Abstract
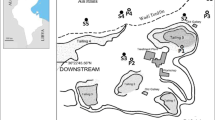
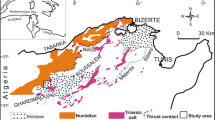
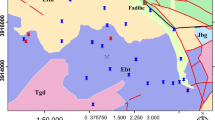
The distribution and mobility of heavy metals in the non-saturated zone of the alluvial plain of a wadi in the Cartagena–La Union mining district was investigated. The elemental chemistry of soils, in-depth sediments and different plant species (namely Hirsfeldia incana, Ditrichia viscosa and Piptatherum miliaceum) was carried out by using X-ray fluorescence and X-ray diffraction techniques. Potential mobility of metals was assessed by using lixiviation test runs (DIN 38414-S4). Concentrations detected in soils and sediments were higher than the acceptable limits reported in official regulations. Regarding metals mobility, values obtained for Pb, Zn and As exceed the limits established by European Union for DIN 38414-S4 leachates. Whilst the obtained leaching percentages for Pb, Cu and As were not especially high (<2%), Zn exhibit a very high leaching potential (up to 60% of the total metal content), involving potential risk of pollution events.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakac, M. (2004). R-mode factor analysis applied to the distribution of radionuclides in Turkey. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 71, 781–782.
BBodSchG (Bundes-Bodenschutzgesetz). (1998). Gesetz zum Schutz des Bodens in der Fassung der Bekanntmachung vom 17.03.1998. Bundesgesetzblatt I, pp. 502–510.
BBodSchV (Bundes-Bodenschutz- und Altlastenverordnung). (1999). Gesetz zum Schutz des Bodens in der Fassung der Bekanntmachung vom 12.07.1999. Bundesgesetzblatt I, pp. 1554–1582.
Bi, X., Feng, X., Yang, Y., Guangle, Q., Li, G., Li, F., et al. (2007). Environmental contamination of heavy metals from zinc smelting areas in Hezhang County, western Guizhou, China. Environment International, 32(7), 883–890.
Buhrke, V. E., Jenkins, R., & Smith, D.-K. (1998). A practical guide for the preparation of specimens for X-ray fluorescence and X-ray diffraction analysis (p. 345). Hoboken: Wiley.
Cappuyns, V., Swennen, R., & Niclaes, M. (2007). Application of the BCR sequential extraction scheme to dredged pond sediments contaminated by Pb-Zn mining: a combined geochemical and mineralogical approach. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 93(2), 78–90.
Cappuyns, V., Swennen, R., Vandamme, A., & Niclaes, M. (2005). Environmental impact of the former Pb-Zn mining and smelting in East Belgium. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 88(1–3), 6–9.
Chung, F. H. (1974). Quantitative interpretation of X-ray diffraction patterns of mixtures. I. Matrix-flushing method for quantitative multicomponent analysis. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 7, 519–525.
Clemente, R., Escolar, A., & Pilar Bernal, M. (2006). Heavy metals fractionation and organic matter mineralisation in contaminated calcareous soil amended with organic materials. Bioresource Technology, 97(15), 1894–1901.
Diaz del Rio, V. (1993). Estudio geoambiental del Mar Menor (in Spanish). Centro de publicaciones del Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación. 223 pp.
DIN 38414-S4. (1984). Schlamm und Sedimente, Bestimmung der Eluierbarkeit mit Wasser. DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung, Berlin; 1984.
EC. (1991). Directive of European Parliament and of the Council 91/689/EC. Brussels: EC.
EC. (1999). Directive of European Parliament and of the Council 1999/31/EC. Brussels: EC.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). (1990). Toxicity Characterisation Leaching Procedure (TCLP), Final Rule 261, 55 FR (pp. 11798–11877). Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office.
Faz, A., Arnaldos, R., Conesa, H.M., Garcia-Fernández, G. (2002). Soils affected by mining and industrial activities in Cartagena (SE Spain): classification problems. European Soil Bureau. Research report n° 7.
Fic, M., & Isenbeck-Schröter, M. (1989). Batch studies for the investigation of the mobility of the heavy metals Cd, Cr, Cu and Zn. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 4, 69–78.
Forstsner, U. (1989). Contaminated sediments: lectures on environmental aspects of particle-associated chemicals in aquatic systems (p. 157). Springer: New York.
García, C. (2004). “Impacto y riesgo ambiental de los residuos minero-metalúrgicos de la sierra minera de Cartagena-La Unión”. Ph D. Thesis. Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena. (in Spanish).
García, G., Faz, A., & Cunha, M. (2004). Performance of Piptatherum miliaceum (Smilo grass) in edaphic Pb and Zn phytoremediation over a short growth period. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 54, 245–250.
Gisbert, C., Clemente, R., Navarro-Aviñó, J., Baixauli, C., Giner, A., Serrano, R., et al. (2006). Tolerance and accumulation of heavy metals by Brassicaceae species grown in contaminated soils from Mediterranean regions of Spain. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 56, 19–27.
Gonzalez-Fernandez, O., Queralt, I., Carvalho, M. L., & Garcia, G. (2007). Elemental analysis of mining wastes by energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF). Nuclear Instruments and Methods on Physics Research B, 262(1), 81–86.
Graf, W. L., Clark, S. L., Kammerer, M. T., Lehman, T., Randall, K., & Schroeder, R. (1991). Geomorphology of heavy metals in the sediments of Queen Creek, Arizona, USA. Catena, 18(6), 567–582.
