Abstract
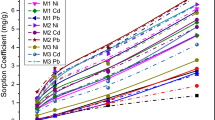
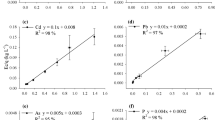
This study evaluated the effect of the soil solution ionic strength (IS) on the adsorption of Zn, Cu, Cd, Pb, As, and P on aluminum mining by-product (AMB), as well as performed the toxicity characteristic leaching procedure test (TCLP) followed by semi-total digestion in order to evaluate whether the adsorbed elements can cause environmental health risks. We measured adsorption by reacting the adsorbent with Zn, Cu, Cd, Pb, As, and P solutions in low IS (47 mmol L−1) and high IS (470 mmol L−1). Subsequent cation and anion desorption was evaluated by adding electrolyte solutions to the remaining adsorption residue. After the desorption experiment, we performed the TCLP test followed by semi-total digestion. Changing the IS interfered on Zn, Cd, Cu, and As adsorption, while no effect was observed for Pb and P. Increasing IS decreased the desorbed amounts of Cd, Zn, Cu, and As. Among the studied elements, Cd and Zn were noteworthy for having adsorbed the least and desorbed the most. Disposal of the AMB after being used as adsorbent of Cd, Pb, and As has to be carefully made as it may present their contents above the concentration causing toxicity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrow, N. J. (1999). The four laws of soil chemistry: the Leeper lecture 1998. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 37(5), 787–830.
Bradl, B. H. (2004). Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soils and soils constituents. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 277(1), 1–18.
Campos, M. L., Guilherme, L. R. G., Lopes, R. S., Antunes, A. S., Marques, J. J. G. S. M., & Curi, N. (2007). Teor e capacidade máxima de adsorção de arsênio em Latossolos brasileiros. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 31(6), 1311–1318.
Campos, M. L., Guilherme, L. R. G., Visioli, E., Antunes, A. S., Curi, N., Marque, J. J., et al. (2006). Força iônica da solução de equilíbrio na adsorção de arsênio em latossolos brasileiros. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 41(3), 457–460.
Christl, I., & Kretzschmar, R. (1999). Competitive sorption of copper and lead at the oxide-water interface: implications for surface site density. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(19/20), 2929–2938.
Costa, E. T. S., Guilherme, L. R. G., Curi, N., Lopes, G., Visioli, E. L., & Oliveira, L. C. A. (2009). Caracterização de subproduto da indústria de alumínio e seu uso na retenção de cádmio e chumbo em sistemas monoelementares. Quimica Nova, 32(4), 868–874.
Echeverría, J. C., Morera, M. T., Mazkiarán, C., & Garrido, J. J. (1998). Competitive sorption of heavy metal by soils. Isotherms and fractional factorial experiments. Environmental Pollution, 101(2), 275–284.
Egirani, D. E., Baker, A. R., & Andrews, J. E. (2005). Copper and zinc removal from aqueous solution by mixed mineral systems I. Reactivity and removal kinetics. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 291(2), 319–325.
Environmental Health and Safety Online - EHSO (2008) Hazardous Waste Fact Sheet: TCLP, Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure and Characteristic Hazardous Wastes, 2008. In EHSO. http://www.ehso.com/cssepa/TCLP%20fact%20sheet%20from%20EHSO.pdf. Accessed 04 Nov 2012.
Ferreira, D.F. (2009). SISVAR, Sistema de análise de variância, Ver. 5.1, Universidade Federal de Lavras, Departamento de Ciências Exatas, Lavras. http://www.dex.ufla.br/~danielff/softwares.htm. Accessed 12 Jun 2013.
Geelhoed, J. S., Hiemstra, T., & Riemsdijk, W. H. V. (1997). Phosphate and sulfate adsorption on goethite: single anion and competitive adsorption. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61(12), 2389–2396.
Genç-Fuhrman, H., Bregnhoj, H., & McConchie, D. (2005). Arsenate removal from water using sand-red mud columns. Water Research, 39(13), 2944–2954.
Genç-Fuhrman, H., Tjell, J. C., & McConchie, D. (2004). Increasing the arsenate adsorption capacity of neutralized red mud (Bauxsol). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 271(2), 313–320.
