Abstract
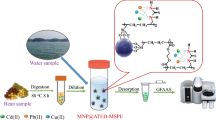
A simple flow-based method was developed for the selective separation of arsenic species (+3 and +5) using a macrocycle-immobilized solid phase extraction (SPE) system, commonly known as molecular recognition technology (MRT) gel. Arsenic species in solution or in the eluent were subsequently quantified with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. The separation behaviors of As(III) and As(V) on MRT–SPE were investigated. It was found that As(V) can be selectively collected on the SPE system within the range of pH 4 to 9, while As(III) was passed through the MRT–SPE. The retention capacity of the MRT–SPE material for As(V) was found to be 0.25 ± 0.04 mmol g−1. The detection limit of the method for As(V) was 0.06 μg L−1, and the relative standard deviation was 2.9 % (n = 10, C = 1 μmol L−1). Interference from the matrix ions was studied. In order to validate the developed method, certified reference materials of effluent wastewater and groundwater samples were analyzed, and the determined values were in good agreement with the certified values. The proposed method was successfully applied to the speciation analysis of tri- and pentavalent arsenic in natural water samples showing satisfactory recoveries (≥ 98.7 %).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2005). AnaLig® data sheet: AN-02. IBC Advanced Technologies, Inc., American Fork, UT.
Bag, H., Lale, M., & Türker, A. R. (1998). Determination of iron and nickel by flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry after preconcentration on Saccharomyces cerevisiae immobilized sepiolite. Talanta, 47, 689–696.
Barra, C. M., Santelli, R. E., Abrão, J. J., & Guardia, M. D. L. (2000). Arsenic speciation—a review. Quimica Nova, 23, 58–70.
Biernat, J. F., Konieczka, P., Tarbet, B. J., Bradshaw, J. S., & Izatt, R. M. (1994). Complexing and chelating agents immobilized on silica gel and related materials and their application for sorption of inorganic species. Separation and Purification Methods, 23, 77–348.
Bissen, M., & Frimmel, F. H. (2000). Speciation of As(III), As(V), MMA and DMA in contaminated soil extracts by HPLC-ICP/MS. Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 367, 51–55.
Bradshaw, J. S., & Izatt, R. M. (1997). Crown ethers: the search for selective ion ligating agents. Accounts of Chemical Research, 30, 338–345.
Bradshaw, J. S., Bruening, R. L., Krakowiak, K. E., Tarbet, B. J., Bruening, M. L., Izatt, R. M., et al. (1988). Preparation of silica gel-bound macrocycles and their cation-binding properties. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, 812–814.
Bradshaw, J. S., Izatt, R. M., Christensen, J. J., Krakowiak, K. E., Tarbet, B. J., Bruening, R. L., et al. (1989). Stable silica gel-bound crown ethers. Selective separation of metal ions and a potential for separations of amine enantiomers. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry, 7, 127–136.
Bruening, M. L., Mitchell, D. M., Bradshaw, J. S., Izatt, R. M., & Bruening, R. L. (1991). Effect of organic solvent and anion type on cation binding constants with silica gel bound macrocycles and their use in designing selective concentrator columns. Analytical Chemistry, 63, 21–24.
Camel, V. (2003). Solid phase extraction of trace elements. Spectrochimica Acta Part B-Atomic Spectroscopy, 58, 1177–1233.
Chen, D., Huang, C., He, M., & Hu, B. (2009). Separation and preconcentration of inorganic arsenic species in natural water samples with 3-(2-aminoethylamino) propyltrimethoxysilane modified ordered mesoporous silica micro-column and their determination by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164, 1146–1151.
Francesconi, K. A., & Kuehnelt, D. (2004). Determination of arsenic species: a critical review of methods and applications, 2000-2003. Analyst, 129, 373–395.
Goken, G., Bruening, R., & Bray, L. (1994). Solid phase extraction membranes for selective radionuclide separation. Denver: AIChE Summer National Meeting.
Hasegawa, H., Matsui, M., Okamura, S., Hojo, M., Iwasaki, N., & Sohrin, Y. (1999). Arsenic speciation including ‘hidden’ arsenic in natural waters. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 13, 113–119.
Hasegawa, H., Rahman, I. M. M., Kinoshita, S., Maki, T., & Furusho, Y. (2010). Non-destructive separation of metal ions from wastewater containing excess aminopolycarboxylate chelant in solution with an ion-selective immobilized macrocyclic material. Chemosphere, 79, 193–198.
Hasegawa, H., Rahman, I. M. M., Begum, Z. A., Umehara, Y., Maki, T., Furusho, Y., et al. (2013). A silica gel-bound macrocycle system for the selective separation of toxic cadmium from metal-affluent aqueous matrix. Central European Journal of Chemistry, 11, 341–347.
