Abstract
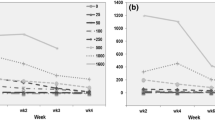
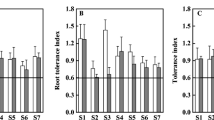
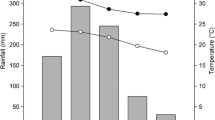
Uptake, bioaccumulation, and assimilation of ferricyanide by three different species of willows was investigated. Intact prerooted weeping willows (Salix babylonica L.), Hankow willows (Salix matsudana Koidz), and hybrid willows (S. matsudana Koidz × alba L.) were grown hydroponically and treated with ferricyanide at 25.0 ± 0.5 °C for 144 h. Willows without leaves were also investigated as a treatment to quantify effect of transpiration on transport and assimilation of ferricyanide. Dissociation of ferricyanide to free cyanide in solution in absence of light was negligible. Phytotransport of ferricyanide was apparent. The phytoremoval rate of ferricyanide obtained varied with willow species (p < 0.05). Remarkable decreases in the removal rate were detected with the trees without leaves compared with the intact trees (p < 0.01). Due to small amounts of the applied ferricyanide recovered in plant materials, ferricyanide removed from the hydroponic solution was largely assimilated by plants. Transpiration stream concentration factor (TSCF) was also estimated using the content of iron (Fe). These information suggests that phytodegradation is a major process involved in botanical assimilation of ferricyanide through an undefined degradation pathway.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bushey, J. T., Ebbs, S. D., & Dzombak, D. (2006). Development of a plant uptake model for cyanide. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 8, 25–43.
Castric, P. A., Farnden, K. J. F., & Conn, E. E. (1972). Cyanide metabolism in higher plants. V. The formation of asparagine from β-cyanoalanine. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 152, 62–69.
Ebbs, S. D., Bushey, J., Poston, S., Kosma, D., Samiotakis, M., & Dzombak, D. (2003). Transport and metabolism of free cyanide and iron cyanide complexes by willow. Plant, Cell & Environment, 26, 1467–1478.
Ebbs, S. D., Piccinin, R. C., Goodger, J. Q. D., Kolev, S. D., Woodrow, I. W., & Baker, A. J. M. (2008). Transport of ferrocyanide by two eucalypt species and sorghum. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 10, 343–357.
Federico, R., & Giartosio, C. E. (1983). A transplasma membrane electron transport system in maize. Plant Physiology, 73, 182–184.
Ghosh, R. S., Dzombak, D. A., Luthy, R. G., & Nakles, D. V. (1999). Subsurface fate and transport of cyanide species at a manufactured-gas plant site. Water Environment Research, 71, 1205–1216.
Ghosh, R. S., Nakles, D. V., Murarka, P., & Neuhauser, E. F. (2004). Cyanide speciation in soil and groundwater at manufactured gas plant (MGP) sites. Environmental Engineering Science, 21, 752–767.
Gibbs, M. M. (1979). A simple method for the rapid determination of iron in natural waters. Water Research, 13, 295–297.
Greenberg, A. E., Clesceri, L. S. E., & Eaton, A. D. (1992). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (18rd ed., pp. 366–368). Washington: American Water Works Association, Water Pollution Control Federation.
Kang, D. H., Hong, L. Y., Schwab, A. P., & Banks, M. K. (2007). Removal of Prussian blue from contaminated soil in the rhizosphere of cyanogenic plants. Chemosphere, 69, 1492–1498.
Larsen, M., & Trapp, S. (2006). Uptake of iron cyanide complexes into willow trees. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 1956–1961.
Larsen, M., Ucisik, A., & Trapp, S. (2005). Uptake, metabolism, accumulation and toxicity of cyanide in willow trees. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 2135–2142.
Mansfeldt, T., Leyer, H., Barmettler, K., & Kretzschmar, R. (2004). Cyanide leaching from soil developed from coking plant purifier waste as influenced by citrate. Vadose Zone Journal, 3, 471–479.
Maruyama, A., Saito, K., & Ishizawam, K. (2001). β-cyanoalanine synthase and cysteine synthase from potato: molecular cloning, biochemical characterization, and spatial and hormonal regulation. Plant Molecular Biology, 46, 749–760.
Meers, E., Hopgood, M., Lesge, E., Vervake, P., Tack, F. M. G., & Verloo, M. G. (2004). Enhanced phytoextraction: in search of EDTA alternatives. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 6, 95–109.
Meeussen, J. C. L., Keizer, M. G., & de Haan, F. A. M. (1992). Chemical stability and decomposition rate of iron cyanide complexes in soil solutions. Environmental Science and Technology, 26, 511–516.
