Abstract
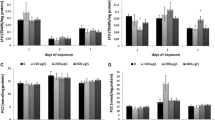
The biocide triclosan (TCS, 5-chloro-2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenol) is commonly used in several personal care products, textiles, and children’s toys. Because the removal of TCS by wastewater treatment plants is incomplete, its environmental fate is to be discharged into freshwater ecosystems, where its ecological impact is largely unknown. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of TCS on the antioxidant enzymatic chain of the freshwater mollusk zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). We measured the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), as well as the phase II detoxifying enzyme glutathione S-transferase (GST) in zebra mussel specimens exposed to 1 nM, 2 nM, and 3 nM TCS in vivo. The mussels were exposed for 96 h, and the enzyme activities were measured every 24 h. We measured clear activation of GST alone at all three dose levels, which shows a poor induction of the antioxidant enzymatic chain by TCS. CAT and SOD were activated only at 3 nM, while GPx values overlapped the baseline levels.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolfsson-Erici, M., Pettersson, M., Parkkonen, J., & Sturve, J. (2002). Triclosan.A commonly used bactericide found in human milk and in the aquatic environment. Chemosphere, 46, 1485–1489.
Binelli, A., Riva, C., Cogni, D., & Provini, A. (2008). Assessment of the genotoxic potential of benzo(α)pyrene and pp′-dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene in zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Mutation Research, 649, 135–145.
Binelli, A., Cogni, D., Parolini, M., Riva, C., & Provini, A. (2009a). Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of in vitro exposures to triclosan and trimethoprim on zebra mussel (D. polymorpha) hemocytes. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology-Part C, 150, 50–56.
Binelli, A., Cogni, D., Parolini, M., Riva, C., & Provini, A. (2009b). In vivo experiments for the evaluation of genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of triclosan in zebra mussel hemocytes. Aquatic Toxicology, 91, 238–244.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein using the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Buth, J. M., Grandbois, M., Vikesland, P. J., McNeill, K., & Arnold, W. A. (2009). Aquatic photochemistry of chlorinated Triclosan derivatives: potential source of polychlorodibenzo-p-dioxins. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 28, 2555–2563.
Canesi, L., Ciacci, C., Lorusso, L. C., Betti, M., Gallo, G., Pojana, G., et al. (2007). Effects of Triclosan on Mytilus galloprovincialis hemocyte function and digestive gland enzyme activities: possible modes of action on non target organisms. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology-Part C, 145, 464–472.
Capdevielle, M., Van Egmond, R., Whelan, M., Versteeg, D., Hofmann-Kamensky, M., Inauen, J., et al. (2007). Consideration of exposure and species sensitivity of triclosan in the freshwater environment. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 4, 15–23.
Cheung, C. C. C., Zheng, G. J., Lam, P. K. S., & Richardson, B. J. (2002). Relationships between tissue concentrations of chlorinated hydrocarbons (polychlorinated biphenyls and chlorinated pesticides) and antioxidative responses of marine mussels, Perna viridis. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 45, 181–191.
Coogan, M. A., & La Point, T. W. (2008). Snail bioaccumulation of triclocarban, triclosan, and methyltriclosan in a North Texas, USA, stream affected by wastewater treatment plant runoff. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27, 1788–1793.
Coogan, M. A., Edziyie, R. E., La Point, T. W., & Venables, B. J. (2007). Algal bioaccumulation of triclocarban, triclosan, and methyl-triclosan in a North Texas wastewater treatment plant receiving stream. Chemosphere, 67, 1911–1918.
Faria, M., Carrasco, L., Diez, S., Riva, M. C., Bayona, J. M., & Barata, C. (2009). Multi-biomarker responses in the freshwater mussel Dreissena polymorpha exposed to polychlorobiphenyls and metals. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology-Part C, 149, 281–288.
Foran, C. M., Bennett, E. R., & Benson, W. H. (2000). Developmental evaluation of a potential non-steroidal estrogen: triclosan. Marine Environmental Resources, 50, 153–156.
