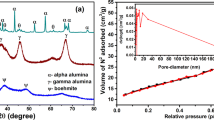
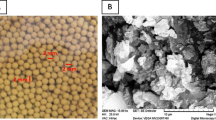
Abstract
The present study was conducted to study the feasibility of alumina impregnated calcium alginate beads to sorb the excess fluoride ions from the potable water. Numerous defluoridation techniques have been explored to remove excess fluoride ions from potable water, no single method has been found to be both effective and inexpensive enough to implement widely. During this work defluoridation was done using alumina impregnated calcium alginate beads without disturbing the drinking water qualities. The optimal condition for synthesis of calcium alginate alumina (Cal-Alg-Alu) beads is 2 % (wt/vol) having 22 % (wt/vol) alumina loading, stirring time: 1 h, drying temperature: 60 °C for 8 h. The nature and morphology of pure and fluoride-sorbed calcium alginate alumina beads were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) analysis. The results of batch sorption experiments suggest that Cal-Alg-Alu beads is very effective for defluoridation in the pH range of 3.5–9.0 and sorption is more than 99.9 % in the concentration range of 1–100 mg l−1. Equilibrium sorption follows Langmuir isotherms well and the maximum fluoride uptake calculated is 17.0 mg g−1. The sorption kinetics can be explained by pseudo-second-order model well and the time needed for equilibrium is 300 min.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amor, Z., Bariou, B., Mameri, N., Taky, M., Nicolas, S., & Elmidaoui, A. (2001). Fluoride removal from brackish water by electro dialysis. Desalination, 133, 215–223.
Bansiwal, A., Pillewan, P., Biniwale, R. B., & Rayalu, S. S. (2010). Copper oxide incorporated mesoporous alumina for defluoridation of drinking water. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 129, 54–61.
Bhargava, D. S., & Killedar, D. J. (1992). Fluoride adsorption on fishbone charcoal through a moving media absorber. Water Research, 26, 781–788.
Binbin, W., Baoshan, Z., Hongying, W., Yakun, P., & Yuehua, T. (2005). Dental caries in fluorine exposure areas in China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 27, 285–288.
Chen, L., Wu, H. X., Wang, T. J., Jin, Y., Zhang, Y., & Dou, X. M. (2009). Granulation ofFe–Al–Ce nano-adsorbent for fluoride removal from drinking water by spray coating on sand in a fluidized bed. Powder Technology, 193, 59–64.
Chen, N., Zhang, Z., Feng, C., Sugiura, N., Li, M., & Chen, R. (2010). Fluoride removal from water by granular ceramic adsorption. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 348, 579–584.
Daifullah, A. A. M., Yakout, S. M., & Elreefy, S. A. (2007). Adsorption of fluoride in aqueous solutions using KMnO4-modified activated carbon derived from steam pyrolysis of rice straw. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147, 633–643.
Ghorai, S., & Pant, K. K. (2004). Investigations on the column performance of fluoride adsorption by activated alumina in a fixed-bed. Chemical Engineering Journal, 98, 165–173.
Harrison, P. T. C. (2005). Fluoride in water: a UK perspective. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 126, 1448–1456.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second-order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34, 451–465.
Hu, C. Y., Lo, S. L., & Kuan, W. H. (2005). Effects of the molar ratio of hydroxide and fluoride to Al(III) on fluoride removal by coagulation and electro coagulation. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 283, 472–476.
Kumar, A., Bhatnagar, M., Jung Ji, W., Lee, S., Kim, S. J., Lee, G., Song, H., Choi, J. Y., Yang, J., & Jeon, B. H. (2009). Defluoridation from aqueous solutions by granular ferric hydroxide (GFH). Water Research, 43, 490–498.
Kumar, E., Bhatnagar, A., Kumar, U., & Mika, S. (2011). Defluoridation from aqueous solutions by nano-alumina: characterization and sorption studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186, 1042–1049.
Lagergren, S. (1898). About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar, 24(4), 1–39.
Ma, W., Ya, F.-Q., Han, M., & Wang, R. (2007). Characteristics of equilibrium, kinetics studies for adsorption of fluoride on magnetic-chitosan particle. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 143, 296–302.
Mahramanlioglu, M., Kizilcikli, I., & Bicer, I. O. (2002). Adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution by acid treated spent bleaching earth. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 115, 41–47.
Maiti, A., Basu, J. K., & De, S. (2011). Chemical treated laterite as promising fluoride adsorbent for aqueous system and kinetic modeling. Desalination, 265, 28–36.
Meenakshi, M., & Maheshwari, R. C. (2006). Fluoride in drinking water and its removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials B, 137, 456–463.
Moges, G., Zewge, F., & Socher, M. (1996). Preliminary investigations on the defluoridation of water using fired clay chips. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 21, 479–482.
Ndiaye, P. I., Moulin, P., Dominguez, L., Millet, J. C., & Charbit, F. (2005). Removal of fluoride from electronic industrial effluent by RO membrane separation. Desalination, 173, 25–32.