Meeussen, J. C. L., van Riemsdijk, W. H., & van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M. (1995). Transport of complexed cyanide in soil. Geoderma, 67, 73–85.
Rader, W. S., Solujic, L., Milosavljevic, E. B., Hendrix, J. L., & Nelson, J. H. (1993). Sunlight-induced photochemistry of aqueous solutions for hexacyanoferrate(II) and (III) ions. Environmental Science and Technology, 27, 1875–1879.
Rennert, T., & Mansfeldt, T. (2002). Sorption of iron-cyanide complexes on goethite in the presence of sulfate and desorption with phosphate and chloride. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 745–751.
Sachs, L. (1992). Angewandte Statistik. Berlin: Springer.
Samiotakis, M., & Ebbs, S. D. (2004). Possible evidence for transport of an iron cyanide complex by plants. Environmental Pollution, 127, 169–173.
Smith, A., & Mudder, T. (1991). The chemistry and treatment of cyanide waste. London: Mining Journal Book Ltd.
State Environmental Protection Administration of China (SEPA). (1989). Analysis method for water and wastewater (3rd ed., pp. 145–154). Beijing: Environmental Science. In Chinese.
Theis, T. L., & West, M. L. (1986). Effects of cyanide complexation on the adsorption of trace metals at the surface of goethite. Environmental Technology and Letter, 7, 309–316.
Trapp, S., & Christiansen, H. (2003). Phytoremediation of cyanide-polluted soils. In S. C. McCutcheon & J. L. Schnoor (Eds.), Phytoremediation: transformation and control of contaminants (pp. 829–862). Hoboken: Wiley.
Trapp, S., Zambrano, K. C., Kusk, K. O., & Karlson, U. (2000). A phytotoxicity test using transpiration of willows. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39, 154–160.
Wang, C., Zhang, S. H., Wang, P. F., Hou, J., Zhang, W. J., Li, W., et al. (2009). The effect of excess Zn on mineral nutrition and antioxidative response in rapeseed seedlings. Chemosphere, 75, 1469–1476.
White, D. M., Pilon, T. A., & Woolard, C. (2000). Biological treatment of cyanide containing wastewater. Water Research, 34, 2105–2109.
Yngard, R., Damrongsiri, S., Osathaphan, K., & Sharma, V. K. (2007). Ferrate (VI) oxidation of zinc–cyanide complex. Chemosphere, 69, 729–735.
Yu, X. Z., & Gu, J. D. (2006). Uptake, metabolism, and toxicity of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) in weeping willows. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B137, 1417–1423.
Yu, X. Z., & Gu, J. D. (2009). Uptake, accumulation and metabolic responses of ferricyanide in weeping willows. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 11, 145–152.
Yu, X. Z., & Gu, J. D. (2010). Effect of temperature on removal of iron cyanides from solution by maize plants. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 17, 106–114.
Yu, X. Z., Trapp, S., Zhou, P. H., Wang, C., & Zhou, X. S. (2004). Metabolism of cyanide by Chinese vegetation. Chemosphere, 56, 121–126.
Yu, X. Z., Trapp, S., & Zhou, P. H. (2005a). Phytotoxicity of cyanide to weeping willow trees. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 12, 109–113.
Yu, X. Z., Trapp, S., Zhou, P. H., & Hu, H. (2005b). The effect of temperature on the rates of cyanide metabolism of two woody plants. Chemosphere, 59, 1099–1104.
Yu, X. Z., Gu, J. D., & Li, T. P. (2008). Availability of ferro- and ferri-cyanide complexes as a nitrogen source to cyanogenic plants. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 55, 229–237.
Yu, X. Z., Lu, P. C., & Yu, Z. (2012). On the role of beta-cyanoalanine synthase (CAS) in metabolism of free cyanide and ferri-cyanide by rice seedlings. Ecotoxicology, 21, 548–556.
Zagury, G. J., Oudjehani, K., & Deschenes, L. (2004). Characterization and availability of cyanide in solid mine tailings from gold extraction plants. Science of the Total Environment, 320, 211–224.
Zimmerman, A. R., Kang, D. H., Ahn, M. Y., Hyun, S., & Banks, M. K. (2008). Influence of a soil enzyme on iron–cyanide complex speciation and mineral adsorption. Chemosphere, 70, 1044–1051.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC: 40971256).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, FZ., Yu, XZ. & Gu, JD. Transport and Assimilation of Ferricyanide by Three Willow Species. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1522 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1522-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1522-4