Abstract
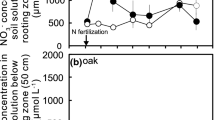
Amount of nitrogen (N) dry deposition on the leaf surface of oak and cedar was compared using throughfall method and foliar rinsing method. The study was conducted at FM Tamakyuryo, located at the northeast edge of the Tama Rolling Hills, Tokyo, Japan. The throughfall method showed that the total N deposition were 19.7, 19.1, and 50.6 kg N ha−1 year−1 for open bulk deposition and total deposition in oak forest and cedar forest, respectively. The deposition of ammonium nitrogen on leaf surface were 0.29 ± 0.38 (average ± standard deviation) and 0.75 ± 1.06 mg N m−2 for oak and cedar, respectively, and that of nitrate nitrogen were 0.15 ± 0.18 and 0.35 ± 0.28 mg N m−2, respectively. Dry deposition on leaf surface was influenced by the cumulative amount of rainfall before sampling and was found to be easily washed off with high amount of precipitation within a few days.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba, M., Okazaki, M., & Hashitani, T. (1995). Effects of acid deposition on forested andisoles in the tama hill region of Japan. Environmental Pollution, 89, 97–106. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(94)00038-F.
Cadle, S. H., Marshall, J. D., & Mulawa, P. A. (1991). A laboratory investigation of the routes of HNO3 dry deposition to coniferous seedlings. Environmental Pollution, 72, 287–305. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(91)90003-F.
Chiwa, M., Oshiro, N., Miyake, T., Nakatani, N., Kimura, N., Yuhara, T., et al. (2003). Dry deposition washoff and dew on the surfaces of pine foliage on the urban- and mountain-facing sides of Mt. Gokurakuji, western Japan. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 327–337. doi:10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00889-0.
Dasch, J. M. (1987). Measurement of dry deposition to surfaces in deciduous and pine canopies. Environmental Pollution, 44, 261–277. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(87)90203-X.
Dolske, D. A. (1988). Dry deposition of airborne sulfate and nitrate to soybeans. Environmental Pollution, 53, 1–12. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(88)90021-8.
Duyzer, J., & Fowler, D. (1994). Modelling land atmosphere exchange of gaseous oxides of nitrogen in Europe. Tellus, 46B, 353–372.
Hanson, P. J., & Lindberg, S. E. (1991). Dry deposition of reactive nitrogen compounds. Atmospheric Environment, 25A, 1615–1634.
JaLTER Information Management Committee (2007). http://jern.info/jalter/en/index.html.
Lindberg, S. E., Lovett, G. M., Richter, D. D., & Johnson, D. W. (1986). Atmospheric deposition and canopy interactions of major ions in a forest. Science, 231, 141–145. doi:10.1126/science.231.4734.141.
Lovett, G. M., & Lindberg, S. E. (1984). Dry deposition and canopy exchange in a mixed oak forest as determined by analysis of throughfall. Journal of Applied Ecology, 21, 1013–1028. doi:10.2307/2405064.
Marshall, J. D., & Cadle, S. H. (1989). Evidence for trans-cuticular uptake of HNO3 vapor by foliage of eastern white pine (Pinus strobus L.). Environmental Pollution, 60, 15–28. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(89)90217-0.
McColl, J. G., & Bush, D. S. (1978). Precipitation and throughfall chemistry of the San Francisco Bay area. Journal of Environmental Quality, 7, 352–357.
Puckett, L. J. (1990). Estimates of ion sources in deciduous and coniferous throughfall. Atmospheric Environment, 24A, 545–555.
Raymond, H. A., Yi, S.-M., Moumena, N., Han, Y., & Holsen, T. (2004). Quantifying the dry deposition of reactive nitrogen and sulfur containing species in remote areas using a surrogate surface analysis approach. Atmospheric Environment, 38, 2687–2697. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.02.011.
Seinfeld, J. H., & Pandis, S. N. (1998). Atmospheric chemistry and physics (p. 1326). New York: Wiley.
Sommer, S. G., & Hutchings, N. J. (2001). Ammonia emission from field applied manure and its reduction—invited paper. European Journal of Agronomy, 15, 1–15. doi:10.1016/S1161-0301(01)00112-5.
Ueno, H., & Komine, M. (2005). Study on development of nitric acid nitrogen removal device. Bulletin of Tokyo Metropolitan Research Institute for Environmental Problems, 2005, 250–251, in Japanese.
Weathers, K. C., Simkin, S. M., Lovett, G. M., & Lindberg, S. E. (2006). Empirical modeling of atmospheric deposition in mountainous landscapes. Ecological Applications, 16, 1590–1607. doi:10.1890/1051-0761(2006)016[1590:EMOADI]2.0.CO;2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, S.D., Saito, M., Hara, H. et al. Comparison of Nitrogen Dry Deposition on Cedar and Oak Leaves in the Tama Hills Using Foliar Rinsing Method. Water Air Soil Pollut 202, 369–377 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-9983-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-9983-1