Abstract
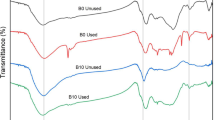
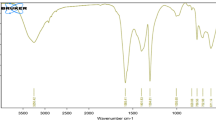
In the present work, goethite (α-FeO(OH)) impregnated calcium alginate (Cal-Alg-Goe) beads were used to sorb the arsenic from groundwater without disturbing its physicochemical characteristics. Beads were formed by dropwise addition of homogenized mixer of goethite and 4 % sodium alginate solution in 0.2 M CaCl2 solution. Charge, size, and morphology of sorbents were characterized by using various techniques. The results of batch sorption experiments suggest that Cal-Alg-Goe beads are very effective for removal of arsenic in the pH range 3.0 to 7.5, and sorption was more than 95 % in the concentration range of 10–10,000 ng mL−1. Beads were successfully tested for groundwater samples collected from areas having elevated levels of arsenic. Equilibrium sorption follows Langmuir isotherm model, and the maximum arsenic uptake calculated was 30.44 mg g−1. The sorption kinetics could be explained by pseudo-first-order model, and the time needed for equilibrium was 24 h.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asta, M. P., Cama, J., Martinez, M., & Gimenez, J. (2009). Arsenic removal by goethite and jarosite in acidic conditions and its environmental implications. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171, 965–972.
Banerjee, A., & Nayak, D. (2007). Biosorption of no-carrier-added radionuclides by calcium alginate beads using ‘tracer packet’ technique. Bioresource Technology, 98, 2771–2774.
Basu, H., Singhal, R. K., Pimple, M. V., & Reddy, A. V. R. (2013). Synthesis and characterization of alumina impregnated alginate beads for fluoride removal from potable water. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 224(6), 1–12.
Bezbaruah Achintya, N., Krajangpan, S., Chisholmb Bret, J., Khan, E., Bermudez, J., & Elorza, J. (2009). Entrapment of iron nanoparticles in calcium alginate beads for groundwater remediation applications. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166, 1339–1343.
Bissen, M., & Frimmel, F. H. (2003). Arsenic—a review part II. Oxidation of arsenic and its removal in water treatment. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 31, 97–107.
Brookins, D. G. (1988). Eh–pH diagrams for geochemistry. Berlin: Springer.
Buddemeier, R. W., & Hunt, J. R. (1988). Transport of colloidal contaminants in groundwater: radionuclide migration at the Nevada test site. Applied Geochemistry, 3, 535.
Crittenden, B., & Thomas, W.J. (1998). Adsorption Technology and Design, Buterworth-Heinemann, 1st edition.
Cullen, W. R., & Reimer, K. J. (1989). Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chemical Reviews, 89, 713–764.
Degueldre, C., Baeyens, B., Goerlich, W., Riga, J., Verbist, J., & Stadelmann, P. (1989). Colloids in water from a subsurface fracture in granitic rock, Grimsel test site, Switzerland. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53, 603–610.
Dinesh, M., & Pittman, C. U., Jr. (2007). Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 142, 1–53.
Ferguson, J. F., & Gavis, J. (1972). A review of the arsenic cycle in nature waters. Water Research, 6.
Ghosh, M. M., & Yuan, J. R. (1987). Adsorption of inorganic arsenic and organoarsenicals on hydrous oxide. Environmental Progress, 6, 150.
Gim’enez, J., Mart’ınez, M.’ı., de Pablo, J., Rovira, M., & Duro, L. (2007). Arsenic sorption onto natural hematite, magnetite, and goethite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 141, 575–580.
Goldberg, S., & Johnston, C. T. (2001). Mechanisms of arsenic adsorption on amorphous oxides evaluated using macroscopic measurements, vibrational spectroscopy, and surface complexation modeling. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 234, 204–216.
Guan, X.-H., Wang, J., & Chusuei, C. C. (2008). Removal of arsenic from water using granular ferric hydroxide: macroscopic and microscopic studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 156, 178–185.
Gupta, S., & Babu, B. V. (2009). Removal of toxic metal Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions using sawdust as adsorbent: equilibrium, kinetics and regeneration studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 150, 352–365.
Gupta, S. K., & Chen, K. Y. (1978). Arsenic removal by adsorption. Journal Water Pollution Control Federation, 50(3), 493–506.
Gupta, V. K., Sharma, S., Yadau, I. S., & Dinesh, M. (1998). Utilisation of bagasses fly ash generated in sugar industry for the removal of phenol and p-nitrophenol from wastewater. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 71, 180–186.
Gupta, V. K., Saini, V. K., & Jain, N. (2005). Adsorption of As(III) from aqueous solutions by iron oxide-coated sand. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 288, 55–60.
Huang, C. P., & Smith, E. H. (1981). Removal of Cd(II) from plating wastewater by an activated carbon process. Chem. Water Reuse, 2, 355–398.
