Abstract
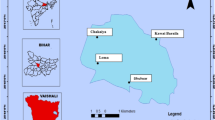
The concentrations of major heavy metals in organs of two cyprinid fish and in water collected from three sections of the Kor River, Iran, were determined using the induction coupled plasma method. The concentrations of heavy metals in tissue of fish from the middle sampling zone were significantly higher (p < 0.05) than those from the other two sampling zones, whereas no significant differences (p > 0.05) were detected between the two sexes and species. Estradiol in females and progesterone and testosterone in males from the middle study site were significantly (p < 0.05) lower than values from the other two sites. Pathological changes in blood cells, liver, and kidneys of fishes were significantly higher in highly polluted areas (middle sampling zone). So heavy metals exposure can effectively decreases estrogenic and androgenic secretion in fish. These results show that industrial activities have polluted the river and that heavy metals exposure can induce pathological changes in fish organs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barregard, L., Svalander, C., et al. (1999). Cadmium, mercury, and lead in kidney cortex of the general Swedish population: A study of biopsies from living kidney donors. Environmental Health Perspectives, 107, 867–71.
Biggeri, A., Lagazio, C., et al. (2006). Report on health status of residents in areas with industrial, mining or military sites in Sardinia, Italy. Epidemiologia e Prevenzione, 30, 5–95.
Buchet, J. P., Roels, H., et al. (1980). Assessment of renal function of workers exposed to inorganic lead, calcium or mercury vapor. Journal of Occupational Medicine, 22, 741–50.
Burger, J., & Gochfeld, M. (2005). Heavy metals in commercial fish in New Jersey. Environmental Research, 99, 403–12.
Cech, I., Smolensky, M. H., et al. (2006). Lead and copper in drinking water fountains—Information for physicians. South Med J, 99, 137–42.
Chetty, C. S., Vemuri, M. C., et al. (2005). Lead-induced cell death of human neuroblastoma cells involves GSH deprivation. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, 10, 413–23.
Damek-Poprawa, M., & Sawicka-Kapusta, K. (2003). Damage to the liver, kidney, and testis with reference to burden of heavy metals in yellow-necked mice from areas around steelworks and zinc smelters in Poland. Toxicology, 186, 1–10.
de Burbure, C., Buchet, J. P., et al. (2006). Renal and neurologic effects of cadmium, lead, mercury, and arsenic in children: Evidence of early effects and multiple interactions at environmental exposure levels. Environmental Health Perspectives, 114, 584–90.
de Conto Cinier, C., Petit-Ramel, M., et al. (1997). Cadmium bioaccumulation in carp (Cyprinus carpio) tissues during long-term high exposure: Analysis by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 38, 137–43.
Delistraty, D., & Stone, A. (2007). Dioxins, metals, and fish toxicity in ash residue from space heaters burning used motor oil. Chemosphere, 68, 907–14.
Devlin, E. W. (2006). Acute toxicity, uptake and histopathology of aqueous methyl mercury to fathead minnow embryos. Ecotoxicology, 15, 97–110.
Diaz, S., Martin-Gonzalez, A., et al. (2006). Evaluation of heavy metal acute toxicity and bioaccumulation in soil ciliated protozoa. Environment International, 32, 711–7.
Drevnick, P. E., & Sandheinrich, M. B. (2003). Effects of dietary methylmercury on reproductive endocrinology of fathead minnows. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 4390–6.
Dua, A., & Gupta, N. (2005). Mercury toxicology as assessed through fish scales. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 74, 1105–10.
Dural, M., Goksu, M. Z., et al. (2006). Bioaccumulation of some heavy metals in different tissues of Dicentrarchus labrax L, 1758, Sparus aurata L, 1758 and Mugil cephalus L, 1758 from the Camlik lagoon of the eastern coast of Mediterranean (Turkey). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 118, 65–74.
Ebrahimi, M. (2004a). Effects of in vivo and in vitro zinc and cadmium treatment on sperm steroidogenesis of the African catfish (Clarias gairepnius). IJVR, 6, 12–25.
Ebrahimi, M. (2004b). Setting up an ELISA method for steroid hormones. Iranian Journal of Veterinary Sciences, 5, 30–55.
Enrique, M. O., Morales, V., et al. (2002). Prevalence of fetal exposure to environmental toxins as determined by meconium analysis. Neurotoxicology, 23, 329–39.
Ettler, V., Johan, Z., et al. (2005). Mineralogy of air-pollution-control residues from a secondary lead smelter: Environmental implications. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 9309–16.
Goswami, K., Gachhui, R., et al. (2005). Hepatorenal dysfunctions in lead pollution. Journal of Environmental Science & Engineering, 47, 75–80.
Graeme, K. A., & Pollack, C. V., Jr. (1998). Heavy metal toxicity, Part I: Arsenic and mercury. The Journal of Emergency Medicine, 16, 45–56.
Hinck, J. E., Blazer, V. S., et al. (2007). Biomarkers of contaminant exposure in Northern Pike (Esox lucius) from the Yukon River Basin, Alaska. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 52, 549–62.
Jeffree, R. A., Warnau, M., et al. (2006a). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and radionuclides from seawater by encased embryos of the spotted dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52, 1278–86.
