Abstract
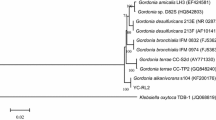
The congener-specific degradation pattern of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in Aroclor 1254 was investigated using a novel bacterial strain, Stenotrophomonas sp. JSG1, and it was accelerated by the surfactant, β-cyclodextrin. In addition, 4-chorobenzoic acid (CBA) degradation was also confirmed by the estimation of CBA depletion rate, microbial growth, and release of free chloride ion in mineral medium. Metal ions such as Ni2+, Hg2+ Ba2+, Cu2+, and NaCl (>4 %) were found greatly influencing the PCB degradation. However, Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe2+, and Mn2+ have not shown any impact on biodegradation. The bphC gene, which encodes an extradiol aromatic ring cleavage dioxygenase was successfully amplified and cloned. Phylogeny-based pairwise alignment of nucleotide sequences suggested that the cloned gene belongs to the extradiol dioxygenase family, but it showed high diversity to the traditional bphC gene. Results of the present investigation revealed that the Stenotrophomonas sp. JSG1 is an effective novel bacterium, which can be used in the PCB remediation studies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebusoye, S. A., Picardal, F. W., Fuqua, C., Ilori, M. O., & Amund, O. O. (2008). Characterization of multiple novel aerobic polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) utilizing bacterial strains indigenous to contaminated tropical African soils. Biodegradation, 19, 145–159.
Angle, J. S., & Chaney, R. L. (1989). Cadmium resistance screening in nitrilotriacetate-buffered minimal media. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 55, 2101–2104.
Arnett, C. M., Parales, J. V., & Haddock, J. D. (2000). Influence of chlorine substituents on rates of oxidation of chlorinated biphenyls by the biphenyl dioxygenase of Burkholderia sp. strain LB400. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66, 2928–2933.
Bai, G., Brusseau, M. L., & Miller, R. M. (1997). Biosurfactant enhanced removal of residual hydrocarbon from soil. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 25, 157–170.
Barber, J. L., Sweetman, A. J., Wijk, D. V., & Jones, K. C. (2005). Hexachlorobenzene in the global environment: Emissions, levels, distribution, trends and processes. The Science of the Total Environment, 349, 1–44.
Bedard, D. L., Unterman, R., Bopp, L. H., Brennan, M. J., Haberl, M. L., & Johnson, C. (1986). Rapid assay for screening and characterizing microorganisms for the ability to degrade polychlorinated biphenyls. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 51, 761–768.
Boyle, A. W., Silvin, C. J., Hassett, J. P., Nakas, J. P., & Tanenbaum, S. W. (1992). Bacterial PCB biodegradation. Biodegradation, 3, 285–298.
Bergmann, J. G., & Sanik, J. (1957). Determination of trace amounts of chlorine in naphtha. Analytical Chemistry, 29, 241–243.
Chae, J. C., Kim, Y., Kim, Y. C., Zylstra, G. J., & Kim, C. K. (2000). Genetic structure and functional implication of the fcb gene cluster for hydrolytic dechlorination of 4-chlorobenzoate from Pseudomonas sp. DJ-12. Gene, 258, 109–116.
Coleman, N. V., Mattes, T. E., Gossett, J. M., & Spain, J. C. (2002). Biodegradation of cis-dichloroethene as the sole carbon source by a β-proteobacterium. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 2726–2730.
Eltis, L., & Bolin, J. (1996). Evolutionary relationships among extradiol dioxygenases. Journal of Bacteriology, 178, 5930–5937.
Felsenstein, J. (1985). Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution, 39, 783–791.
Ferrer, M. R., Ruiz, B. F., & Ramos, C. A. (1986). Utilization of the herbicide dicamba (2-methoxy-3,6-dichlorobenzoic acid) by soil bacteria. Agrochimica, 30, 458–464.
Ganesh-Kumar, S., Solomon, R. D. J., Kalimuthu, K., & Vimalan, J. (2010). Evidence of aerobic degradation of polychlorinated biphenyl as growth substrate by new bacteria Stenotrophomonas sp. JSG1 and Cupriavidus taiwanensis JSG2. Carpathian Journal of Earth and Envionmental Science, 5, 169–176.
Gibello, A., Ferrer, E., Martin, M., & Garrido-Pertierra, A. (1994). 3,4-Dihydroxy phenylacetate 2,3-dioxygenase from Klebsiella pneumoniae, a Mg21-containing dioxygenase involved in aromatic catabolism. The Biochemical Journal, 301, 145–150.
Haggblom, M. M. (1992). Microbial breakdown of halogenated aromatic pesticides and related compounds. FEMS Microbiology Review, 103, 29–72.
Hernandez, B. S., Higson, F. K., Kondrat, R., & Focht, D. D. (1991). Metabolism of and inhibition by chlorobenzoates in Pseudomonas putida P111. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 57, 3361–3366.
