Abstract
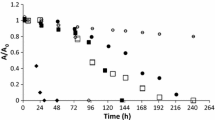
Four room temperature ionic liquids, [BMIM][PF6], [BMIM][NTf2], [PEGMIM][PF6], and Aliquat, were investigated regarding their use in a two-phase partition bioreactor dedicated to remove two hydrophobic VOC, dimethyldisulfide and toluene. Aliquat and [PEGMIM][PF6] cannot be further considered, owing to the toxicity of the former shown during glucose uptake inhibition tests and the water solubility of the latter. The partition coefficients of [BMIM][PF6] and [BMIM][NTf2] were found comparable to those recorded for typical liquid solvents used in multiphase bioreactors. They were also non-biodegradable, showed during long-term biodegradability tests. After 1 day of lag time, similar glucose biodegradation rates were recorded in the presence of 5 % [BMIM][PF6] or [BMIM][NTf2], if compared to controls deprived of ionic liquid. However, a clear inhibitory effect of the ionic liquids was observed during VOC biodegradation experiments. This phenomenon was significantly minimized after acclimation of activated sludge to VOC, since nearly similar consumption rates of toluene were recorded in the control deprived of IL and in the presence of 5 % bmimPF6, 0.49 and 0.48 g m−3 h−1, respectively. These promising results showed that more complex acclimation strategies, including microbial acclimation to both ionic liquids and VOC, will have to be considered.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahosseini, A., & Scurto, A. M. (2008). Viscosity of imidazolium-based ionic liquids at elevated pressures: cation and anion effects. International Journal of Thermophysics, 29, 1222–1243.
Aldric, J. M., Lecomte, J. P., & Thonat, P. (2009). Study on mass transfer of isopropylbenzene and oxygen in a two-phase partitioning bioreactor in the presence of silicone oil. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 153, 67–79.
Azimova, M. A., Morton, S. A., & Frymier, P. D. (2009). Comparison of three bacterial toxicity assays for imidazolium-derived ionic liquids. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 135, 1388–1392.
Baumann, M. D., Daugulis, A. J., & Jessop, P. G. (2005). Phosphonium ionic liquids for degradation of phenol in a two-phase partitioning bioreactor. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 67, 131–137.
Branco, L. C., Rosa, J. N., Ramos, J. J. M., & Afonso, C. A. M. (2002). Preparation and characterization of new room temperature ionic liquids. Chemistry-A European Journal, 8, 3671–3677.
Cascon, H. R., Choudhari, S. K., Nisola, G. M., Vivas, E. L., Lee, D.-J., & Chung, W.-J. (2011). Partitioning of butanol and other fermentation broth components in phosphonium and ammonium-based ionic liquids and their toxicity to solventogenic clostridia. Separation and Purification Technology, 78, 164–174.
Chaumont, A., Schurhammer, R., & Wipff, G. J. (2005). Aqueous interfaces with hydrophobic room-temperature ionic liquids: a molecular dynamics study. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 109, 18964–18973.
Chun, S., Dzyuba, S. V., & Bartsch, R. A. (2001). Influence of structural variation in room-temperature ionic liquids on the selectivity and efficiency of competitive alkali metal salt extraction by a crown ether. Analytical Chemistry, 73, 3737–3741.
Darracq, G., Couvert, A., Couriol, C., Amrane, A., & Le Cloirec, P. (2010). Kinetics of toluene and sulfur compounds removal bymeans of an integrated process involving the coupling of absorption and biodegradation. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 85, 1156–1161.
Darracq, G., Couvert, A., Couriol, C., Amrane, A., Thomas, D., Dumont, E., et al. (2010). Silicone oil: an effective absorbent for hydrophobic Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) removal. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 85, 309–313.
Domínguez-Pérez, M., Tomé, L. I. N., Freire, M. G., Marrucho, I. M., Cabeza, O., & Coutinho, J. A. P. (2010). (Extraction of biomolecules using) aqueous biphasic systems formed by ionic liquids and aminoacids. Separation and Purification Technology, 72, 85–91.