Jeffree, R. A., Warnau, M., et al. (2006b). Comparison of the bioaccumulation from seawater and depuration of heavy metals and radionuclides in the spotted dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula (Chondrichthys) and the turbot Psetta maxima (Actinopterygii: Teleostei). The Science of the Total Environment, 368, 839–52.
Johnson, V. G., Peterson, R. E., et al. (2005). Heavy metal transport and behavior in the lower Columbia River, USA. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 110, 271–89.
Kime, D. E. (1995). The effects of pollution on reproduction in fish. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 5, 52–96.
Kime, D. E., Ebrahimi, M., et al. (1996). Use of computer assisted sperm analysis (CASA) for monitoring the effects of pollution on sperm quality of fish; application to effects of heavy metals. Aquatic Toxicology, 36, 223–37.
Kime, D. E., Van Look, K. J., et al. (2001). Computer-assisted sperm analysis (CASA) as a tool for monitoring sperm quality in fish. Biology of Reproduction, 130, 425–33.
Krishnani, K. K., Azad, I. S., et al. (2003). Acute toxicity of some heavy metals to Lates calcarifer fry with a note on its histopathological manifestations. Journal of environmental science and health, 38, 645–55.
Liu, Z. P. (2003). Lead poisoning combined with cadmium in sheep and horses in the vicinity of non-ferrous metal smelters. The Science of the Total Environment, 309, 117–26.
Martin-Diaz, M. L., Tuberty, S. R., et al. (2006). The use of bioaccumulation, biomarkers and histopathology diseases in Procambarus clarkii to establish bioavailability of Cd and Zn after a mining spill. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 116, 169–84.
Munoz, O., Bastias, J. M., et al. (2005). Estimation of the dietary intake of cadmium, lead, mercury, and arsenic by the population of Santiago (Chile) using a Total Diet Study. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 43, 1647–55.
Patra, R. C., Swarup, D., et al. (2006). Trace mineral profile in blood and hair from cattle environmentally exposed to lead and cadmium around different industrial units. Journal of Veterinary Medicine. A: Physiology, Pathology, Clinical Medicine, 53, 511–7.
Peris, M., C. Mico, et al. (2007). "Heavy metal contents in horticultural crops of a representative area of the European Mediterranean region." Sci Total Environ.
Raldua, D., Diez, S., et al. (2007). Mercury levels and liver pathology in feral fish living in the vicinity of a mercury cell chlor-alkali factory. Chemosphere, 66, 1217–25.
Rurangwa, E., Roelants, I., et al. (1998). The minimum acceptable spermatozoa to egg ratio for artificial insemination and the effects of heavy metal pollutants on sperm motility and fertilization ability in the African catfish (Clarias gariepinus, Burchell 1822). Journal of Fish Biology, 53, 402–13.
Saxena, D. K., Murthy, R. C., et al. (1989). Zinc protects testicular injury induced by concurrent exposure to cadmium and lead in rats. Research Communications In Chemical Pathology And Pharmacology, 64, 317–30.
Siitonen, P. H., & Thompson, H. C., Jr. (1994). Analysis of calcium and lead in calcium supplements by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Journal of AOAC International, 77, 1299–304.
Singh, H. (1989). Interaction of xenobiotics with reproductive endocrine functions in a protogynous teleost, Monopterus albus. Marine Environment Research, 28, 285–9.
Song, Y., Xu, H., et al. (2002). Eco-toxicological effects of heavy metals on the inhibition of seed germination and root elongation of Chinese cabbages in soils. Huan Jing Ke Xue, 23, 103–7.
Sprocati, A. R., Alisi, C., et al. (2006). Investigating heavy metal resistance, bioaccumulation and metabolic profile of a metallophile microbial consortium native to an abandoned mine. The Science of the Total Environment, 366, 649–58.
Sun, Y., Xie, Z., et al. (2006). Assessment of toxicity of heavy metal contaminated soils by the toxicity characteristic leaching procedure. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28, 73–8.
Thomas, P. (1990). Teleost model for studying the effects of chemical on female reproductive endocrine function. The Journal of Experimental Zoology, Suppl 4, 126–8.
Thomas, P., & Trant, J. M. (1989). Evidence that 17α, 20β, 21-trihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one is a maturation inducing steroid in spotted sea trout. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 7, 185–91.
Tipping, E., Lawlor, A. J., et al. (2006). Simulating the long-term chemistry of an upland UK catchment: Heavy metals. Environmental Pollution, 141, 139–50.
Webb, M. A., Feist, G. W., et al. (2006). Mercury concentrations in gonad, liver, and muscle of white sturgeon Acipenser transmontanus in the lower Columbia River. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 50, 443–51.
Yayintas, O. T., Yilmaz, S., et al. (2007). Determination of heavy metal pollution with environmental physicochemical parameters in waste water of Kocabas Stream (Biga, Canakkale, Turkey) by ICP-AES. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 127, 389–97.
Zhang, Y. M., Huang, D. J., et al. (2005). Heavy metal accumulation and tissue damage in goldfish Carassius auratus. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 75, 1191–9.
Acknowledgment
The authors greatly appreciate the support of Budget and Planning Organization, Fars province, for funding this project and Shiraz University and Green Research Center for supporting the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebrahimi, M., Taherianfard, M. Pathological and Hormonal Changes in Freshwater Fishes Due to Exposure to Heavy Metals Pollutants. Water Air Soil Pollut 217, 47–55 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0566-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0566-y