Abstract
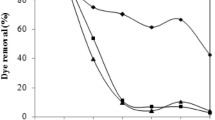
The present study was conducted to maximize the biosorption of dye by utilizing the native (untreated) pellets of Aspergillus lentulus. The native (55.0 mg/g) and heat-treated (56.7 mg/g) pellets showed excellent dye biosorption capacity which declined upon alginate immobilization (27.2 mg/g). Fourier transform infrared and EDX spectra revealed that phosphate and –CH3 groups are important in determining the biosorption capacity of the pretreated fungal biomass. The operating conditions of the aerated fed batch reactor were optimized and 90 % removal of Acid Blue 120 in 12 h was achieved after five biosorption–desorption cycles. At the end of the fifth cycle, 508.57 mg/L dye could be removed in 60 h with the removal rate of 8.48 mg/L/h. Further, the potential utilization of fungal biomass for the treatment of complex effluent was validated by studying the dye removal from unprocessed textile effluent wherein 58.0 % dye was removed within 4 h of contact.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akar, T., Kulcu, A., & Akar, S. T. (2013). Effective decolorization potential of Thamnidium elegans: biosorption optimization, modelling, characterization and application studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 221, 461–468.
Aksu, Z. (2005). Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutants: a review. Process Biochemistry, 40, 997–1026.
Arica, M. Y., & Bayramoglu, G. (2007). Biosorption of reactive Red-120 dye from aqueous solution by native and modified fungus biomass preparations of Lentinus sajor-caju. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 149, 499–507.
Bayramoglu, G., & Arica, M. Y. (2007). Biosorption of benzidine based textile dyes “Direct Blue 1 and Direct Red 128” using native and heat-treated biomass of Trametes versicolor. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 143, 135–143.
Binupriya, A. R., Sathishkumar, M., Swaminathan, K., Ku, C. S., & Yun, S. E. (2008). Comparative studies on removal of Congo red by native and modified mycelial pellets of Trametes versicolor in various reactor modes. Bioresource Technology, 99, 1080–1088.
Brahimi-Horn, M. C., Lim, K. K., Liang, S. L., & Mou, D. G. (1992). Binding of textile azo dyes by Myrothecium verrucaria. Journal of Industrial Microbiology, 10, 31–36.
Couto, S. R. (2009). Dye removal by immobilised fungi. Biotechnology Advances, 27, 227–235.
El-Naggar, M. A., El-Aasar, S. A., & Barakat, K. I. (2004). Bioremediation of crystal violet using air bubble bioreactor packed with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Water Research, 38, 4313–4322.
Freundlich, H. (1906). Adsorption in solution. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 57, 385–470.
Fu, Y., & Viraraghavan, T. (2001). Fungal decolourization of dye wastewaters: a review. Bioresource Technology, 79, 251–262.
Fu, Y., & Viraraghavan, T. (2002). Removal of Congo Red from an aqueous solution by fungus Aspergillus niger. Advances in Environmental Research, 7, 239–247.
Gupta, V. K., & Suhas. (2009). Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—a review. Journal of Environment Management, 90, 2313–2342.
Hadibarata, T., Yusoff, A. R. M., & Kristanti, R. A. (2012). Acceleration of anthraquinone-type dye removal by white-rot fungus under optimized environmental conditions. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 223, 4669–4677.
Iqbal, M., & Saeed, A. (2007). Biosorption of reactive dye by loofa sponge-immobilized fungal biomass of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Process Biochemistry, 42, 1160–1164.
Kaushik, P., & Malik, A. (2010a). Alkali, thermo and halo tolerant fungal isolate for the removal of textile dyes. Colloid Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 81, 321–328.
Kaushik, P., & Malik, A. (2010b). Effect of nutritional conditions on dye removal from textile effluent by Aspergillus lentulus. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 26, 1957–1964.
Kaushik, P., & Malik, A. (2013). Comparative performance evaluation of Aspergillus lentulus for dye removal through bioaccumulation and biosorption. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 2882–2892.
Kippert, F. (1995). A rapid permeabilization method procedure for accurate quantitative determination of β-galactosidase activity in yeast cells. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 128, 201–206.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40, 1361–1403.
Lata, H., Mor, S., Garg, V. K., & Gupta, R. K. (2008). Removal of a dye from simulated wastewater by adsorption using treated parthenium biomass. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153, 213–220.
Liu, Y., Hama, H., Fujita, Y., Kondo, A., Inoue, Y., Kimura, A., et al. (1999). Production of S-lactoylglutathione by high activity whole cell biocatalysts prepared by permeabilization of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae with alcohols. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 64, 54–60.
Maurya, N. S., Mittal, A. K., Cornel, P., & Rother, E. (2006). Biosorption of dyes using dead macro fungi: effect of dye structure, ionic strength and pH. Bioresource Technology, 97, 512–521.
Mishra, A., & Malik, A. (2013). Recent advances in microbial metal bioaccumulation. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 1162–1222.
O’Mahony, T., Guibal, E., & Tobin, J. M. (2002). Reactive dye biosorption by Rhizopus arrhizus biomass. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 31, 456–463.
Sharma, S., Malik, A., Satya, S., & Mishra, A. (2011). Development of a biological system employing Aspergillus lentulus for Cr removal from a small-scale electroplating industry effluent. Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering, 6, 55–63.
Sumathi, S., & Manju, B. S. (2000). Uptake of reactive textile dyes by Aspergillus foetidus. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 27, 347–355.
Volesky, B. (2007). Biosorption and me. Water Research, 41, 4017–4029.
Zeroual, Y., Kim, B. S., Kim, C. S., Blaghen, M., & Lee, K. M. (2006). Biosorption of Bromophenol blue from aqueous solutions by Rhizopus stolonifer biomass. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 177, 135–146.
Zhang, F. M., Knapp, J. S., & Tapley, K. N. (1999). Development of bioreactor systems for decolorization of Orange II using white rot fungus. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 24, 48–53.
Acknowledgements
CSIR Research Associateship to one of the authors (PK) is gratefully acknowledged. Authors also express their gratitude to Prof. Harpal Singh (CMBE, IIT Delhi, India) and Mr. D.C. Sharma for providing the FTIR and SEM-EDX facility, respectively. Mr. Sabal Singh (IIT Delhi) is thankfully acknowledged for his assistance in experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 31 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaushik, P., Mishra, A., Malik, A. et al. Biosorption of Textile Dye by Aspergillus lentulus Pellets: Process Optimization and Cyclic Removal in Aerated Bioreactor. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 1978 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1978-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1978-x