Duchet, L., Legeay, J. C., Carrie, D., Paquin, L., Vanden-Eynde, J. J., & Bazureau, J. P. (2010). Synthesis of 3,5-disubstituted 1,2,4-oxadiazoles using ionic liquid-phase organic synthesis (IoLiPOS) methodology. Tetrahedron, 66, 986–994.
Dumont, E., Darracq, G., Couvert, A., Couriol, C., Amrane, A., Thomas, D., et al. (2011). VOC absorption in a countercurrent packed-bed column using water/silicone oil mixtures: influence of silicone oil volume fraction. Chemical Engineering Journal, 168, 241–248.
Earle, M. J., & Seddon, K. R. (2000). Ionic liquids, green solvents for the future. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 72, 1391–1398.
Every, H., Bishop, A. G., Forsyth, M., & MacFarlane, D. R. (2000). Ion diffusion in molten salt mixtures. Electrochimica Acta, 45, 1279–1284.
Forsyth, C. M., MacFarlane, D. R., Golding, J. J., Huang, J., Sun, J., & Forsyth, M. (2002). Structural characterization of novel ionic materials incorporating the bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide anion. Chemistry of Materials, 14, 2103–2108.
Garcia, M. T., Gathergood, N., & Scammells, P. J. (2005). Biodegradable ionic liquids. Part II. Effect of the anion and toxicology. Green Chemistry, 7, 9–14.
Huddleston, J. G., Visser, A. E., Reichert, W. M., Willauer, H. D., Broker, G. A., & Rogers, R. D. (2001). Characterization and comparaison of hydrophilic and hydrophobic room temperature ionic liquids incorporating the imidazolium cation. Green Chemistry, 3, 156–164.
MacFarlane, D. R., Golding, J., Forsyth, S., Forsyth, M., & Deacon, G. B. (2001). Low viscosity ionic liquids based on organic salts of the dicyanamide anion. Chemical Communications, 16, 1430–1431.
Matsumoto, M., Mochiduki, K., Fukunishi, K., & Kondo, K. (2004). Extraction of organic acids using imidazolium-based ionic liquids and their toxicity to Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Separation and Purification Technology, 40, 97–101.
Ochoa-Herrera, V., Banihani, Q., Leon, G., Khatri, C., Field, J. A., & Sierra-Alvarez, R. (2009). Toxicity of fluoride to microorganisms in biological wastewater treatment systems. Water Research, 43, 3177–3186.
Ortiz, A., Ruiz, A., Gorri, D., & Ortiz, I. (2008). Room temperature ionic liquid with silver salt as efficient reaction media for propylene/propane separation: absorption equilibrium. Separation and Purification Technology, 63, 311–318.
Palomar, J., Gonzalez-Miquel, M., Bedia, J., Rodriguez, F., & Rodriguez, J. J. (2011). Task-specific ionic liquids for efficient ammonia absorption. Separation and Purification Technology, 82, 43–52.
Pei, Y., Wang, J., Wu, K., Xuan, X., & Lu, X. (2009). Ionic liquid-based aqueous two-phase extraction of selected proteins. Separation and Purification Technology, 64, 288–295.
Pham, T. P. T., Cho, C. W., & Yun, Y. S. (2010). Environmental fate and toxicity of ionic liquids: a review. Water Research, 44, 352–372.
Quijano, G., Couvert, A., & Amrane, A. (2010). Ionic liquids: applications and future trends in bioreactor technology. Bioresource Technology, 101, 8923–8930.
Quijano, G., Couvert, A., Amrane, A., Darracq, G., Couriol, C., Le Cloirec, P., et al. (2011a). Potential of ionic liquids for VOC absorption and biodegradation in multiphase systems. Chemical Engineering Science, 66, 2707–2712.
Quijano, G., Couvert, A., Amrane, A., Darracq, G., Couriol, C., Le Cloirec, P., et al. (2011b). Toxicity and biodegradability of ionic liquids: new perspectives towards whole-cell biotechnological applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 174, 27–32.