Hiraoka, M. (1982). Crown compounds: Their characteristics and applications. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Hiraoka, M. (1992). Crown ethers and analogous compounds. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Horwitz, E., Dietz, M., & Chiarizia, R. (1992). The application of novel extraction chromatographic materials to the characterization of radioactive waste solutions. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 161, 575–583.
Izatt, R. M. (1997). Review of selective ion separations at BYU using liquid membrane and solid phase extraction procedures. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry, 29, 197–220.
Izatt, R. M., Clark, G. A., Bradshaw, J. S., Lamb, J. D., & Christensen, J. J. (1986). Macrocycle-facilitated transport of ions in liquid membrane systems. Separation and Purification Methods, 15, 21–72.
Izatt, R. M., Bruening, R. L., Bruening, M. L., Tarbet, B. J., Krakowiak, K. E., Bradshaw, J. S., et al. (1988). Removal and separation of metal ions from aqueous solutions using a silica-gel-bonded macrocycle system. Analytical Chemistry, 60, 1825–1826.
Izatt, R. M., Bradshaw, J. S., Bruening, R. L., & Bruening, M. L. (1994). Solid phase extraction of ions of analytical interest using molecular recognition technology. American Laboratory, 26, 28C–28M.
Izatt, R. M., Bradshaw, J. S., Bruening, R. L., Tarbet, B. J., & Bruening, M. L. (1995). Solid phase extraction of ions using molecular recognition technology. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 67, 1069–1074.
Karim, M. (2000). Arsenic in groundwater and health problems in Bangladesh. Water Research, 34, 304–310.
Kumar, A. R., & Riyazuddin, P. (2007). Non-chromatographic hydride generation atomic spectrometric techniques for the speciation analysis of arsenic, antimony, selenium, and tellurium in water samples—a review. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 87, 469–500.
Liang, P., & Liu, R. (2007). Speciation analysis of inorganic arsenic in water samples by immobilized nanometer titanium dioxide separation and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Analytica Chimica Acta, 602, 32–36.
Lintschinger, J., Schramel, P., Hatalak-Rauscher, A., Wendler, I., & Michalke, B. (1998). A new method for the analysis of arsenic species in urine by using HPLC–ICP–MS. Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 362, 313–318.
Liska, I. (2000). Fifty years of solid-phase extraction in water analysis—historical development and overview. Journal of Chromatography. A, 885, 3–16.
Mahoney, J. M., Beatty, A. M., & Smith, B. D. (2001). Selective recognition of an alkali halide contact ion-pair. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 123, 5847–5848.
Mahoney, J. M., Beatty, A. M., & Smith, B. D. (2004). Selective solid–liquid extraction of lithium halide salts using a ditopic macrobicyclic receptor. Inorganic Chemistry, 43, 7617–7621.
Mandal, B. K., & Suzuki, K. T. (2002). Arsenic round the world: a review. Talanta, 58, 201–235.
Mays, D. E., & Hussam, A. (2009). Voltammetric methods for determination and speciation of inorganic arsenic in the environment —a review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 646, 6–16.
Muñoz, E., & Palmero, S. (2005). Analysis and speciation of arsenic by stripping potentiometry: a review. Talanta, 65, 613–620.
Nabeshima, T., Saiki, T., Iwabuchi, J., & Akine, S. (2005). Stepwise and dramatic enhancement of anion recognition with a triple-site receptor based on the calix[4]arene framework using two different cationic effectors. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 127, 5507–5511.
Nickson, R. A., Hill, S. J., & Worsfold, P. J. (1995). Analytical perspective. Solid phase techniques for the preconcentration of trace metals from natural waters. Analytical Proceedings including Analytical Communications, 32, 387–395.
Pergantis, S. A., Winnik, W., & Betowski, D. (1997). Determination of ten organoarsenic compounds using microbore high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray mass spectrometry mass spectrometry. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 12, 531–536.
Poole, C. F. (2000). Solid-phase extraction. In D. W. Ian (Ed.), Encyclopedia of separation science. Oxford: Academic.
Quevauviller, P., Andersen, K., Merry, J., & Jagt, H. V. D. (1998). The certification of the contents (mass fractions) of aluminium, arsenic, cadmium, copper and lead in groundwater (low content CRM 609; high content CRM 610). Luxembourg: Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements, European Commission.
Rahman, I. M. M., Nazim Uddin, M., Hasan, M. T., & Hossain, M. M. (2008). Assimilation of arsenic into edible plants grown in soil irrigated with contaminated groundwater. In J. Bundschuh, M. A. Armienta, P. Birkle, P. Bhattacharya, J. Matschullat, & A. B. Mukherjee (Eds.), Natural arsenic in groundwaters of Latin America Leiden. CRC/Balkema: The Netherlands.
