj, M., Ramakrishnan, B., Venkateswarlu, K., Sethunathan, N., & Naidu, R. (2011). Bioremediation approaches for organic pollutants: a critical perspective. Environment International, 37(8), 1362–1375.
Momin, S. A., & Yeole, P. (2011). Comparative study of effect of surfactant-polymer interactions on properties of alkyl polyglucosides and alpha olefin sulphonate. Journal of Surfactants and Detergents, 15(3), 291–298.
Mulligan, C. N., Yong, R. N., & Gibbs, B. F. (2001). Surfactant-enhanced remediation of contaminated soil: a review. Engineering Geology, 60, 371–380.
Obuekwe, I. S., & Semple, K. T. (2013). Impact of zinc-copper mixtures on the development of phenanthrene catabolism in soil. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 85, 228–236.
Ochoa-Loza, F. J., Artiola, J. F., & Maier, R. M. (2001). Stability constants for the complexation of various metals with a rhamnolipid biosurfactant. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 479–485.
Ortega-Calvo, J. J., Tejeda-Agredano, M. C., Jimenez-Sanchez, C., Congiu, E., Sungthong, R., Niqui-Arroyo, J. L., & Cantos, M. (2013). Is it possible to increase bioavailability but not environmental risk of PAHs in bioremediation? Journal of Hazardous Materials, 261, 733–745.
Ramamurthy, A. S., Vo, D., Li, X. J., & Qu, J. (2007). Surfactant-enhanced removal of Cu (II) and Zn (II) from a contaminated sandy soil. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 190(1-4), 197–207.
Roy, D., Kommalapati, R. R., Mandava, S. S., Valsaraj, K. T., & Constant, W. D. (1997). Soil washing potential of a natural surfactant. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(3), 670–675.
Singh, P., & Cameotra, S. S. (2004). Enhancement of metal bioremediation by use of microbial surfactants. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 319(2), 291–297.
Urum, K., & Pekdemir, T. (2004). Evaluation of biosurfactants for crude oil contaminated soil washing. Chemosphere, 57(9), 1139–1150.
Wang, G., Zhou, Y., Wang, X., Chai, X., Huang, L., & Deng, N. (2010). Simultaneous removal of phenanthrene and lead from artificially contaminated soils with glycine-beta-cyclodextrin. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 184(1-3), 690–695.
Wei, J., Liu, X., Wang, Q., Wang, C., Chen, X., & Li, H. (2014). Effect of rhizodeposition on pyrene bioaccessibility and microbial structure in pyrene and pyrene-lead polluted soil. Chemosphere, 97, 92–97.
Xia, H., Chi, X., Yan, Z., & Cheng, W. (2009). Enhancing plant uptake of polychlorinated biphenyls and cadmium using tea saponin. Bioresource Technology, 100(20), 4649–4653.
Zhang, X. Y., Liu, X. Y., Liu, S. S., Liu, F. H., Chen, L. S., Xu, G., Zhong, C. L., Su, P. C., & Cao, Z. N. (2012). Response characteristics of scirpus triqueterand its rhizosphere to pyrene contaminated soils at different growth stages. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 14(7), 691–702.
Zhao, B., Zhu, L., & Gao, Y. (2005). A novel solubilization of phenanthrene using Winsor I microemulsion-based sodium castor oil sulfate. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 119(1-3), 205–211.
Zhou, W., Yang, J., Lou, L., & Zhu, L. (2011). Solubilization properties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by saponin, a plant-derived biosurfactant. Environmental Pollution, 159(5), 1198–1204.
Acknowledgments
The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41373097, 41073072, 41101230, 41203051), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 2013 M541506), Program for Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT13078).
Ethical Statement
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• Tea saponin (TS) improved the solubilization of pyrene(PY) and Cd.
• Surfactants obviously enhanced the accessibility of PY and Cd in polluted soils.
• Surfactants changed pollutants from difficultly utilized to accessible fractions.
• Solubilization of PY was promoted in the existence of Cd in PY-Cd soil.
• Solubilization of Cd was hindered in the presence of PY in PY-Cd soil.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Liu, X., Wang, C. et al. Solubilization Effect of Surfactants on Morphological Transformation of Cadmium and Pyrene in Co-Contaminated Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 147 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2409-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2409-3