Rivera-Rubero, S., & Baldelli, S. J. (2004). Influence of water on the surface of hydrophilic and hydrophobic room-temperature ionic liquids. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 126, 11788–11789.
Robinson, J., & Osteryoung, R. A. (1979). An electrochemical and spectroscopic study of some aromatic hydrocarbons in the room temperature molten salt system aluminum chloride-n-butylpyridinium chloride. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 101, 323–327.
Rols, J. L., Condoret, J. S., Fonade, C., & Goma, G. (1990). Mechanisms of enhanced oxygen transfer in fermentation using emulsified oxygen-vectors. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 35, 427–435.
Ruivo, R., Couto, R., & Simões, P. C. (2010). Screening of ionic liquids as promising separation agents of oil mixtures for application in membranes. Separation and Purification Technology, 76, 84–88.
Sheldon, R. (2001). Catalytic reactions in ionic liquids. Chemical Communications, 23, 2399–2407.
Swatloski, R. P., Holbrey, J. D., & Rogers, R. D. (2003). Ionic liquids are not always green: hydrolysis of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. Green Chemistry, 5, 361–363.
Swatloski, R. P., Visser, A. E., Reichert, W. M., Broker, G. A., Farina, L. M., Holbrey, J. D., et al. (2001). Solvation of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate in aqueous ethanol—a green solution for dissolving ‘hydrophobic’ ionic liquids. Chemical Communications, 2070–2071.
Swatloski, R. P., Visser, A. E., Reichert, W. M., Broker, G. A., Farina, L. M., Holbrey, J. D., et al. (2002). On the solubilization of water with ethanol in hydrophobic hexafluorophosphate ionic liquids. Green Chemistry, 4, 81–87.
Tokuda, H., Hayamizu, K., Ishii, K., Susan, M. A. B. H., & Watanabe, M. (2005). Physicochemical properties and structures of room temperature ionic liquids. 2. Variation of alkyl chain length in imidazolium cation. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 109, 6103–6110.
Tokuda, H., Ishii, K., Susan, M. A. B. H., Tsuzuki, S., Hayamizu, K., & Watanabe, M. (2006). How ionic are room-temperature ionic liquids? An indicator of the physicochemical properties. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 110, 19593–19600.
Tomé, L. I. N., Catambas, V. R., Teles, A. R. R., Freire, M. G., Marrucho, I. M., & Coutinho, J. A. P. (2010). Tryptophan extraction using hydrophobic ionic liquids. Separation and Purification Technology, 72, 167–173.
Trinci, A. P. J. (1969). A kinetic study of the growth of Aspergillus nidulans and other fungi. Journal of General Microbiology, 57, 11–24.
Vestergaard, B., Bjerrum, N. J., Petrushina, I., Hjuler, H. A., Berg, R. W., & Begtrup, M. J. (1993). Molten triazolium chloride systems as new aluminum battery electrolytes. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 140, 3108–3113.
Vuong, M. D., Couvert, A., Couriol, C., Amrane, A., Le Cloirec, P., & Renner, C. (2009). Determination of the Henry’s constant and the mass transfer rate of VOCs in solvents. Chemical Engineering Journal, 150, 426–443.
Wasserscheid, P., & Welton, T. (2008). Ionic liquid in synthesis (2nd ed.). Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
Weingärtner, H. (2008). Understanding ionic liquids at the molecular level: facts, problems and controversies. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 47, 654–670.
Wilkes, J. S., Levisky, J. A., Wilson, R. A., & Hussey, C. L. (1982). Dialkylimidazolium chloroaluminate melts: a new class of room-temperature ionic liquids for electrochemistry, spectroscopy and synthesis. Inorganic Chemistry, 21, 1263–1264.
Wilkes, J. S., & Zaworotko, M. J. (1992). Air and water stable 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium based ionic liquids. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, 13, 965–967.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quijano, G., Couvert, A., Amrane, A. et al. Absorption and Biodegradation of Hydrophobic Volatile Organic Compounds in Ionic Liquids. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1528 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1528-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1528-y