Jekel, M. R. (1994). Removal of arsenic in drinking water treatment. In J. O. Nriagu (Ed.), Arsenic in the environment part I. Cycling and characterization (pp. 119–132). New York: Wiley.
Katsoyiannis, I., Zouboulis, A., & Anastasios, I. (2004). Application of biological processes for the removal of arsenic from groundwaters. Water Research, 38, 17–26.
Lezehari, M., Baudu, M., Bouras, O., & Basly, J. P. (2012). Fixed-bed column studies of pentachlorophenol removal by use of alginate-en-capsulated pillared clay microbeads. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 379(1), 101–106.
Li, N., Zhang, L., Yongzhou Tian, Y., & Wang, H. (2011). Adsorption behavior of Cu(II) onto titanate nanofibers prepared by alkali treatment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 189, 265–272.
Mandal, B. K., & Suzuki, K. T. (2002). Arsenic round the world: a review. Talanta, 58, 201–235.
Manning, B. A., & Goldberg, S. (1996). Modeling competitive adsorption of arsenate with phosphate and molybdate on oxide minerals. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 60, 121–131.
Manning, B. A., Fendorf, S. E., & Goldberg, S. (1998). Surface structures and stability of arsenic (III) on goethite: spectroscopic evidence for inner-sphere complexes. Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 2383–2388.
McCarthy, J. F., & Degueldre, C. (1993). Sampling and characterization of colloids and particles in groundwater for studying their role in contaminant transport. In J. Buffle & H. P. van Leeuwen (Eds.), Environmental particles (Vol. 2, pp. 247–315). Boca Raton: Lewis.
Mimura, H., Ohta, H., Hoshi, H., Akiba, K., Wakui, Y., & Onodera, Y. (2001). Uptake behavior of americium on alginic acid and alginate polymer gels. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 247, 33–38.
Mimura, A., Ohta, H., Hoshi, H., Akiba, H., & Wakui, K. Y. (2002). Onodera, Uptake and recovery of platinum group metals ions by alginate microcapsules immobilizing cyanex 302 emulsions. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39, 283–285.
Mok, W. M., & Wai, C. M. (1994). Mobilization of arsenic in contaminated river waters. In C. M. Wai & J. O. Nriagu (Eds.), Arsenic in the environment part I. Cycling and characterization (pp. 99–117). New York: Wiley.
Outokesh, M., Mimura, H., Niibori, Y., & Tanaka, K. (2006). Preparation of stable alginate microcapsules coated with chitosan or polyethyleneimine for extraction of heavy metal ions. Journal of Microencapsulation, 17(2), 291–301.
Puigdom’enech, I. (2004). MEDUSA. http://www.w1.156.telia.com/ u15651596. Accessed 30 May 2014.
Sakaguchi, T., Tsuji, T., Akira, N., & Horikoshi, T. (1979). Accumulation of cadmium by green microalgae. European Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 8, 207–215.
Singhal, R. K., Joshi, S., Tirumalesh, K., & Gurg, R. P. (2004). Reduction of uranium concentration in well water by chlorella (Chlorella pyrendoidosa) a fresh water algae immobilised in calcium alginate. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 261(1), 73–78.
Singhal, R. K., Basu, H., Manish, V., Reddy, A. V. R., & Mukherjee, T. (2011). Removal of Low level of Am-241 from potable water originated from different geochemical environments by calcium alginate. Desalination, 280, 313–318.
Singhal, R. K., Basu, H., & Reddy, A. V. R. (2013). Removal of environmental level of 239 + 240 Pu and 241Am from groundwater by using humic coated colloidal suspension of goethite (α-FeO(OH)). Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 295, 1345–1351.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 517–568.
Sullivan, K. A., & Aller, R. C. (1996). Diagenetic cycling of arsenic in Amazon shelf sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60, 1465–1477.
USEPA (2000). Arsenic treatment technology evaluation handbook for small system. EPA 816-R-03-014, Washington, DC.
Wang, S., & Mulligan, C. N. (2006). Occurrence of arsenic contamination in Canada: 3127 sources, behavior and distribution. Science of the Total Environment, 366, 701–721.
WHO (1993). Guidelines for drinking water quality recommendations. Geneva.
WHO (2006). Guidelines for drinking-water quality [electronic resource]: incorporating first addendum (vol. I) recommendations. pp. 375–377, 448–1456.
Zouboulis, A. I., & Katsoyiannis, I. A. (2002). Removal of arsenates from contaminated water by coagulation–direct filtration. Separation Science and Technology, 37(12), 2859–73.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely acknowledge the encouragement and guidance provided by Dr. B.N. Jagatap, Director, Chemistry group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basu, H., Singhal, R.K., Pimple, M.V. et al. Arsenic Removal from Groundwater by Goethite Impregnated Calcium Alginate Beads. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 22 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2251-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2251-z