Nordstrom, D. K., Ball, J. W., Donahoe, R. J., & Whittemore, D. (1989). Ground water chemistry and water–rock interactions at Stripa. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53, 1727–1740.
Nordstrom, D. K., & Jenne, E. A. (1977). Fluorite solubility equilibria in selected geothermal waters. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 41, 175–188.
Onyango, M. S., Kojima, Y., Kumar, A., Kuchar, D., Kubota, M., & Matsuda, H. (2006). Uptake of fluoride by Al3+-pretreated low-silica synthetic zeolites: adsorption equilibrium and rate studies. Separation Science and Technology, 41, 683–704.
Rankama, K., & Edgington, G. (1946). Fluorine in soils. Soil Science, 61, 341–353.
Rao, N. V. R., Rao, N., Rao, K. S. P., & Schuiling, R. D. (1993). Fluorine distribution in waters of Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology, 21, 84–89.
Reardon, E. J., & Wang, Y. (2000). A limestone reactor for fluoride removal from wastewaters. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 3247–3253.
Saha, S. (1993). Treatment of aqueous effluent for fluoride removal. Water Research, 27, 1347–1350.
Saxena, V. K., & Ahmed, S. (2001). Dissolution of fluoride in groundwater: a water–rock interaction study. Environmental Geology, 49(9), 1084–1087.
Singhal, R. K., Basu, H., Manish, V., Reddy, A. V. R., & Mukherjee, T. (2011). Removal of low level of Am-241 from potable water originated from different geochemical environments by calcium alginate. Desalination, 280, 313–318.
Singhal, R. K., Joshi, S. R. K., Shobha, T. K., & Gurg, R. P. (2004). Reduction of uranium concentration in well water by Chlorella (Chlorella pyrendoidosa) a fresh water algae immobilised in calcium alginate. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 261(1), 73–78.
Tchomgui-Kamga, E., Alonzo, V., Nanseu-Njiki, C. P., Audebrand, N., Ngameni, E., & Darchen, A. (2010). Preparation and characterization of charcoals that contain dispersed aluminum oxide as adsorbents for removal of fluoride from drinking water. Carbon, 48, 333–343.
Teng, S.-X., Wang, S.-G., Gong, W.-X., Liu, X.-W., & Gao, B.-Y. (2009). Removal of fluoride by hydrous manganese oxide-coated alumina: performance and mechanism. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168, 1004–1011.
Thakre, D., Jagtap, S., Bansiwal, A., Labhsetwar, N., & Rayalu, S. (2010). Synthesis of La-incorporated chitosan beads for fluoride removal from water. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 131, 373–377.
Tsuchida, T. (1993). Preparation and reactivity of acicular αAl2O3 from synthetic diaspore βAl2O3·H2O. Solid State Ionics, 63, 464–470.
Vaaramaa, K., & Lehto, J. (2003). Removal of metals and anions from drinking water by ion exchange. Desalination, 155, 157–170.
Viswanathana, N., & Meenakshi, S. (2010). Selective fluoride adsorption by a hydrotalcite/chitosan composite. Applied Clay Science, 48, 607–611.
Wang, Y., & Reardon, E. J. (2001). Activation and regeneration of a soil sorbent for defluoridation of drinking water. Applied Geochemistry, 16, 531–539.
World Health Organization (2006). Guidelines for drinking-water quality [Electronic Resource]: Incorporating first addendum (vol. I). Recommendations (pp. 375–377). Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press.
Wu, X., Zhang, Y., Dou, X., & Yang, M. (2007). Fluoride removal performance of a novel Fe–Al–Ce trimetal oxide adsorbent. Chemosphere, 69, 1758–1764.
Yang, M., Hashimoto, T., Hoshi, N., & Myoga, H. (1999). Fluoride removal in a fixed bed packed with granular calcite. Water Research, 33, 3395–3402.
Zhang, W., Sun, M., & Prins, R. (2002). Multinuclear MAS NMR identification of fluorine species on the surface of fluorinated –alumina. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 106, 11805–11809.
Zhao, X., Wang, J., Wu, F., Wang, T., Cai, Y., Shi, Y., & Jiang, G. (2010). Removal of fluoride from aqueous media by Fe3O4@Al(OH)3 magnetic nano particles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173, 102–109.
Zhareslu, M., Crisan, P. M., Fruth, V., & Preda, S. (2003). Al2TiO5-based ceramics obtained by hydrothermal process. Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, 5, 1411–1416.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the encouragement and guidance provided by Prof. T. Mukherjee, director of chemistry group. The authors also thank Shri Ajay Kumar and Shri Sabyasachi Rout of Health Physics Division for analysing the samples by ion chromatography.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basu, H., Singhal, R.K., Pimple, M.V. et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Alumina Impregnated Alginate Beads for Fluoride Removal from Potable Water. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1572 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1572-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1572-7