Genç, H., Tjell, J. C., McConchie, D., & Schuiling, O. (2003). Adsorption of arsenate from water using neutralized red mud. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 264(2), 327–334.
Guan, X. H., Wang, J., & Chusuei, C. C. (2008). Removal of arsenic from water using granular ferric hydroxide: macroscopic and microscopic studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 156(1/3), 178–185.
Gustaffson, J. P. (2010). Visual Minteq, ver, 2.53, KTH, Kungliga Tekniska Högskolgn, Royal Institute of Technology. Department of Land and Water Resources Engineering. Stockholm. http://www.lwr.kth.se/English/OurSoftware/vminteq/. Accessed 20 Dec 2010.
Juang, R. S., & Chung, J. Y. (2004). Equilibrium sorption of heavy metal and phosphate from single- and binary-sorbate solutions on goethite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 275(1), 53–60.
Kersten, M., & Vlasova, M. (2009). Arsenite adsorption on goethite at elevated temperatures. Applied Geochemistry, 24(1), 32–43.
Kosma, C., Balomenou, G., Salahas, G., & Deligiannakis, Y. (2009). Electrolyte ion effects on Cd2+ binding at Al2O3 surface: specific synergism versus bulk effects. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 331(2), 263–274.
Lindsay, W. L. (1979). Chemical equilibria in soils. New York: Wiley-Interscience.
McBride, M. B. (1994). Environmental chemistry of soils. New York: Oxford University.
Morera, M. T., Echeverría, J. C., Mazkiarán, C., & Garrido, J. J. (2001). Isotherms and sequential extraction procedures for evaluating sorption and distribution of heavy metals in soils. Environmental Pollution, 113(2), 135–144.
Mustafa, G., Singh, B., & Kookana, R. S. (2004). Cadmium adsorption and desorption behaviour on goethite at low equilibrium concentrations: effects of pH and index cations. Chemosphere, 57(10), 1325–1333.
Pierangeli, M. A. P., Guilherme, L. R. G., Oliveira, L. R., Curi, N., & Silva, M. L. N. (2001). Efeito da força iônica da solução de equilíbrio sobre a adsorção/dessorção de chumbo em Latossolos brasileiros. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 36(8), 1077–1084.
Pierangeli, M. A. P., Guilherme, L. R. G., Oliveira, L. R., Curi, N., & Silva, M. L. N. (2003). Efeito da força iônica da solução de equilíbrio na adsorção de cádmio em Latossolos brasileiros. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 38(6), 737–745.
Sparks, D. L. (2003). Environmental soil chemistry (2nd ed.). San Diego: Academic.
Sprynskyy, M., Buszewski, B., Terzyk, A. P., & Namiesnik, J. (2006). Study of the selection mechanism of heavy metal (Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Cd2+) adsorption on clinoptilolite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 304(1), 21–28.
Stachowicz, M., Hiemstra, T., & Riemsdijk, W. H. V. (2008). Multi-competitive interaction of As (III) and As (V) oxyanions with Ca2+, Mg2+, PO3 4−, and CO3 2– ions on goethite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 320(2), 400–414.
Trivedi, P., Axe, L., & Dyer, J. (2001). Adsorption of metal ions onto goethite: single-adsorbate and competitive systems. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 191(1/2), 107–121.
USEPA. (1998). United States Environmental Protection Agency Method 3051A, Microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils, and oils. SW-846. In Test methods for evaluating solid waste, physical/chemical methods (pp. 1–20). Washington DC: Environmental Protection Agency.
USEPA. (1992) United States Environmental Protection Agency Method 1311, TCLP - Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure. In SW-846, Test methods for evaluating solid waste, physical/chemical methods (pp. 1–38). Office of solid Waste. Washington DC: Environmental Protection Agency.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank CNPq, CAPES, and FAPEMIG for sponsoring part of the project and for granting scholarships to the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de S. Costa, E.T., Guilherme, L.R.G., Lopes, G. et al. Effect of Equilibrium Solution Ionic Strength on the Adsorption of Zn, Cu, Cd, Pb, As, and P on Aluminum Mining By-Product. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 1894 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1894-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1894-0