Abstract
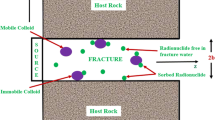
Application of one-dimensional transport considering multiple member of decay chain in a single rock fracture has been studied. Input sources for constant, pulse, impulse, Heaviside, and exponential decay have been used to demonstrate the suitability of relevant solutions. It shows that the breakthrough curves of dimensionless concentration for the three-member decay chain for Np-237 and the seven-member chain for Cm-246 can be well presented in the temporal and spatial domains. The analytical solutions of this study can clearly demonstrate the general form of contaminant transport with complete multiple-member decay chain in one-dimensional fractured or porous media of arbitrary analytical input sources without considering the matrix diffusion, which the conceptual model provides an alternative type to demonstrate the fate of radionuclide transport in the geosphere. The solutions are conservatively used to support the performance assessment for disposal site of radioactive waste. An application to a hybrid test site for the final disposal of spent nuclear fuel is newly demonstrated. Proposed solution to simulate the transport of nuclides in the one-dimensional pathway of host rock becomes feasible, so that the simulation and prediction of radionuclide transport of fractured media existing in geosphere can be conservatively performed in the future.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, B. W., Altman, S. J., Robey, T. H., Barnard, R. W., & Brown, T. J. (1995). Unsaturated-zone fast-path flow calculations for Yucca Mountain groundwater travel time analyses (GWTT-94). SAND95-0857 (p. 169). Albuquerque: Sandia National Laboratories.
Barker, J. A. (1982). Laplace transform solutions for solute transport in fissured aquifers. Advances in Water Resources, 5(2), 98–104.
Bear, J. (1972). Dynamics of fluids in porous media. New York: Elsevier.
Crump, K. S. (1976). Numerical inversions of Laplace transforms using a Fourier series approximation. Journal of the Association for Computing Machinery, 23, 89–96.
de Hoog, F. R., Knight, J. H., & Stokes, A. N. (1982). An improved method for numerical inversion of Laplace transforms. SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing, 3, 357–366.
Dudley, A. L., Peters, R. R., Gauthier, J. H., Wilson, M. L., Tierney, M. S., & Klavetter, E. A. (1988). Total System Performance Assessment Code (TOSPAC) Vol. 1 physical and mathematical bases. SAND85-0002 (p. 212). Albuquerque: Sandia National Laboratories.
Endo, H. K., Long, J. C. S., Wilson, C. R., & Witherspoon, P. A. (1984). A model for investigating mechanical transport in fracture networks. Water Resources Research, 20(10), 1390–1400.
Fetter, C. W. (1999). Contaminant hydrology (pp. 107–117). Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Firestone, R. B. (1996). Table of isotopes (Vol. I and II). New York: Wiley.
Freeze, R. A., & Cherry, J. A. (1979). Groundwater (p. 604). Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Garbow, B. S., Guinta, G., & Lyness, J. N. (1988). Algorithm 662, a FORTRAN software package for the numerical inversion of the Laplace transform based on weeks’ method. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 14(2), 171–176.
Grisak, G. E., & Pickens, J. F. (1980). Solute transport through fractured media, 1. The effect of matrix diffusion. Water Resources Research, 16(4), 719–730.
Grisak, G. E., & Pickens, J. F. (1981). An analytical solution for solute transport through fractured media with matrix diffusion. Journal of Hydrology, 52, 47–57.
IMSL. (2000). Compaq visual fortran professional edition, Version 6.6.a. Fremont: Compaq Computer Corporation.
JNC (1999). H12 project to establish technical basis for HLW disposal in Japan, supporting report 3, safety assessment. Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute, JNC TN1400 99-013.
JNC (2000). H12 project to establish technical basis for HLW disposal in Japan, project overview report. Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute, JNC TN1400 2000-001.
Kreyszig, E. (1993). Advanced engineering mathematics (pp. 261–324). New York: Wiley.
Lester, D. H., Jansen, G., & Burkholder, H. C. (1975). Migration of radionuclide chains through an adsorbing medium. AIChE Symposium Series, 71, 202–213.
Lindgren, M., & Skagius, K. (1989). SKB WP-Cave project: Radionuclide release from the near-field in a WP-Cave repository. SKB TR89-04. Stockholm: Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co.
Mereno, L., Arve, S., & Neretnieks, I. (1989). SKB WP-Cave project: Transport of escaping radionuclides from the WP-Cave repository to the biosphere. SKB TR89-05. Stockholm: Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co.
Neretnieks, I. (1980). Diffusion in the rock matrix: an important factor in radionuclide migration. Journal of Geophysical Research, 85(B8), 4379–4397.
Norman, S., & Kjellbert, N. (1990). FARF31-A far field radionuclide migration code for use with the PROPER package. SKB TR90-01. Stockholm: Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co.
Norman, S., & Kjellbert, N. (1991). NEAR21-A near field radionuclide migration code for use with the PROPER package. SKB TR91-19. Stockholm: Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co.
PNC. (1992). Research and development on geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, first progress report. PNC TN1410 93-059. Tokyo: Power Reactor and Nuclear Fuel Development Corporation.
Rasmuson, L., & Neretneiks, I. (1981). Migration of radionuclides in fissured rock: the influence of micropore diffusion and longitudinal dispersion. Journal of Geophysical Research, 86(B5), 3749–3758.
Robey, T. H. (1994). Development of models for fast fluid pathways through unsaturated heterogeneous porous media. SAND93-7 109. Albuquerque: Sandia National Laboratories.
Shih, D. C.-F., Lin, G. F., & Wang, I. S. (2002). Contaminant transport in a single fractured media: analytical solution and sensitivity for considering pulse, Dirac delta and single sinusoid input sources. Hydrological Processes, 16, 3265–3278.
Shih, D. C. F. (2004). Uncertainty analysis: one-dimensional radioactive nuclide transport in a single fractured media. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 18, 198–204.
Smith, L., & Schwartz, F. W. (1984). An analysis of the influence of fracture geometry on mass transport in fractured media. Water Resources Research, 20(9), 1241–1252.
Spiegel, M. R. (1968). Mathematical handbook of formulas and tables, Schaum’s outline series (pp. 161–173). New-York: McGraw-Hill.
Sudicky, E. K., & Frind, E. O. (1982). Contaminant transport in fractured porous media: Analytical solution for a system of parallel fractures. Water Resources Research, 18(6), 1634–1642.
Sudicky, E. K., & Frind, E. O. (1984). Contaminant transport in fractured porous media: Analytical solution for a two-member decay chain in a single fracture. Water Resources Research, 20(7), 1021–1029.
Tang, D. H., Frind, E. O., & Sudicky, E. A. (1981). Contaminant transport in fractured porous media: Analytical solution for a single fracture. Water Resources Research, 17(3), 555–564.
Weeks, W. T. (1966). Numerical inversion of Laplace transforms using Laguerre functions. Journal of the Association for Computing Machinery, 13(3), 419–426.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shih, D.CF. Radionuclide Transport in Granitic Rock Considering Multiple-Member Decay Chain: Application of Spent Nuclear Fuel Final Disposal. Water Air Soil Pollut 215, 205–219 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0470-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0470-5