Rahman, I. M. M., Begum, Z. A., & Hasegawa, H. (2011a). Application of molecular recognition technology: for selective solid phase extraction of ions. Saarbrücken: LAP LAMBERT Academic.
Rahman, I. M. M., Begum, Z. A., Nakano, M., Furusho, Y., Maki, T., & Hasegawa, H. (2011b). Selective separation of arsenic species from aqueous solutions with immobilized macrocyclic material containing solid phase extraction columns. Chemosphere, 82, 549–556.
Rahman, I. M. M., Furusho, Y., Begum, Z. A., Izatt, N., Bruening, R., Sabarudin, A., et al. (2011a). Separation of lead from high matrix electroless nickel plating waste solution using an ion-selective immobilized macrocycle system. Microchemical Journal, 98, 103–108.
Rahman, I. M. M., Furusho, Y., Begum, Z. A., Sabarudin, A., Motomizu, S., Maki, T., et al. (2011b). Selective separation of some ecotoxic transition metal ions from aqueous solutions using immobilized macrocyclic material containing solid phase extraction system. Central European Journal of Chemistry, 9, 1019–1026.
Ritsema, R., Dukan, L., Navarro, T. R. I., van Leeuwen, W., Oliveira, N., Wolfs, P., et al. (1998). Speciation of arsenic compounds in urine by LC-ICP MS. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 12, 591–599.
Rossi, D. T., & Zhang, N. (2000). Automating solid-phase extraction: current aspects and future prospects. Journal of Chromatography. A, 885, 97–113.
Sanchez, W. M., Zwicker, B., & Chatt, A. (2009). Determination of As(III), As(V), MMA and DMA in drinking water by solid phase extraction and neutron activation. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 282, 133–138.
Segura, M., Madrid, Y., Cámara, C., Rebollo, C., Azcarate, J., Kramer, G. N., et al. (2004). The certification of the mass concentrations of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, Se and Zn in wastewater, BCR-713 (effluent wastewater), BCR-714 (influent wastewater), BCR-715 (industrial effluent wastewater). Luxembourg: Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements, European Commission.
Smichowski, P., Valiente, L., & Ledesma, A. (2002). Simple method for the selective determination of As(III) and As(V) by ETAAS after separation with anion exchange mini-column. Atomic Spectroscopy, 23, 92–97.
Squibb, K. S., & Fowler, B. A. (1983). The toxicity of arsenic and its compounds. In B. A. Fowler (Ed.), Biological and environmental effects of arsenic. New York: Elsevier Science B.V.
Terlecka, E. (2005). Arsenic speciation analysis in water samples: a review of the hyphenated techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 107, 259–284.
Tsukube, H. (1993). Double armed crown ethers and armed macrocycles as a new series of metal-selective reagents: a review. Talanta, 40, 1313–1324.
USEPA (2002). Implementation guidance for the arsenic rule—drinking water regulations for arsenic and clarifications to compliance and new source contaminants monitoring (EPA-816-K-02-018). Washington, DC: United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA).
Vogelsberger, W., Seidel, A., & Rudakoff, G. (1992). Solubility of silica gel in water. Journal of the Chemical Society-Faraday Transactions, 88, 473–476.
Walkowiak, W., & Kozlowski, C. A. (2009). Macrocycle carriers for separation of metal ions in liquid membrane processes—a review. Desalination, 240, 186–197.
Walkowiak, W., Ulewicz, M., & Kozłowski, C. (2002). Application of macrocycle compounds for metal ions separation and removal—a review. Ars Separatoria Acta, 1, 87–98.
WHO. (2001). Environmental health criteria 224: arsenic and arsenic compounds. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO).
Xiong, C., He, M., & Hu, B. (2008). On-line separation and preconcentration of inorganic arsenic and selenium species in natural water samples with CTAB-modified alkyl silica microcolumn and determination by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry. Talanta, 76, 772–779.
Yalcin, S., & Le, X. C. (2001). Speciation of arsenic using solid phase extraction cartridges. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 3, 81–85.
Yu, C. H., Cai, Q. T., Guo, Z. X., Yang, Z. G., & Khoo, S. B. (2003). Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry study of the retention behavior of arsenic species on various solid phase extraction cartridges and its application in arsenic speciation. Spectrochimica Acta Part B-Atomic Spectroscopy, 58, 1335–1349.
Acknowledgments
This research was partially supported by the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (24310056 and 24 · 02029) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, I.M.M., Begum, Z.A., Furusho, Y. et al. Selective Separation of Tri- and Pentavalent Arsenic in Aqueous Matrix with a Macrocycle-Immobilized Solid-Phase Extraction System. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1526 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1526-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1526-0