Hopke, P. K. (1992). Factor and correlation of multi-variate environmental data. In C. N. Hewitt (Ed.), Methods of environmental data analysis (pp 139–180). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
INM. (2000). National meteorology institute. Meteorological values database. Spanish Ministry of Environment. (http://www.aemet.es).
Latimer, W. M. (1952). Oxidation states of the elements and their potentials in aqueous solution (p. 392). New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Linares Martínez, F. (2005). Juegos de estrategia y consecuencias inintencionadas: un modelo con resultados perversos de la crisis de la minería de Cartagena-La Unión*. Papers Journal, 75, 36–61.
MacKenzie, A. B., & Pulford, I. D. (2002). Investigation of contaminant metal dispersal from a disused mine site at Tyndrum, Scotland, using concentration gradients and stable Pb isotope ratios. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 1093–1103.
Marguí, E., Queralt, I., Carvalho, M. L., & Hidalgo, M. (2007). Assesment of metal availability to vegetation (Betula pendula) in Pb-Zn ore concentrate residues with different features. Environmental Pollution, 145(1), 179–184.
Marguí, E., Queralt, I., & Van Grieken, R. (2009). Sample preparation for X-ray fluorescence analysis: Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry. Chichester: Wiley.
Marguí, E., Salvadó, V., Queralt, I., & Hidalgo, M. (2004). Comparison of three stage sequential extraction and toxicity characteristic leaching tests to evaluate toxicity in mining wastes. Analytica Chimica Acta, 524, 151–159.
Marques, A. F., Queralt, I., Carvalho, M. L., & Bordalo, M. (2003). Total reflection X-ray fluorescence and energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence analysis of runoff water and vegetation from abandoned mining of Pb-Zn ores. Spectrochimica acta Part B: Atomic spectroscopy, 58(12), 2191–2198.
Martín Camino, M. (1996). «Del final de la Edad de Bronce al Mundo Bizantino». En Tornel Cobacho, C. (coord.). Manual de Historia de Cartagena.Murcia: Universidad de Murcia. (in Spanish).
Moreno-Grau, S., Cascales-Pujalte, J. A., Martínez-García, M. J., Angosto, J. M., Moreno, J., Bayo, J., et al. (2002). Relationships between levels of lead, cadmium, zinc and copper in soil in settleable particulate matter in Cartagena. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 137, 365–383.
Nogales, R., & Benítez, E. (2006). Absorption of zinc and lead by Dittrichia Viscosa grown in a contaminated soil amended with olive-derived wastes. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 76, 538–544.
NRCS (Natural Resources Conservation Services). (2004). Soil survey laboratory methods manual. Version 4.0. Soil survey investigations report N° 42. 735 pp. Accessed at: http://soils.usda.gov/technical/lmm/.
Quartacci, M. F., Argilla, A., Baker, A. J. M., & Navarri-Izzo, F. (2005). Phytoextraction of metals from a multiply contaminated soil by Indian mustard. Chemosphere, 59(9), 1249–1255.
Rindby, A. (1989). Software for energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence. X-Ray Spectrometry, 18, 113–118.
Robles-Arenas, V. M., Rodríguez, R., García, C., Manteca, J. I., & Pascual, L. (2006). Sulphide-mining impacts in the physical environment: Sierra de Cartagena–La Unión (SE Spain) case study. Environmental Geology, 51(1), 47–64.
Simonneau, J. (1973). Mar Menor. Evolution sedimentologique et geoquimique recent du remplissage. Ph.D. thesis, University Paul Sabatier, France, 172 pp.
Smith, K. S., Desborough, G. A., Meeker, G. P., Sutley, S. J., Leinz, R. W., Anthony, M. W. (2000). Fine-grained anglesite as a source of leachable lead in polymetallic mine-waste material. In 2000 GSA Annual Meeting, Reno, Nevada
Taylor, M. P. (2007). Distribution and storage of sediment-associated heavy metals downstream of the remediated Rum Jungle Mine on the East Branch of the Finniss River, Northern Territory, Australia. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 92(1), 55–72.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51, 844–851.
Ukonmaanaho, L., Nieminen, T., Rausch, N., & Shotyk, W. (2004). Heavy metal and arsenic profiles in ombrogenous peat cores from four differently loaded areas in Finland. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 158, 277–294.
Wilding, L. P., & Drees, L. R. (1983). Spatial variability and pedology. In Pedogenesis and soil taxonomy: Concepts and interactions (Vol. 1, pp. 83–113). Amsterdam, Netherlands: Oxford University Press.
Yang, Q., Shu, W., Qiu, J., Wang, H., & Lan, C. (2004). Lead in paddy soils and rice plants and its potential health risk around Lechang lead/zinc mine, Guangdong, China. Environment International, 30, 883–889.
Acknowledgements
This study was financed by the Spanish National Research Programme (CGL2007-66861-C04). O. Gonzalez-Fernandez gratefully acknowledges a grant from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Education (Ref. BES2005-6810). J. A. Montiel is acknowledged for his kind language revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonzalez-Fernandez, O., Queralt, I., Carvalho, M.L. et al. Lead, Zinc, Arsenic and Copper Pollution in the Alluvial Plain of a Mining Wadi: The Beal Case (Cartagena–La Union Mining District, SE Spain). Water Air Soil Pollut 220, 279–291 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0753-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0753-5