Li, A., Qu, Y., Zhou, J., & Ma, F. (2009). Characterization of a newly isolated biphenyl-degrading bacterium Dyella ginsengisoli LA-4. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 159, 687–695.
Liebert, C. A., Barkay, T., & Turner, R. R. (1991). Acclimation of aquatic microbial communities to Hg (II) and CH3Hg+ in polluted fresh water ponds. Microbial Ecology, 21, 139–149.
Katayama, A., Bhula, R., Burns, G. R., Carazo, E., Felsot, A., Hamilton, D., Harris, C., Kim, Y. H., Kleter, G., Koedel, W., Linders, J., Peijnenburg, J. G. M. W., Sabljic, A., Stephenson, R. G., Racke, D. K., Rubin, B., Tanaka, K., Unsworth, J., & Wauchope, R. D. (2012). Bioavailability of xenobiotics in the soil environment. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 203, 1–86.
Kim, S., & Picardal, F. W. (2000). A novel bacterium that utilizes monochlorobiphenyls and 4-chlorobenzoate as growth substrates. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 185, 225–229.
Miguez, C. B., Greer, C. W., & Ingram, J. M. (1990). Degradation of monochlorobenzoic and dichlorobenzoic acid isomers by two natural isolates of Alcaligenes denitrificans. Archives of Microbiology, 154, 139–143.
Mondello, F. J., Turcich, M. P., Lobos, J. H., & Erickson, B. D. (1997). Identification and modification of biphenyl dioxygenase sequences that determine the specificity of polychlorinated biphenyl degradation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63, 3096–3103.
Nies. (1999). Microbial heavy metal resistance. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 67, 730–750.
Pieper, D. H. (2005). Aerobic degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 67, 170–191.
Pitcher, G. S., Saunders, N. A., & Owen, R. J. (1989). Rapid extraction of bacterial genomic DNA with guanidium thiocyanate. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 8, 151–156.
Providenti, M. A., Lee, H., & Trevors, J. T. (1993). Selected factors limiting the microbial degradation of recalcitrant compounds. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 12, 379–395.
Reineke, W., & Knackmuss, H. J. (1980). Hybrid pathway for chlorobenzoate metabolism in Pseudomonas sp. B13 derivatives. Journal of Bacteriology, 142, 467–473.
Rodrigues, J. L. M., Kachel, C. A., Aiello, M. R., Quenssen, J. F., Maltseva, O. V., Tsoi, T. V., & Tiedje, J. M. (2006). Degradation of Aroclor 1242 dechlorination products in sediments by Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 (ohb) and Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1 (fcb). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 2476–2482.
Sandrin, T. R., & Maier, R. M. (2003). Impact of metals on the biodegradation of organic pollutants. Environmental Health Perspectives, 111, 1093–1101.
Stratford, J., Wright, M. A., Reineke, W., Mokross, H., Havel, J., Knowles, C. J., & Robinson, G. R. (1996). Influence of chlorobenzoates on the utilization of chlorobiphenyls and chlorobenzoate mixtures by chlorobiphenyl/chlorobenzoate-mineralizing hybrid bacterial strains. Achieves of Microbiology, 165, 213–218.
Sylvestre, M., Mailhiot, K., Ahmad, D., & Masse, R. (1989). Isolation and preliminary characterization of a 2 chlorobenzoate degrading Pseudomonas. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 35, 439–443.
Takami, H., Kudo, T., & Horikoshi. (1997). Isolation of extradiol dioxygenase genes that are phylogenetically distant from other meta-cleavage dioxygenase genes. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 61, 530–532.
Vaillancourt, F. H., Labbe, G., Drouin, N. M., Fortin, P. D., & Eltis, L. D. (2002). The mechanism-based inactivation of 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 2019–2027.
Volkering, F., Breure, A. M., Van Andel, J. G., & Rulkens, W. H. (1995). Influence of nonionic surfactants on bioavailability and biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 61, 1699–1705.
Vrana, B., Dercova, K., Balaz, S., & Sevcikova, A. (1996). Effect of chlorobenzoates on the degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) by Pseudomonas stutzeri. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 12, 323–326.
Yi, H. R., Min, K. H., Kim, C. K., & Ka, J. O. (2000). Phylogenetic and phenotypic diversity of 4-chlorobenzoate-degrading bacteria isolated from soils. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 31, 53–60.
Acknowledgments
This work has been financially supported by the ‘Council of Scientific & Industrial Research-Human resource Development group’ (CSIR-HRDG) and the ‘Department of Biotechnology’ (DBT), India, which we gratefully thank.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganesh-Kumar, S., Kalimuthu, K. & Jebakumar, S.R. A Novel Bacterium That Degrades Aroclor-1254 and Its bphC Gene Encodes an Extradiol Aromatic Ring Cleavage Dioxygenase (EARCD). Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1587 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1587-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1587-0