Gomez, M. J., Martinez Bueno, M. J., Lacorte, S., Fernandez-Alba, A. R., & Aguera, A. (2007). Pilot survey monitoring pharmaceuticals and related compounds in a sewage treatment plant located on the Mediterranean coast. Chemosphere, 66, 993–1002.
Ishibashi, H., Matsumura, N., Hirano, M., Matsuoka, M., Shiratsuchi, H., Ishibashi, Y., et al. (2004). Effects of triclosan on the early life stages and reproduction of medaka Oryzias latipes and induction of hepatic vitellogenin. Aquatic Toxicology, 67, 167–179.
Kolpin, D. W., Furlong, E. T., Meyer, M. T., Thurman, E. M., Zaugg, S. D., Barber, L. B., et al. (2002). Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, 1999–2000: a national reconnaissance. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 1202–1211.
Oliveira, R., Domingues, I., Grisolia, C. K., & Soares, A. M. V. M. (2009). Effects of triclosan on zebrafish early-life stages and adults. Environmental Science Pollution Resource, 16, 679–688.
Orbea, A., Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M., Solé, M., Porte, C., & Cajaraville, M. P. (2002). Antioxidant enzymes and peroxisome proliferation in relation to contaminant body burdens of PAHs and PCBs in bivalve molluscs, crabs and fish from the Urdaibai and Plentzia estuaries (Bay of Biscay). Aquatic Toxicology, 58, 75–98.
Orvos, D. R., Versteeg, D. J., Inauen, J., Capdevielle, M., Rothenstein, A., & Cunningham, V. (2002). Aquatic toxicity of triclosan. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 21, 1338–1349.
Osman, A. M., & van Noort, P. C. M. (2007). Comparison of key enzymes in the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, the earthworm Allolobophora chlorotica and Chironomus riparius larvae. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 67, 212–217.
Osman, A. M., Rotteveel, S., den Besten, P. J., & van Noort, P. C. M. (2004). In vivo exposure of Dreissena polymorpha mussels to the quinones menadione and lawsone: menadione is more toxic to Mussels than Lawsone. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 24, 135–141.
Osman, A. G. M., Mekkawy, I. A., Verreth, J., & Kirschbaum, F. (2007). Effects of lead nitrate on the activity of metabolic enzymes during early developmental stages of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 33, 1–13.
Regoli, F., Winston, G. W., Gorbi, S., Frenzilli, G., Nigro, M., Corsi, I., et al. (2003). Integrating enzymatic responses to organic chemical exposure with total oxyradical absorbing capacity and DNA damage in the European eel Anguilla anguilla. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 22, 2120–2129.
Singer, H., Muller, S., Tixier, C., & Pillonel, L. (2002). Triclosan: occurrence and fate of a widely used biocide in the aquatic environment. Field measurements in wastewater treatment plants, surface waters, and lake sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 4998–5004.
Veldhoen, N., Skirrow, R. C., Osachoff, H., Wigmore, H., Clapson, D. J., Gunderson, M. P., et al. (2006). The bactericidal agent triclosan modulates thyroid hormone-associated gene expression and disrupts postembryonic anuran development. Aquatic Toxicology, 80, 217–227.
Xiao, Q., Zhang, Z., Guo, H., Su, F., & Xu, Y. (2007). Nonylphenol causes decrease in antioxidant enzyme activities, increase in O -2 content, and alterations in ultrastructures of FG cells, a Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) gill cell line. Toxicology Mechanisms and Methodology, 17, 127–134.
Yu, J. C., Kwong, T. Y., Luo, Q., & Cai, Z. (2006). Photocatalytic oxidation of triclosan. Chemosphere, 65, 390–399.
Zhang, H., & Huang, C. (2003). Oxidative transformation of triclosan and chlorophene by manganese oxides. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 2421–2430.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binelli, A., Parolini, M., Pedriali, A. et al. Antioxidant Activity in the Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) in Response to Triclosan Exposure. Water Air Soil Pollut 217, 421–430 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0597-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0597-4